Mirer, Franklin E.
Address: International Union, United Auto Workers (UAW), 8000 East Jefferson Avenue, Detroit, MI 48214
Country: United States
Phone: 1 (313) 926-5563
Fax: 1 (313) 824-4473
Foundries
Founding, or metal casting, involves the pouring of molten metal into the hollow inside of a heat-resistant mould which is the outside or negative shape of the pattern of the desired metal object. The mould may contain a core to determine the dimensions of any internal cavity in the final casting. Foundry work comprises:
- making a pattern of the desired article
- making the mould and cores and assembling the mould
- melting and refining the metal
- pouring the metal into the mould
- cooling the metal casting
- removing the mould and core from the metal casting
- removing extra metal from the finished casting.
The basic principles of foundry technology have changed little in thousands of years. However, processes have become more mechanized and automatic. Wooden patterns have been replaced by metal and plastic, new substances have been developed for producing cores and moulds, and a wide range of alloys are used. The most prominent foundry process is sand moulding of iron.
Iron, steel, brass and bronze are traditional cast metals. The largest sector of the foundry industry produces grey and ductile iron castings. Gray iron foundries use iron or pig iron (new ingots) to make standard iron castings. Ductile iron foundries add magnesium, cerium or other additives (often called ladle additives) to the ladles of molten metal before pouring to make nodular or malleable iron castings. The different additives have little impact on workplace exposures. Steel and malleable iron make up the balance of the ferrous foundry industrial sector. The major customers of the largest ferrous foundries are the auto, construction and agricultural implement industries. Iron foundry employment has decreased as engine blocks become smaller and can be poured in a single mould, and as aluminium is substituted for cast iron. Non-ferrous foundries, especially aluminium foundry and die-cast operations, have heavy employment. Brass foundries, both free standing and those producing for the plumbing equipment industry, are a shrinking sector which, however, remains important from an occupational health perspective. In recent years, titanium, chromium, nickel and magnesium, and even more toxic metals such as beryllium, cadmium and thorium, are used in foundry products.
Although the metal founding industry may be assumed to start by remelting solid material in the form of metal ingots or pigs, the iron and steel industry in the large units may be so integrated that the division is less obvious. For instance, the merchant blast furnace may turn all its output into pig iron, but in an integrated plant some iron may be used to produce castings, thus taking part in the foundry process, and the blast furnace iron may be taken molten to be turned into steel, where the same thing can occur. There is in fact a separate section of the steel trade known for this reason as ingot moulding. In the normal iron foundry, the remelting of pig iron is also a refining process. In the non-ferrous foundries the process of melting may require the addition of metals and other substances, and thus constitutes an alloying process.
Moulds made from silica sand bound with clay predominate in the iron foundry sector. Cores traditionally produced by baking silica sand bound with vegetable oils or natural sugars have been substantially replaced. Modern founding technology has developed new techniques to produce moulds and cores.
In general, the health and safety hazards of foundries can be classified by type of metal cast, moulding process, size of casting and degree of mechanization.
Process Overview
On the basis of the designer’s drawings, a pattern conforming to the external shape of the finished metal casting is constructed. In the same way, a corebox is made that will produce suitable cores to dictate the internal configuration of the final article. Sand casting is the most widely used method, but other techniques are available. These include: permanent mould casting, using moulds of iron or steel; die casting, in which the molten metal, often a light alloy, is forced into a metal mould under pressures of 70 to 7,000 kgf/cm2; and investment casting, where a wax pattern is made of each casting to be produced and is covered with refractory which will form the mould into which the metal is poured. The “lost foam” process uses polystyrene foam patterns in sand to make aluminium castings.
Metals or alloys are melted and prepared in a furnace which may be of the cupola, rotary, reverberatory, crucible, electric arc, channel or coreless induction type (see table 1). Relevant metallurgical or chemical analyses are performed. Molten metal is poured into the assembled mould either via a ladle or directly from the furnace. When the metal has cooled, the mould and core material are removed (shakeout, stripping or knockout) and the casting is cleaned and dressed (despruing, shot-blasting or hydro-blasting and other abrasive techniques). Certain castings may require welding, heat treatment or painting before the finished article will meet the specifications of the buyer.
Table 1. Types of foundry furnaces
|
Furnace |
Description |
|
Cupola furnace |
A cupola furnace is a tall, vertical furnace, open at the top with hinged doors at the bottom. It is charged from the top with alternate layers of coke, limestone and metal; the molten metal is removed at the bottom. Special hazards include carbon monoxide and heat. |
|
Electric arc furnace |
The furnace is charged with ingots, scrap, alloy metals and fluxing agents. An arc is produced between three electrodes and the metal charge, melting the metal. A slag with fluxes covers the surface of the molten metal to prevent oxidation, to refine the metal and protect the furnace roof from excessive heat. When ready, the electrodes are raised and the furnace tilted to pour the molten metal into the receiving ladle. Special hazards include metal fumes and noise. |
|
Induction furnace |
An induction furnace melts the metal by passing a high electric current through copper coils on the outside of the furnace, inducing an electric current in the outer edge of the metal charge that heats the metal because of the high electrical resistance of the metal charge. Melting progresses from the outside of the charge to the inside. Special hazards include metal fumes. |
|
Crucible furnace |
The crucible or container holding the metal charge is heated by a gas or oil burner. When ready, the crucible is lifted out of the furnace and tilted for pouring into moulds. Special hazards include carbon monoxide, metal fumes, noise and heat. |
|
Rotary furnace |
A long, inclined rotating cylindrical furnace that is charged from the top and fired from the lower end. |
|
Channel furnace |
A type of induction furnace. |
|
Reverberatory furnace |
This horizontal furnace consists of a fireplace at one end, separated from the metal charge by a low partition wall called the fire-bridge, and a stack or chimney at the other end. The metal is kept from contact with the solid fuel. Both the fireplace and metal charge are covered by an arched roof. The flame in its path from the fireplace to the stack is reflected downwards or reverberated on the metal beneath, melting it. |
Hazards such as the danger arising from the presence of hot metal are common to most foundries, irrespective of the particular casting process employed. Hazards may also be specific to a particular foundry process. For example, the use of magnesium presents flare risks not encountered in other metal founding industries. This article emphasizes iron foundries, which contain most of the typical foundry hazards.
The mechanized or production foundry employs the same basic methods as the conventional iron foundry. When moulding is done, for example, by machine and castings are cleaned by shot blasting or hydroblasting, the machine usually has built-in dust control devices, and the dust hazard is reduced. However, sand is frequently moved from place to place on an open-belt conveyor, and transfer points and sand spillage may be sources of considerable quantities of airborne dust; in view of the high production rates, the airborne dust burden may be even higher than in the conventional foundry. A review of air sampling data in the middle 1970s showed higher dust levels in large American production foundries than in small foundries sampled during the same period. Installation of exhaust hoods over transfer points on belt conveyors, combined with scrupulous housekeeping, should be normal practice. Conveying by pneumatic systems is sometimes economically possible and results in a virtually dust-free conveying system.
Iron Foundries
For simplicity, an iron foundry can be presumed to comprise the following six sections:
- metal melting and pouring
- pattern-making
- moulding
- coremaking
- shakeout/knockout
- casting cleaning.
In many foundries, almost any of these processes may be carried out simultaneously or consecutively in the same workshop area.
In a typical production foundry, iron moves from melting to pouring, cooling, shakeout, cleaning and shipping as a finished casting. Sand is cycled from sand mix, moulding, shakeout and back to sand mixing. Sand is added to the system from core making, which starts with new sand.
Melting and pouring
The iron founding industry relies heavily on the cupola furnace for metal melting and refining. The cupola is a tall, vertical furnace, open at the top with hinged doors at the bottom, lined with refractory and charged with coke, scrap iron and limestone. Air is blown through the charge from openings (tuyers) at the bottom; combustion of coke heats, melts and purifies the iron. Charge materials are fed into the top of the cupola by crane during operation and must be stored close at hand, usually in compounds or bins in the yard adjacent to the charging machinery. Tidiness and efficient supervision of the stacks of raw materials are essential to minimize the risk of injury from slippages of heavy objects. Cranes with large electromagnets or heavy weights are often used to reduce the scrap metal to manageable sizes for charging into the cupola and for filling the charging hoppers themselves. The crane cab should be well protected and the operators properly trained.
Employees handling raw materials should wear hand leathers and protective boots. Careless charging can overfill the hopper and can cause dangerous spillage. If the charging process is found to be too noisy, the noise of metal-on-metal impact can be reduced by fitting rubber noise-dampening liners to storage skips and bins. The charging platform is necessarily above ground level and can present a hazard unless it is level and has a non-slip surface and strong rails around it and any floor openings.
Cupolas generate large quantities of carbon monoxide, which may leak from the charging doors and be blown back by local eddy currents. Carbon monoxide is invisible, odourless and can quickly produce toxic ambient levels. Employees working on the charging platform or surrounding catwalks should be well trained in order to recognize the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning. Both continuous and spot monitoring of exposure levels are needed. Self-contained breathing apparatus and resuscitation equipment should be maintained in readiness, and operators should be instructed in their use. When emergency work is carried out, a confined-space entry system of contaminant monitoring should be developed and enforced. All work should be supervised.
Cupolas are usually sited in pairs or groups, so that while one is being repaired the others operate. The period of use must be based on experience with durability of refractories and on engineering recommendations. Procedures must be worked out in advance for tapping out iron and for shutting down when hot spots develop or if the water cooling system is disabled. Cupola repair necessarily involves the presence of employees inside the cupola shell itself to mend or renew refractory linings. These assignments should be considered confined-space entries and appropriate precautions taken. Precautions should also be taken to prevent the discharge of material through the charging doors at such times. To protect the workers from falling objects, they should wear safety helmets and, if working at a height, safety harnesses.
Workers tapping cupolas (transferring molten metal from the cupola well to a holding furnace or ladle) must observe rigorous personal protection measures. Goggles and protective clothing are essential. The eye protectors should resist both high velocity impact and molten metal. Extreme caution should be exercised in order to prevent remaining molten slag (the unwanted debris removed from the melt with the aid of the limestone additives) and metal from coming into contact with water, which will cause a steam explosion. Tappers and supervisors must ensure that any person not involved in the operation of the cupola remains outside the danger area, which is delineated by a radius of about 4 m from the cupola spout. Delineation of a non-authorized no-entry zone is a statutory requirement under the British Iron and Steel Foundries Regulations of 1953.
When the cupola run is at an end, the cupola bottom is dropped to remove the unwanted slag and other material still inside the shell before employees can carry out the routine refractory maintenance. Dropping the cupola bottom is a skilled and dangerous operation requiring trained supervision. A refractory floor or layer of dry sand on which to drop the debris is essential. If a problem occurs, such as jammed cupola bottom doors, great caution must be exercised to avoid risks of burns to workers from the hot metal and slag.
Visible white-hot metal is a danger to workers’ eyes due to the emission of infrared and ultraviolet radiation, extensive exposure to which can cause cataracts.
The ladle must be dried before filling with molten metal, to prevent steam explosions; a satisfactory period of flame heating must be established.
Employees in metal and pouring sections of the foundry should be provided with hard hats, tinted eye protection and face shields, aluminized clothing such as aprons, gaiters or spats (lower-leg and foot coverings) and boots. Use of protective equipment should be mandatory, and there should be adequate instruction in its use and maintenance. High standards of housekeeping and exclusion of water to the highest degree possible are needed in all areas where molten metal is being manipulated.
Where large ladles are slung from cranes or overhead conveyors, positive ladle-control devices should be employed to ensure that spillage of metal cannot occur if the operator releases his or her hold. Hooks holding molten metal ladles must be periodically tested for metal fatigue to prevent failure.
In production foundries, the assembled mould moves along a mechanical conveyor to a ventilated pouring station. Pouring may be from a manually controlled ladle with mechanical assist, an indexing ladle controlled from a cab, or it can be automatic. Typically, the pouring station is provided with a compensating hood with a direct air supply. The poured mould proceeds along the conveyor through an exhausted cooling tunnel until shakeout. In smaller, job shop foundries, moulds may be poured on a foundry floor and allowed to burn off there. In this situation, the ladle should be equipped with a mobile exhaust hood.
Tapping and transport of molten iron and charging of electric furnaces creates exposure to iron oxide and other metal oxide fumes. Pouring into the mould ignites and pyrolyses organic materials, generating large amounts of carbon monoxide, smoke, carcinogenic polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and pyrolysis products from core materials which may be carcinogenic and also respiratory sensitizers. Moulds containing large polyurethane bound cold box cores release a dense, irritating smoke containing isocyanates and amines. The primary hazard control for mould burn off is a locally exhausted pouring station and cooling tunnel.
In foundries with roof fans for exhausting pouring operations, high metal fume concentrations may be found in the upper regions where crane cabs are located. If the cabs have an operator, the cabs should be enclosed and provided with filtered, conditioned air.
Pattern making
Pattern making is a highly skilled trade translating the two-dimensional design plans to a three-dimensional object. Traditional wooden patterns are made in standard workshops containing hand tools and electric cutting and planing equipment. Here, all reasonably practicable measures should be taken to reduce the noise to the greatest extent possible, and suitable ear protectors must be provided. It is important that the employees are aware of the advantages of using such protection.
Power-driven wood cutting and finishing machines are obvious sources of danger, and often suitable guards cannot be fitted without preventing the machine from functioning at all. Employees must be well versed in normal operating procedure and should also be instructed in the hazards inherent in the work.
Wood sawing can create dust exposure. Efficient ventilation systems should be fitted to eliminate wood dust from the pattern shop atmosphere. In certain industries using hard woods, nasal cancer has been observed. This has not been studied in the founding industry.
Casting in permanent metal moulds, as in die-casting, has been an important development in the foundry industry. In this case, pattern making is largely replaced by engineering methods and is really a die manufacture operation. Most of the pattern-making hazards and the risks from sand are eliminated, but are replaced by the risk inherent in the use of some sort of refractory material to coat the die or mould. In modern die-foundry work, increasing use is made of sand cores, in which case the dust hazards of the sand foundry are still present.
Moulding
The most common moulding process in the iron founding industry uses the traditional “green sand” mould made from silica sand, coal dust, clay and organic binders. Other methods of mould production are adapted from coremaking: thermosetting, cold self-setting and gas-hardened. These methods and their hazards will be discussed under coremaking. Permanent moulds or the lost foam process may also be used, especially in the aluminium foundry industry.
In production foundries, sand mix, moulding, mould assembly, pouring and shakeout are integrated and mechanized. Sand from shakeout is recycled back to the sand mix operation, where water and other additives are added and the sand is mixed in mullers to maintain the desired physical properties.
For ease of assembly, patterns (and their moulds) are made in two parts. In manual mould-making, the moulds are enclosed in metal or wooden frames called flasks. The bottom half of the pattern is placed in the bottom flask (the drag), and first fine sand and then heavy sand are poured around the pattern. The sand is compacted in the mould by a jolt-squeeze, sand slinger or pressure process. The top flask (the cope) is prepared similarly. Wooden spacers are placed in the cope to form the sprue and riser channels, which are the pathway for the molten metal to flow into the mould cavity. The patterns are removed, the core inserted, and then the two halves of the mould assembled and fastened together, ready for pouring. In production foundries, the cope and drag flasks are prepared on a mechanical conveyor, cores are placed in the drag flask, and the mould assembled by mechanical means.
Silica dust is a potential problem wherever sand is handled. Moulding sand is usually either damp or mixed with liquid resin, and is therefore less likely to be a significant source of respirable dust. A parting agent such as talc is sometimes added to promote the ready removal of the pattern from the mould. Respirable talc causes talcosis, a type of pneumoconiosis. Parting agents are more widespread where hand moulding is employed; in the larger, more automatic processes they are rarely seen. Chemicals are sometimes sprayed onto the mould surface, suspended or dissolved in isopropyl alcohol, which is then burned off to leave the compound, usually a type of graphite, coating the mould in order to achieve a casting with a finer surface finish. This involves an immediate fire risk, and all employees involved in applying these coatings should be provided with fire-retardant protective clothing and hand protection, as organic solvents can also cause dermatitis. Coatings should be applied in a ventilated booth to prevent the organic vapours from escaping into the workplace. Strict precautions should also be observed to ensure that the isopropyl alcohol is stored and used with safety. It should be transferred to a small vessel for immediate use, and the larger storage vessels should be kept well away from the burning-off process.
Manual mould making can involve the manipulation of large and cumbersome objects. The moulds themselves are heavy, as are the moulding boxes or flasks. They are often lifted, moved and stacked by hand. Back injuries are common, and power assists are needed so employees do not need to lift objects too heavy to be carried safely.
Standardized designs are available for enclosures of mixers, conveyors and pouring and shakeout stations with appropriate exhaust volumes and capture and transport velocities. Adherence to such designs and strict preventive maintenance of control systems will attain compliance with international recognized limits for dust exposure.
Coremaking
Cores inserted into the mould determine the internal configuration of a hollow casting, such as the water jacket of an engine block. The core must withstand the casting process but at the same time must not be so strong as to resist removal from the casting during the knocking-out stage.
Prior to the 1960s, core mixtures comprised sand and binders, such as linseed oil, molasses or dextrin (oil sand). The sand was packed in a core box with a cavity in the shape of the core, and then dried in an oven. Core ovens evolve harmful pyrolysis products and require a suitable, well maintained chimney system. Normally, convection currents within the oven will be sufficient to ensure satisfactory removal of fumes from the workplace, although they contribute enormously to air pollution After removal from the oven, the finished oil sand cores can still give rise to a small amount of smoke, but the hazard is minor; in some cases, however, small amounts of acrolein in the fumes may be a considerable nuisance. Cores may be treated with a “flare-off coating” to improve the surface finish of the casting, which calls for the same precautions as in the case of moulds.
Hot box or shell moulding and coremaking are thermosetting processes used in iron foundries. New sand may be mixed with resin at the foundry, or resin-coated sand may be shipped in bags for addition to the coremaking machine. Resin sand is injected into a metal pattern (the core box). The pattern is then heated—by direct natural gas fires in the hot box process or by other means for shell cores and moulding. Hot boxes typically use a furfuryl alcohol (furan), urea- or phenol-formaldehyde thermosetting resin. Shell moulding uses a urea- or phenol-formaldehyde resin. After a short curing time, the core hardens considerably and can be pushed clear of the pattern plate by ejector pins. Hot box and shell coremaking generate substantial exposure to formaldehyde, which is a probable carcinogen, and other contaminants, depending on the system. Control measures for formaldehyde include direct air supply at the operator station, local exhaust at the corebox, enclosure and local exhaust at the core storage station and low-formaldehyde-emission resins. Satisfactory control is difficult to achieve. Medical surveillance for respiratory conditions should be provided to coremaking workers. Phenol- or urea-formaldehyde resin contact with the skin or eyes must be prevented because the resins are irritants or sensitizers and can cause dermatitis. Copious washing with water will help to avoid the problem.
Cold-setting (no-bake) hardening systems presently in use include: acid-catalyzed urea- and phenol-formaldehyde resins with and without furfuryl alcohol; alkyd and phenolic isocyanates; Fascold; self-set silicates; Inoset; cement sand and fluid or castable sand. Cold-setting hardeners do not require external heating to set. The isocyanates employed in binders are normally based on methylene diphenyl isocyanate (MDI), which, if inhaled, can act as a respiratory irritant or sensitizer, causing asthma. Gloves and protective goggles are advisable when handling or using these compounds. The isocyanates themselves should be carefully stored in sealed containers in dry conditions at a temperature between 10 and 30°C. Empty storage vessels should be filled and soaked for 24 hours with a 5% sodium carbonate solution in order to neutralize any residual chemical left in the drum. Most general housekeeping principles should be strictly applied to resin moulding processes, but the greatest caution of all should be exercised when handling the catalysts used as setting agents. The catalysts for the phenol and oil isocyanate resins are usually aromatic amines based on pyridine compounds, which are liquids with a pungent smell. They can cause severe skin irritation and renal and hepatic damage and can also affect the central nervous system. These compounds are supplied either as separate additives (three-part binder) or are ready mixed with the oil materials, and LEV should be provided at the mixing, moulding, casting and knockout stages. For certain other no-bake processes the catalysts used are phosphoric or various sulphonic acids, which are also toxic; accidents during transport or use should be adequately guarded against.
Gas-hardened coremaking comprises the carbon dioxide (CO2)-silicate and the Isocure (or “Ashland”) processes. Many variations of the CO2-silicate process have been developed since the 1950s. This process has generally been used for the production of medium to large moulds and cores. The core sand is a mixture of sodium silicate and silica sand, usually modified by adding such substances as molasses as breakdown agents. After the core box is filled, the core is cured by passing carbon dioxide through the core mixture. This forms sodium carbonate and silica gel, which acts as a binder.
Sodium silicate is an alkaline substance, and can be harmful if it comes into contact with the skin or eyes or is ingested. It is advisable to provide an emergency shower close to areas where large quantities of sodium silicate are handled and gloves should always be worn. A readily available eye-wash fountain should be located in any foundry area where sodium silicate is used. The CO2 can be supplied as a solid, liquid or gas. Where it is supplied in cylinders or pressure tanks, a great many housekeeping precautions should be taken, such as cylinder storage, valve maintenance, handling and so on. There is also the risk from the gas itself, since it can lower the oxygen concentration in the air in enclosed spaces.
The Isocure process is used for cores and moulds. This is a gas-setting system in which a resin, frequently phenol-formaldehyde, is mixed with a di-isocyanate (e.g., MDI) and sand. This is injected into the core box and then gassed with an amine, usually either triethylamine or dimethylethylamine, to cause the crosslinking, setting reaction. The amines, often sold in drums, are highly volatile liquids with a strong smell of ammonia. There is a very real risk of fire or explosion, and extreme care should be taken, especially where the material is stored in bulk. The characteristic effect of these amines is to cause halo vision and corneal swelling, although they also affect the central nervous system, where they can cause convulsions, paralysis and, occasionally, death. Should some of the amine come into contact with the eyes or skin, first-aid measures should include washing with copious quantities of water for at least 15 minutes and immediate medical attention. In the Isocure process, the amine is applied as a vapour in a nitrogen carrier, with excess amine scrubbed through an acid tower. Leakage from the corebox is the principle cause of high exposure, although offgassing of amine from manufactured cores is also significant. Great care should be taken at all times when handling this material, and suitable exhaust ventilation equipment should be installed to remove vapours from the working areas.
Shakeout, casting extraction and core knockout
After the molten metal has cooled, the rough casting must be removed from the mould. This is a noisy process, typically exposing operators well above 90 dBA over an 8 hour working day. Hearing protectors should be provided if it is not practicable to reduce the noise output. The main bulk of the mould is separated from the casting usually by jarring impact. Frequently the moulding box, mould and casting are dropped onto a vibrating grid to dislodge the sand (shakeout). The sand then drops through the grid into a hopper or onto a conveyor where it can be subjected to magnetic separators and recycled for milling, treatment and re-use, or merely dumped. Sometimes hydroblasting can be used instead of a grid, creating less dust. The core is removed here, also sometimes using high-pressure water streams.
The casting is then removed and transferred to the next stage of the knockout operation. Often small castings can be removed from the flask by a “punch-out” process before shakeout, which produces less dust. The sand gives rise to hazardous silica dust levels because it has been in contact with molten metal and is therefore very dry. The metal and sand remain very hot. Eye protection is needed. Walking and working surfaces must be kept free of scrap, which is a tripping hazard, and of dust, which can be resuspended to pose an inhalation hazard.
Relatively few studies have been carried out to determine what effect, if any, the new core binders have on the health of the de-coring operator in particular. The furanes, furfuryl alcohol and phosphoric acid, urea- and phenol-formaldehyde resins, sodium silicate and carbon dioxide, no-bakes, modified linseed oil and MDI, all undergo some type of thermal decomposition when exposed to the temperatures of the molten metals.
No studies have yet been conducted on the effect of the resin-coated silica particle on the development of pneumoconiosis. It is not known whether these coatings will have an inhibiting or accelerating effect on lung-tissue lesions. It is feared that the reaction products of phosphoric acid may liberate phosphine. Animal experiments and some selected studies have shown that the effect of the silica dust on lung tissue is greatly accelerated when silica has been treated with a mineral acid. Urea- and phenol-formaldehyde resins can release free phenols, aldehydes and carbon monoxide. The sugars added to increase collapsibility produce significant amounts of carbon monoxide. No-bakes will release isocyanates (e.g., MDI) and carbon monoxide.
Fettling (cleaning)
Casting cleaning, or fettling, is carried out following shakeout and core knockout. The various processes involved are variously designated in different places but can be broadly classified as follows:
- Dressing covers stripping, roughing or mucking-off, removal of adherent moulding sand, core sand, runners, risers, flash and other readily disposable matter with hand tools or portable pneumatic tools.
- Fettling covers removal of burnt-on moulding sand, rough edges, surplus metal, such as blisters, stumps of gates, scabs or other unwanted blemishes, and the hand cleaning of the casting using hand chisels, pneumatic tools and wire brushes. Welding techniques, such as oxyacetylene-flame cutting, electric arc, arc-air, powder washing and the plasma torch, may be employed for burning off headers, for casting repair and for cutting and washing.
Sprue removal is the first dressing operation. As much as half of the metal cast in the mould is not part of the final casting. The mould must include reservoirs, cavities, feeders and sprue in order that it be filled with metal to complete the cast object. The sprue usually can be removed during the knockout stage, but sometimes this must be carried out as a separate stage of the fettling or dressing operation. Sprue removal is done by hand, usually by knocking the casting with a hammer. To reduce noise, the metal hammers can be replaced by rubber-covered ones and the conveyors lined with the same noise-damping rubber. Hot metal fragments are thrown off and pose an eye hazard. Eye protection must be used. Detached sprues should normally be returned to the charging region of the melting plant and should not be permitted to accumulate at the despruing section of the foundry. After despruing (but sometimes before) most castings are shot blasted or tumbled to remove mould materials and perhaps to improve the surface finish. Tumbling barrels generate high noise levels. Enclosures may be necessary, which can also require LEV.
Dressing methods in steel, iron and non-ferrous foundries are very similar, but special difficulties exist in the dressing and fettling of steel castings owing to greater amounts of burnt-on fused sand compared to iron and non-ferrous castings. Fused sand on large steel castings may contain cristobalite, which is more toxic than the quartz found in virgin sand.
Airless shot blasting or tumbling of castings before chipping and grinding is needed to prevent overexposure to silica dust. The casting must be free of visible dust, although a silica hazard may still be generated by grinding if silica is burnt into the apparently clean metal surface of the casting. The shot is centrifugally propelled at the casting, and no operator is required inside the unit. The blast cabinet must be exhausted so no visible dust escapes. Only when there is a breakdown or deterioration of the shot-blast cabinet and/or the fan and collector is there a dust problem.
Water or water and sand or pressure shot blasting may be used to remove adherent sand by subjecting the casting to a high-pressure stream of either water or iron or steel shot. Sand blasting has been banned in several countries (e.g., the United Kingdom) because of the silicosis risk as the sand particles become finer and finer and the respirable fraction thus continually increases. The water or shot is discharged through a gun and can clearly present a risk to personnel if not handled correctly. Blasting should always be carried out in an isolated, enclosed space. All blasting enclosures should be inspected at regular intervals to ensure that the dust extraction system is functioning and that there are no leaks through which shot or water could escape into the foundry. Blasters’ helmets should be approved and carefully maintained. It is advisable to post a notice on the door to the booth, warning employees that blasting is under way and that unauthorized entry is prohibited. In certain circumstances delay bolts linked to the blast drive motor can be fitted to the doors, making it impossible to open the doors until blasting has ceased.
A variety of grinding tools are used to smooth the rough casting. Abrasive wheels may be mounted on floor-standing or pedestal machines or in portable or swing-frame grinders. Pedestal grinders are used for smaller castings that can be easily handled; portable grinders, surface disc wheels, cup wheels and cone wheels are used for a number of purposes, including smoothing of internal surfaces of castings; swing-frame grinders are used primarily on large castings that require a great deal of metal removal.
Other Foundries
Steel founding
Production in the steel foundry (as distinct from a basic steel mill) is similar to that in the iron foundry; however, the metal temperatures are much higher. This means that eye protection with coloured lenses is essential and that the silica in the mould is converted by heat to tridymite or crystobalite, two forms of crystalline silica which are particularly dangerous to the lungs. Sand often becomes burnt on to the casting and has to be removed by mechanical means, which give rise to dangerous dust; consequently, effective dust exhaust systems and respiratory protection are essential.
Light-alloy founding
The light-alloy foundry uses mainly aluminium and magnesium alloys. These often contain small amounts of metals which may give off toxic fumes under certain circumstances. The fumes should be analysed to determine their constituents where the alloy might contain such components.
In aluminium and magnesium foundries, melting is commonly done in crucible furnaces. Exhaust vents around the top of the pot for removing fumes are advisable. In oil-fired furnaces, incomplete combustion due to faulty burners may result in products such as carbon monoxide being released into the air. Furnace fumes may contain complex hydrocarbons, some of which may be carcinogenic. During furnace and flue cleaning there is the hazard of exposure to vanadium pentoxide concentrated in furnace soot from oil deposits.
Fluorspar is commonly used as a flux in aluminium melting, and significant quantities of fluoride dust may be released to the environment. In certain cases barium chloride has been used as a flux for magnesium alloys; this is a significantly toxic substance and, consequently, considerable care is required in its use. Light alloys may occasionally be degassed by passing sulphur dioxide or chlorine (or proprietary compounds that decompose to produce chlorine) through the molten metal; exhaust ventilation and respiratory protective equipment are required for this operation. In order to reduce the cooling rate of the hot metal in the mould, a mixture of substances (usually aluminium and iron oxide) which react highly exothermically is placed on the mould riser. This “thermite” mixture gives off dense fumes which have been found to be innocuous in practice. When the fumes are brown in colour, alarm may be caused due to suspicion of the presence of nitrogen oxides; however, this suspicion is unfounded. The finely divided aluminium produced during the dressing of aluminium and magnesium castings constitutes a severe fire hazard, and wet methods should be used for dust collection.
Magnesium casting entails considerable potential fire and explosion hazard. Molten magnesium will ignite unless a protective barrier is maintained between it and the atmosphere; molten sulphur is widely employed for this purpose. Foundry workers applying the sulphur powder to the melting pot by hand may develop dermatitis and should be provided with gloves made of fireproof fabric. The sulphur in contact with the metal is constantly burning, so considerable quantities of sulphur dioxide are given off. Exhaust ventilation should be installed. Workers should be informed of the danger of a pot or ladle of molten magnesium catching fire, which may give rise to a dense cloud of finely divided magnesium oxide. Protective clothing of fireproof materials should be worn by all magnesium foundry workers. Clothing coated with magnesium dust should not be stored in lockers without humidity control, since spontaneous combustion may occur. The magnesium dust should be removed from the clothing.French chalk is used extensively in mould dressing in magnesium foundries; the dust should be controlled to prevent talcosis. Penetrating oils and dusting powders are employed in the inspection of light-alloy castings for the detection of cracks.
Dyes have been introduced to improve the effectiveness of these techniques. Certain red dyes have been found to be absorbed and excreted in sweat, thus causing soiling of personal clothing; although this condition is a nuisance, no effects on health have been observed.
Brass and bronze foundries
Toxic metal fumes and dust from typical alloys are a special hazard of brass and bronze foundries. Exposures to lead above safe limits in both melting, pouring and finishing operations are common, especially where alloys have a high lead composition. The lead hazard in furnace cleaning and dross disposal is particularly acute. Overexposure to lead is frequent in melting and pouring and can also occur in grinding. Zinc and copper fumes (the constituents of bronze) are the most common causes of metal fume fever, although the condition has also been observed in foundry workers using magnesium, aluminium, antimony and so on. Some high-duty alloys contain cadmium, which can cause chemical pneumonia from acute exposure and kidney damage and lung cancer from chronic exposure.
Permanent-mould process
Casting in permanent metal moulds, as in die-casting, has been an important development in the foundry. In this case, pattern making is largely replaced by engineering methods and is really a die-sinking operation. Most of the pattern making hazards are thereby removed and the risks from sand are also eliminated but are replaced by a degree of risk inherent in the use of some sort of refractory material to coat the die or mould. In modern die-foundry work, increasing use is made of sand cores, in which case the dust hazards of the sand foundry are still present.
Die casting
Aluminium is a common metal in die casting. Automotive hardware such as chrome trim is typically zinc die cast, followed by copper, nickel and chrome plating. The hazard of metal fume fever from zinc fumes should be constantly controlled, as must be chromic acid mist.
Pressure die-casting machines present all the hazards common to hydraulic power presses. In addition, the worker may be exposed to the mist of oils used as die lubricants and must be protected against the inhalation of these mists and the danger of oil-saturated clothing. The fire-resistant hydraulic fluids used in the presses may contain toxic organophosphorus compounds, and particular care should be taken during maintenance work on hydraulic systems.
Precision founding
Precision foundries rely on the investment or lost-wax casting process, in which patterns are made by injection moulding wax into a die; these patterns are coated with a fine refractory powder which serves as a mould-facing material, and the wax is then melted out prior to casting or by the introduction of the casting metal itself.
Wax removal presents a definite fire hazard, and decomposition of the wax produces acrolein and other hazardous decomposition products. Wax-burnout kilns must be adequately ventilated. Trichloroethylene has been used to remove the last traces of wax; this solvent may collect in pockets in the mould or be absorbed by the refractory material and vaporize or decompose during pouring. The inclusion of asbestos investment casting refractory materials should be eliminated due to the hazards of asbestos.
Health Problems and Disease Patterns
Foundries stand out among industrial processes because of a higher fatality rate arising from molten metal spills and explosions, cupola maintenance including bottom drop and carbon monoxide hazards during relining. Foundries report a higher incidence of foreign body, contusion and burn injuries and a lower proportion of musculoskeletal injuries than other facilities. They also have the highest noise exposure levels.
A study of several dozen fatal injuries in foundries revealed the following causes: crushing between mould conveyor cars and building structures during maintenance and trouble-shooting, crushing while cleaning mullers which were remotely activated, molten metal burns after crane failure, mould cracking, overflowing transfer ladle, steam eruption in undried ladle, falls from cranes and work platforms, electrocution from welding equipment, crushing from material-handling vehicles, burns from cupola bottom drop, high-oxygen atmosphere during cupola repair and carbon monoxide overexposure during cupola repair.
Abrasive wheels
The bursting or breaking of abrasive wheels may cause fatal or very serious injuries: gaps between the wheel and the rest at pedestal grinders may catch and crush the hand or forearm. Unprotected eyes are at risk at all stages. Slips and falls, especially when carrying heavy loads, may be caused by badly maintained or obstructed floors. Injuries to the feet may be caused by falling objects or dropped loads. Sprains and strains may result from overexertion in lifting and carrying. Badly maintained hoisting appliances may fail and cause materials to fall on workers. Electric shock may result from badly maintained or unearthed (ungrounded) electrical equipment, especially portable tools.
All dangerous parts of machinery, especially abrasive wheels, should have adequate guarding, with automatic lockout if the guard is removed during processing. Dangerous gaps between the wheel and the rest at pedestal grinders should be eliminated, and close attention should be paid to all precautions in the care and maintenance of abrasive wheels and in regulation of their speed (particular care is required with portable wheels). Strict maintenance of all electrical equipment and proper grounding arrangements should be enforced. Workers should be instructed in correct lifting and carrying techniques and should know how to attach loads to crane hooks and other hoisting appliances. Suitable PPE, such as eye and face shields and foot and leg protection, should also be provided. Provision should be made for prompt first aid, even for minor injuries, and for competent medical care when needed.
Dust
Dust diseases are prominent among foundry workers. Silica exposures are often close to or exceed prescribed exposure limits, even in well-controlled cleaning operations in modern production foundries and where castings are free of visible dust. Exposures many times above the limit occur where castings are dusty or cabinets leak. Overexposures are likely where visible dust escapes venting in shakeout, sand preparation or refractory repair.
Silicosis is the predominant health hazard in the steel fettling shop; a mixed pneumoconiosis is more prevalent in iron fettling (Landrigan et al. 1986). In the foundry, the prevalence increases with length of exposure and higher dust levels. There is some evidence that conditions in steel foundries are more likely to cause silicosis than those in iron foundries because of the higher levels of free silica present. Attempts to set an exposure level at which silicosis will not occur have been inconclusive; the threshold is probably less than 100 micrograms/m3 and perhaps as low as half that amount.
In most countries, the occurrence of new cases of silicosis is declining, in part because of changes in technology, a move away from silica sand in foundries and a shift away from silica brick and towards basic furnace linings in steel melting. A major reason is the fact that automation has resulted in the employment of fewer workers in steel production and foundries. Exposure to respirable silica dust remains stubbornly high in many foundries, however, and in countries where processes are labour intensive, silicosis remains a major problem.
Silico-tuberculosis has long been reported in foundry workers. Where the prevalence of silicosis has declined, there has been a parallel falling off in reported cases of tuberculosis, although that disease has not been completely eradicated. In countries where dust levels have remained high, dusty processes are labour intensive and the prevalence of tuberculosis in the general population is elevated, tuberculosis remains an important cause of death amongst foundry workers.
Many workers suffering from pneumoconiosis also have chronic bronchitis, often associated with emphysema; it has long been thought by many investigators that, in some cases at least, occupational exposures may have played a part. Cancer of the lung, lobar pneumonia, bronchopneumonia and coronary thrombosis have also been reported to be associated with pneumoconiosis in foundry workers.
A recent review of mortality studies of foundry workers, including the American auto industry, showed increased deaths from lung cancer in 14 of 15 studies. Because high lung cancer rates are found among cleaning room workers where the primary hazard is silica, it is likely that mixed exposures are also found.
Studies of the carcinogens in the foundry environment have concentrated on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons formed in the thermal breakdown of sand additives and binders. It has been suggested that metals such as chromium and nickel, and dusts such as silica and asbestos, may also be responsible for some of the excess mortality. Differences in moulding and core-making chemistry, sand type and the composition of iron and steel alloys may be responsible for different levels of risk in different foundries (IARC 1984).
Increased mortality from non-malignant respiratory disease was found in 8 of 11 studies. Silicosis deaths were recorded as well. Clinical studies found x-ray changes characteristic of pneumoconiosis, lung function deficits characteristic of obstruction, and increased respiratory symptoms among workers in modern “clean” production foundries. These resulted from exposures after the l960s and strongly suggest that the health risks prevalent in the older foundries have not yet been eliminated.
Prevention of lung disorders is essentially a matter of dust and fume control; the generally applicable solution is providing good general ventilation coupled with efficient LEV. Low-volume, high-velocity systems are most suitable for some operations, particularly portable grinding wheels and pneumatic tools.
Hand or pneumatic chisels used to remove burnt-on sand produce much finely divided dust. Brushing off excess materials with revolving wire brushes or hand brushes also produces much dust; LEV is required.
Dust control measures are readily adaptable to floor-standing and swing-frame grinders. Portable grinding on small castings can be carried out on exhaust-ventilated benches, or ventilation may be applied to the tools themselves. Brushing can also be carried out on a ventilated bench. Dust control on large castings presents a problem, but considerable progress has been made with low-volume, high-velocity ventilation systems. Instruction and training in their use is needed to overcome the objections of workers who find these systems cumbersome and complain that their view of the working area is impaired.
Dressing and fettling of very large castings where local ventilation is impracticable should be done in a separate, isolated area and at a time when few other workers are present. Suitable PPE that is regularly cleaned and repaired, should be provided for each worker, along with instruction in its proper use.
Since the 1950s, a variety of synthetic resin systems have been introduced into foundries to bind sand in cores and moulds. These generally comprise a base material and a catalyst or hardener which starts the polymerization. Many of these reactive chemicals are sensitizers (e.g., isocyanates, furfuryl alcohol, amines and formaldehyde) and have now been implicated in cases of occupational asthma among foundry workers. In one study, 12 out of 78 foundry workers exposed to Pepset (cold-box) resins had asthmatic symptoms, and of these, six had a marked decline in airflow rates in a challenge test using methyl di-isocyanate (Johnson et al. 1985).
Welding
Welding in fettling shops exposes workers to metal fumes with the consequent hazard of toxicity and metal fever, depending on the composition of the metals involved. Welding on cast iron requires a nickel rod and creates exposure to nickel fumes. The plasma torch produces a considerable amount of metal fumes, ozone, nitrogen oxide and ultraviolet radiation, and generates high levels of noise.
An exhaust-ventilated bench can be provided for welding small castings. Controlling exposures during welding or burning operations on large castings is difficult. A successful approach involves creating a central station for these operations and providing LEV through a flexible duct positioned at the point of welding. This requires training the worker to move the duct from one location to another. Good general ventilation and, when necessary, the use of PPE will aid in reducing the overall dust and fume exposures.
Noise and vibration
The highest levels of noise in the foundry are usually found in knockout and cleaning operations; they are higher in mechanized than in manual foundries. The ventilation system itself may generate exposures close to 90 dBA.
Noise levels in the fettling of steel castings may be in the range of 115 to 120 dBA, while those actually encountered in the fettling of cast iron are in the 105 to 115 dBA range. The British Steel Casting Research Association established that the sources of noise during fettling include:
- the fettling tool exhaust
- the impact of the hammer or wheel on the casting
- resonance of the casting and vibration against its support
- transmission of vibration from the casting support to surrounding structures
- reflection of direct noise by the hood controlling air flow through the ventilation system.
Noise control strategies vary with the size of the casting, the type of metal, the work area available, the use of portable tools and other related factors. Certain basic measures are available to reduce noise exposure of individuals and co-workers, including isolation in time and space, complete enclosures, partial sound-absorbing partitions, execution of work on sound-absorbing surfaces, baffles, panels and hoods made from sound-absorbing or other acoustical materials. The guidelines for safe daily exposure limits should be observed and, as a last resort, personal protective devices may be used.
A fettling bench developed by the British Steel Casting Research Association reduces the noise in chipping by about 4 to 5 dBA. This bench incorporates an exhaust system to remove dust. This improvement is encouraging and leads to hope that, with further development, even greater noise reductions will become possible.
Hand-arm vibration syndrome
Portable vibrating tools may cause Raynaud’s phenomenon (hand-arm vibration syndrome—HAVS). This is more prevalent in steel fettlers than in iron fettlers and more frequent among those using rotating tools. The critical vibratory rate for the onset of this phenomenon is between 2,000 and 3,000 revolutions per minute and in the range of 40 to 125 Hz.
HAVS is now thought to involve effects on a number of other tissues in the forearm apart from peripheral nerves and blood vessels. It is associated with carpal tunnel syndrome and degenerative changes in the joints. A recent study of steelworks chippers and grinders showed they were twice as likely to develop Dupuytren’s contracture than a comparison group (Thomas and Clarke 1992).
Vibration transmitted to the hands of the worker can be considerably reduced by: selection of tools designed to reduce the harmful ranges of frequency and amplitude; direction of the exhaust port away from the hand; use of multiple layers of gloves or an insulating glove; and shortening of exposure time by changes in work operations, tools and rest periods.
Eye problems
Some of the dusts and chemicals encountered in foundries (e.g., isocyanates, formaldehyde and tertiary amines, such as dimethlyethylamine, triethylamine and so on) are irritants and have been responsible for visual symptoms among exposed workers. These include itchy, watery eyes, hazy or blurred vision or so called “blue-grey vision”. On the basis of the occurrence of these effects, reducing time-weighted average exposures below 3 ppm has been recommended.
Other problems
Formaldehyde exposures at or above the US exposure limit are found in well-controlled hot-box core-making operations. Exposures many times above the limit may be found where hazard control is poor.
Asbestos has been used widely in the foundry industry and, until recently, it was often used in protective clothing for heat-exposed workers. Its effects have been found in x-ray surveys of foundry workers, both among production workers and maintenance workers who have been exposed to asbestos; a cross-sectional survey found the characteristic pleural involvement in 20 out of 900 steel workers (Kronenberg et al. 1991).
Periodic examinations
Preplacement and periodic medical examinations, including a survey of symptoms, chest x rays, pulmonary function tests and audiograms, should be provided for all foundry workers with appropriate follow-up if questionable or abnormal findings are detected. The compounding effects of tobacco smoke on the risk of respiratory problems among foundry workers mandate inclusion of advice on smoking cessation in a programme of health education and promotion.
Conclusion
Foundries have been an essential industrial operation for centuries. Despite continuing advances in technology, they present workers with a panoply of hazards to safety and health. Because hazards continue to exist even in the most modern plants with exemplary prevention and control programmes, protecting the health and well-being of workers remains an ongoing challenge to management and to the workers and their representatives. This remains difficult both in industry downturns (when concerns for worker health and safety tend to give way to economic stringencies) and in boom times (when the demand for increased output may lead to potentially dangerous short cuts in the processes). Education and training in hazard control, therefore, remain a constant necessity.
Automobile and Transportation Equipment History
General Profile
Distinct segments of the automobile and transportation equipment industry produce:
- cars and light trucks
- medium and heavy trucks
- buses
- farm and construction equipment
- industrial trucks
- motorcycles.
The characteristic assembly line for the finished vehicle is supported by separate manufacturing facilities for various parts and components. Vehicle components may be manufactured within the parent enterprise or purchased from separate corporate entities. The industry is a century old. Production in the North American, European and (since the Second World War) Japanese sectors of the industry became concentrated in a few corporations which maintained branch assembly operations in South America, Africa and Asia for sales to those markets. International trade in finished vehicles has increased since the 1970s, and trade in original equipment and replacement auto parts from facilities in the developing world is increasingly important.
Manufacture of heavy trucks, buses and farm and construction equipment are distinct businesses from car production, although some auto producers manufacture for both markets, and farm and construction equipment are also made by the same corporations. This line of products uses large diesel engines rather than gasoline engines. Production rates are typically slower, volumes smaller and processes less mechanized.
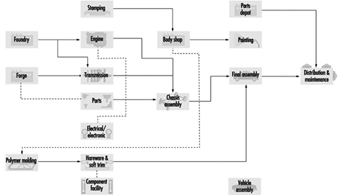
The types of facilities, the production processes and the typical components in car production are shown in table 1. Figure 1provides a flow chart for the steps in automobile production. The standard industrial classifications that are found in this industry include: motor vehicles and car body assembly, truck and bus body assembly, motor vehicle parts and accessories, iron and steel foundries, non-ferrous foundries, automotive stampings, iron and steel forgings, engine electrical equipment, auto and apparel trimmings and others. The number of people employed in the manufacture of parts exceeds that employed in assembly. These processes are supported by facilities for design of the vehicle, construction and maintenance of plant and equipment, clerical and managerial functions and a dealer and repair function. In the United States, car dealers, service stations and wholesale auto parts facilities employ about twice as many workers as the manufacturing functions.
Table 1. Production processes for automobile production.
|
Facility type |
Product and process |
|
Ferrous foundry |
Castings for machining into engine blocks and heads, other components |
|
Aluminium foundry and die cast |
Engine blocks and heads, transmission casings, other cast components |
|
Forging and heat treatment |
Pre-machined parts for engines, suspensions and transmissions |
|
Stamping |
Body panels and subassemblies |
|
Engine |
Machining of castings, assembly into finished product |
|
Transmission |
Machining of castings and forgings, assembly into product |
|
Glass |
Windshields, side windows and backlights |
|
Automotive parts |
Machining, stamping and assembly, including brakes, suspension parts, heating and air conditioning, pollution-control equipment, vehicle lighting |
|
Electrical and electronic |
Ignition systems, radios, motors, controllers |
|
Hardware and hard trim |
Polymer moulded exterior body panels, trim components |
|
Soft trim |
Seat cushions, built up seats, dashboard assemblies, interior body panels |
|
Vehicle assembly |
Body shop, painting, chassis assembly, final assembly |
|
Parts depots |
Warehousing, parts painting and assembly, packaging and shipping |
Figure 1. Flow chart for automobile production.
The workforce is predominantly male. In the United States, for example, it is about 80% male. Female employment is higher in trim and other lighter manufacturing processes. There is limited opportunity for job transfer from hourly work to clerical work or to technical and professional employment. Assembly line supervisors do, however, often come from the production and maintenance units. About 20% of hourly employees are employed in the skilled trades, although the fraction of employees in any particular facility who are in skilled trades varies greatly, from less than 10% in assembly operations to almost 50% in stamping operations. Because of contractions in employment levels over the decade of the 1980s, the average age of the workforce in the late 1990s exceeds 45 years, with hiring of new workers appearing only since 1994.
Major Sectors and Processes
Ferrous casting
Founding or metal casting involves the pouring of molten metal into a hollow inside a heat-resistant mould, which is the outside or negative shape of the pattern of the desired metal object. The mould may contain a core to determine the dimensions of any internal cavity in the final metal object. Foundry work consists of the following basic steps:
- making a pattern of the desired article from wood, metal, plastic or some other material
- making the mould by pouring sand and a binder around the pattern and compacting or setting it
- removing the pattern, inserting any core and assembling the mould
- melting and refining the metal in a furnace
- pouring the molten metal into the mould
- cooling the metal casting
- removing the mould and core from the metal casting by the “punch-out” process (for small castings) and by vibrating screens (shakeout) or hydro-blasting
- removing extra metal (e.g., the metal in the sprue—the pathway for molten metal to enter the mould) and burnt-on sand from the finished casting (fettling) by blasting with steel shot, hand chipping and grinding.
Ferrous foundries of the production type are a characteristic auto industry process. They are used in the automobile industry to produce engine blocks, heads and other parts. There are two basic types of ferrous foundries: gray iron foundries and ductile iron foundries. Gray iron foundries use scrap iron or pig iron (new ingots) to make standard iron castings. Ductile iron foundries add magnesium, cerium or other additives (often called ladle additives) to the ladles of molten metal before pouring to make nodular or malleable iron castings. The different additives have little impact on workplace exposures.
Typical automobile foundries use cupola or induction furnaces to melt the iron. A cupola furnace is a tall vertical furnace, open at the top, with hinged doors at the bottom. It is charged from the top with alternate layers of coke, limestone and metal; the molten metal is removed at the bottom. An induction furnace melts the metal by passing a high electric current through copper coils on the outside of the furnace. This induces an electric current in the outer edge of the metal charge, which heats the metal due to the high electrical resistance of the metal charge. Melting progresses from the outside of the charge to the inside.
In ferrous foundries, moulds are traditionally made from green sand (silica sand, coal dust, clay and organic binders), which is poured around the pattern, which is usually in two parts, and then compacted. This can be done manually or mechanically on a conveyor belt in production foundries. The pattern is then removed and the mould assembled mechanically or manually. The mould must have a sprue.
If the metal casting is to have a hollow interior, a core must be inserted into the mould. Cores can be made from thermosetting phenol-formaldehyde resins (or similar resins) mixed with sand which is then heated (hot box method) or from amine-cured urethane/sand mixtures which cure at room temperature (cold box method). The resin/sand mixture is poured into a core box which has a cavity in the desired shape of the core.
The products produced in gray iron castings are typically of a large size, such as engine blocks. The physical size increases the physical hazards on the job and also presents more difficult dust control problems.
Atmospheric contaminants in foundry processes
Silica-containing dusts. Silica-containing dusts are found in finishing, in shakeout-knockout, in moulding, in core making and in sand system and melt department maintenance activities. Air sampling studies during the 1970s typically found severalfold overexposures to silica, with the highest levels in finishing. Exposures were higher in mechanized production foundries than job shops. Improved control measures including enclosure and exhaust of sand systems and shakeout, mechanization and periodic industrial hygiene measurements have reduced levels. Standard ventilation designs are available for most foundry operations. Exposures above current limits persist in finishing operations due to inadequate sand removal after shakeout and silica burn-in on casting surfaces.
Carbon monoxide. Acutely dangerous carbon monoxide levels are encountered during cupola furnace maintenance and during upsets in process ventilation in the melt department. Excessive levels can also be encountered in cooling tunnels. Carbon monoxide exposures have also been associated with cupola melting and with the combustion of carbon material in green sand moulds. Exposure to sulphur dioxide of unknown origin can also occur, perhaps from sulphur contaminants in the mould.
Metal fumes. Metal fumes are found in melting and pouring operations. It is necessary to use compensating hoods over pouring stations in order to exhaust both metal fumes and combustion gases. Excessive exposures to lead fumes are occasionally encountered in iron foundries and are pervasive in brass foundries; lead fumes in gray iron arise from lead contamination of the scrap iron starting materials.
Other chemical and physical hazards. Formaldehyde, amine vapours and isocyanate pyrolysis products can be found in coremaking and core burn-off products. High-production coremaking is characteristic of the auto industry. Hot box phenol-formaldehyde coremaking replaced oil-sand cores in the mid-1960s and brought substantial formaldehyde exposures, which, in turn, increased the risks of respiratory irritation, lung function abnormalities and lung cancer. Protection requires local exhaust ventilation (LEV) at the core machine, core check stations and conveyor and low emission resins. When the phenol-formaldehyde coremaking has been replaced by cold box amine-cured polyurethane systems, effective maintenance of seals at the core box, and LEV where the cores are stored prior to insertion in the mould, are needed to protect employees against ocular effects of amine vapours.
Workers who are employed in these areas should undergo pre-placement and periodic medical examinations, including a chest x ray reviewed by an expert reader, a lung function test and a symptoms questionnaire, which are essential to detect early signs of pneumoconiosis, chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Periodic audiograms are needed, as hearing protection is often ineffective.
High levels of noise and vibration are encountered in processes such as furnace loading, mechanical de-coring, stripping and knockout of castings and fettling with pneumatic tools.
Foundry processes are heat intensive. The radiant heat load in melting, pouring, shakeout, core knockout and sprue removal requires special protective measures. Some of these measures include increased relief time (time away from the job), which is a common practice. Still extra relief during hot, summer months is also commonly provided. Workers should be outfitted with heat-protective clothing and eye and face protection in order to prevent the formation of cataracts. Climatized break areas near the work area improve the protective value of heat relief.
Aluminium casting
Aluminium casting (foundry and die-casting) is used to produce cylinder heads, transmission cases, engine blocks and other automotive parts. These facilities typically cast the products in permanent moulds, with and without sand cores, although the lost foam process has been introduced. In the lost foam process, the polystyrene foam pattern is not removed from the mould but is vaporized by the molten metal. Die casting involves the forcing of molten metal under pressure into metal moulds or dies. It is used to make large numbers of small, precise parts. Die-casting is followed by trim removal on a forge press and some finishing activities. Aluminium may be melted onsite or it can be delivered in molten form.
Hazards can arise because of significant pyrolysis of the core. Silica exposures may be found in permanent mould foundries where large cores are present. Local exhaust on shakeout is needed to prevent hazardous levels of exposure.
Other non-ferrous casting
Other non-ferrous die casting and electroplating processes are used to produce the trim on automotive products, the hardware and the bumpers. Electroplating is a process in which a metal is deposited onto another metal by an electrochemical process.
Bright metal trim traditionally was die-cast zinc, successively plated with copper, nickel and chrome, and then finished by polishing. Carburettor and fuel-injector parts are also die cast. Manual extraction of parts from die-casting machines is increasingly being replaced by mechanical extraction, and bright metal parts are being replaced by painted metal parts and plastic. Bumpers had been produced by pressing steel, followed by plating, but these methods are increasingly being replaced by the use of polymer parts in passenger vehicles.
Electroplating with chrome, nickel, cadmium, copper and so on is normally carried out in separate workshops and involves exposure to, inhalation of or contact with vapours from the acid plating baths. An increased incidence of cancer has been associated with both chromic acid and sulphuric acid mists. These mists are also extremely corrosive to the skin and respiratory tract. Electroplating baths should be labelled as to contents and should be fitted with special push-pull local exhaust systems. Anti-foaming surface tension agents should be added to the liquid in order to minimize mist formation. Workers should wear eye and face protection, hand and arm protection and aprons. Workers need periodic health checks as well.
Inserting and removing components from open-surface tanks are very hazardous operations which are increasingly becoming more mechanized. The buffing and polishing of plated components on felt belts or discs is strenuous and entails exposure to cotton, hemp and flax dust. This hazard can be minimized by providing a fixture or by mechanizing with transfer-type polishing machines.
Forging and heat treatment
Hot forging and cold forging followed by heat treatment are used to produce engine, transmission and suspension parts and other components.
Historically, automotive forging involved heating iron billets (bars) in individual oil-fired furnaces set close to individually operated steam hammer forges. In these drop hammer forges, the heated iron is placed in the bottom half of a metal die; the top half of the die is attached to the drop hammer. The iron is formed into the desired size and shape by multiple impacts of the dropping hammer. Today, such processes are replaced by induction heating of billets, which are worked in forging presses, which use pressure instead of impact to form the metal part, and drop hammer forges (upsetters) or by cold forging followed by heat treatment.
The forging process is extremely noisy. Noise exposure can be abated by replacing oil furnaces with induction heating devices, and the steam hammers with forging presses and upsetters. The process is also smoky. Oil smoke can be reduced by modernizing the furnace.
Forging and heat treatment are heat-intensive operations. Spot cooling using make-up air that circulates over workers in process areas is needed to reduce heat stress.
Machining
High production machining of engine blocks, crankshafts, transmissions and other components is characteristic of the auto industry. Machining processes are found within various parts manufacturing facilities and are the dominant process in engine, transmission and bearing production. Components such as camshafts, gears, differential pinions and brake drums are produced in machining operations. One-person machining stations are increasingly replaced by multiple station machines, machining cells and transfer lines which may be up to 200 metres in length. Soluble oils and synthetic and semi-synthetic coolants increasingly predominate over straight oils.
Foreign body injuries are common in machining operations; increased mechanical material handling and personal protective equipment are key preventive measures. Increased automation, particularly long transfer lines, increases the risk of severe acute trauma; improved machine guarding and energy lockout are preventive programmes.
The highest level of control measures for coolant mist include full enclosure of machining stations and fluid circulation systems, local exhaust directed outside or recirculated only through a high-efficiency filter, coolant system controls to reduce mist generation and coolant maintenance to control micro-organisms. Addition of nitrite to amine-containing fluids must be prohibited due to risk of nitrosamine production. Oils with substantial polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) content must not be used.
In case-hardening, tempering, nitrate salt baths and other metal heat-treatment processes using furnaces and controlled atmospheres, the microclimate may be oppressive and various airborne toxic substances encountered (e.g., carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, cyanides).
Machine attendants and workers handling swarf and centrifuging cutting oil prior to filtration and regeneration are exposed to the risk of dermatitis. Exposed workers should be provided with oil-resistant aprons and encouraged to wash thoroughly at the end of each shift.
Grinding and tool sharpening may present a danger of hard metal disease (interstitial lung disease) unless cobalt exposure is measured and controlled. Grinding wheels should be fitted with screens, and eye and face protection and respiratory protective equipment should be worn by grinders.
Machined parts are typically assembled into a finished component, with attendant ergonomic risks. In engine facilities engine testing and running-in must be carried out at test stations fitted with equipment for removing exhaust gases (carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, unburned hydrocarbons, aldehydes, nitrogen oxides) and with noise-control facilities (booths with sound-absorbent walls, insulated bedplates). Noise levels may be as high as 100 to 105 dB with peaks at 600 to 800 Hz.
Stamping
Pressing of sheet metal (steel) into body panels and other components, often combined with subassembly by welding, is done in large facilities with large and small mechanical power presses. Individual load and unload presses were successively replaced by mechanical extraction devices and now shuttle transfer mechanisms which can load as well, yielding fully automated press lines. Fabrication of subassemblies such as hoods and doors is accomplished with resistance welding presses and is increasingly performed in cells with robot transfer of parts.
The main process is the pressing of steel sheet, strip and light sections on mechanical power presses ranging in capacity from roughly 20 to 2,000 tonnes.
Modern press safety requires effective machinery guarding, prohibition of hands in dies, safety controls including anti-tie down two-hand controls, part revolution clutches and brake monitors, automatic feed and ejection systems, collection of press scrap and the use of personal protective equipment such as aprons, foot and leg protection and hand and arm protection. Outmoded and hazardous full-revolution clutch machines and pull-back devices must be eliminated. Handling rolled steel with cranes and loading of decoilers prior to blanking at the head of a press lines poses a severe safety hazard.
Press operators are exposed to substantial mist levels from drawing compounds which are similar in composition to machining fluids such as soluble oils. Welding fumes are present in fabrication. Noise exposures are high in stamping. Control measures for noise include mufflers on air valves, lining metal chutes with vibration-damping equipment, quieting parts carts, and isolation of presses; the point of operation of the press is not the main site of noise generation.
Following pressing, the pieces are assembled into sub-groups such as hoods and doors using resistance welding presses. Chemical hazards include welding fumes from primarily resistance welding and pyrolysis products of surface coatings, including drawing compound and sealers.
Plastic body panels and trim components
Metal trim parts such as chrome strips are being increasingly replaced by polymer materials. Hard body parts may be made from fibrous glass-reinforced polyester polystyrene systems, acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) thermosetting systems or polyethylene. Polyurethane systems may be high density for body parts, such as nose cones, or low-density foam for seats and interior padding.
Polyurethane foam moulding presents severe respiratory sensitization problems from inhalation of di-isocyanate monomer and possibly catalysts. Complaints persist in operations which are in compliance with limits for toluene di-isocyanate (TDI). Methylene chloride exposures from gun flushing can be substantial. Pouring stations need enclosure and LEV; spills of isocyanate should be minimized by safety devices and cleaned promptly by trained crews. Fires in curing ovens are also a problem in these facilities. Seat manufacture has severe ergonomic stresses, which can be reduced by fixtures, especially for stretching upholstery over cushions.
Styrene exposure from fibrous glass lay-up should be controlled by enclosing storage of mats and local exhaust. Dusts from grinding cured parts contain fibrous glass and should also be controlled by ventilation.
Vehicle assembly
Assembly of components into the finished vehicle typically takes place on a mechanized conveyor involving upwards of a thousand employees per shift, with additional support personnel. The largest segment of employees in the industry are in this process type.
A vehicle assembly plant is divided into distinct units: the body shop, which can include subassembly activities also found in a stamping; paint; chassis assembly; cushion room (which can be outsourced); and final assembly. Paint processes have evolved toward lower-solvent, more reactive formulations in recent years, with increasing use of robot and mechanical application. The body shop has become increasingly automated with reduced arc welding and replacement of hand-operated spot-welding guns with robots.
Light truck assembly (vans, pickups, sport utility vehicles) is similar in process to car assembly. Heavy truck, farm and construction equipment manufacture involves less mechanization and automation, longer cycle jobs, heavier physical labour, more arc welding and different paint systems.
The body shop of an assembly plant assembles the shell of the vehicle. Resistance welding machines may be transfer type, robotic or individually operated. Suspended spot welding machines are heavy and cumbersome to manipulate even when fitted with a counterbalance system. Transfer machines and robots have eliminated many manual jobs and removed workers from close, direct exposure to hot metal, sparks and combustion products of the mineral oil which contaminates the sheet metal. However, increased automation carries increased risk of severe injury to maintenance workers; energy lockout programmes and more elaborate and automatic machine guarding systems, including presence-sensing devices, are needed in automated body shops. Arc welding is employed to a limited degree. During this work, employees are exposed to intense visible and ultraviolet radiation and risk inhalation of combustion gases. LEV, protective screens and partitions, welding visors or goggles, gloves and aprons are needed for arc welders.
The body shop has the greatest laceration and foreign body injury hazards.
In past years assembly techniques and body panel defect retouching processes entailed soldering with lead and tin alloys (also containing traces of antimony). Soldering and especially the grinding away of excess solder produced a severe risk of lead poisoning, including fatal cases when the process was introduced in the 1930s. Protective measures included an isolated solder grind booth, respirators supplying positive-pressure air for solder grinders, hygiene facilities and lead-in-blood monitoring. Nevertheless, increased body burdens of lead and occasional cases of lead poisoning among workers and families persisted into the 1970s. Lead body solder has been eliminated in US passenger vehicles. In addition, noise levels in these processes may range up to 95 to 98 dB, with peaks at 600 to 800 Hz.
Automobile bodies from the body shop enter the paint shop on a conveyor where they are degreased, often by the manual application of solvents, cleaned in a closed tunnel (bonderite) and undercoated. The undercoat is then rubbed down by hand with an oscillating tool using wet abrasive paper, and the final layers of paint are applied and then cured in an oven. In paint shops, workers may inhale toluene, xylene, methylene chloride, mineral spirits, naphtha, butyl and amyl acetate and methyl alcohol vapours from body, booth and paint gun cleaning. Spray painting is carried on in downdraft booths with a continuously filtered air supply. Solvent vapour at painting stations is typically well controlled by down-draft ventilation, which is needed for product quality. Inhalation of paint particulate was formerly less well controlled, and some paints in the past contained salts of chromium and lead. In a well controlled booth, the workers should not have to wear respiratory protective equipment to achieve compliance with exposure limits. Many voluntarily wear respirators for overspray. Recently introduced two-component polyurethane paints should be sprayed only when air-supplied helmets are used with suitable booth re-entry times. Environmental regulations have spurred the development of high-solids paints with lower solvent content. Newer resin systems may generate substantial formaldehyde exposure, and powdered paints now being introduced are epoxy formulations which may be sensitizers. Recirculation of paint booth and oven exhaust from roof ventilating units into work areas outside the booth is a common complaint; this problem can be prevented by exhaust stacks of sufficient height.
In the production of commercial vehicles (lorries (trucks), trams, trolley buses) and farm and construction equipment, manual spray painting is still widely employed due to the large surfaces to be covered and the need for frequent retouching. Lead and chromate paints may still be employed in these operations.
The painted body work is dried in hot air and infra-red ovens fitted with exhaust ventilation and then moves on to join the mechanical components in the final assembly shop, where the body, engine and transmission are joined together and the upholstery and internal trim are fitted. It is here that conveyor belt work is to be seen in its most highly developed version. Each worker carries out a series of tasks on each vehicle with cycle times of about 1 minute. The conveyor system transports the bodies gradually along the assembly line. These processes demand constant vigilance and may be highly monotonous and act as stressors on certain subjects. Although normally not imposing excessive metabolic lead, these processes virtually all involve moderate to severe risk factors for musculoskeletal disorders.
The postures or movements the worker is obliged to adopt, such as when installing components inside the vehicle or working under the body (with hands and forearms above head level) are the most readily abated hazards, although force and repetition must also be reduced to abate risk factors. After final assembly the vehicle is tested, finished and dispatched. Inspection can be limited to roller tests on a roller bed (where ventilation of exhaust fumes is important) or can include track trials on different types of surface, water and dust tightness trials and road trials outside the factory.
Parts depots
Parts depots are integral to distributing the finished product and supplying repair parts. Workers in these high-production warehouses use order pickers to retrieve parts from elevated locations, with automated parts-delivery systems in three-shift operations. Manual handling of packaged parts is common. Painting and other production processes may be found in parts depots.
Testing of prototypes
Testing of automobile prototypes is specialized to the industry. Test drivers are exposed to a variety of physiological stresses, such as violent acceleration and deceleration, jolting and vibration, carbon monoxide and exhaust fumes, noise, work spells of prolonged duration and different ambient and climatic conditions. Endurance drivers endure special stresses. Fatal vehicle accidents occur in this occupation.
Assembly of heavy trucks and farm and construction equipment
The processes in these industry sectors are essentially the same as in the assembly of cars and light trucks. Contrasts include: slower pace of production, including non-assembly-line operations; more arc welding; riveting of truck cabs; movement of components by crane; use of chromate-containing pigments; and diesel on drive-off at the end of the assembly line. These sectors include more producers relative to volume and are less vertically integrated.
Manufacture of locomotives and rail cars
Distinct segments of railroad equipment manufacture include locomotives, passenger cars, freight cars and electric self-propelled passenger cars. Compared to car and truck manufacture, assembly processes involve longer cycles; there is more reliance on cranes for material handling; and arc welding is more heavily used. The large size of the products makes engineering control of spray paint operations difficult and creates situations where workers are completely enclosed in the product while welding and spray painting.
Health Problems and Disease Patterns
Production processes are not unique to the auto industry, but often the scale of production and the high degree of integration and automation combine to present special hazards to employees. Hazards to employees in this complex industry must be arrayed in three dimensions: process type, job classification group and adverse outcome.
Adverse outcomes with distinct cause and prevention methods can be distinguished as: fatal and severe acute injuries; injuries generally; repeated trauma disorders; short-onset chemical effects; occupational disease from long-term chemical exposure; service sector hazards (including infectious disease and client- or customer-initiated violence); and work environment hazards such as psychosocial stress.
Job classification groups in the automobile industry can usefully be divided by divergent hazard spectra: skilled trades (maintenance, service, fabrication and installation of production equipment); mechanical material handling (powered industrial truck and crane operators); production service (including non-skilled maintenance and cleaners); fixed production (the largest grouping, including assemblers and machine operators); clerical and technical; and executive and managerial.
Health and safety outcomes common to all processes
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the auto industry has one of the highest injury rates overall, with 1 in 3 employees hurt each year, 1 in 10 seriously enough to lose time from work. Lifetime risk of occupational fatality from acute traumatic injury is 1 in 2,000. Certain hazards are generally characteristic of occupational groupings throughout the industry. Other hazards, particularly chemicals, are characteristic of specific production processes.
Skilled trades and mechanical material-handling occupations are at high risk for fatal and severe acute traumatic injuries. The skilled trades are less than 20% of the workforce, yet suffer 46% of fatal occupational injuries. Mechanical material-handling occupations suffer 18% of fatalities. The skilled-trades fatalities largely occur during maintenance and service activities, with uncontrolled energy as the leading cause. Preventive measures include energy lockout programmes, machine guarding, fall prevention and industrial truck and crane safety, all based on directed job safety analysis.
By contrast, fixed production occupations suffer higher rates of injuries generally and repeated trauma disorders, but are at reduced risk to fatal injury. Musculoskeletal injuries, including repeated trauma disorders and closely related strains and sprains caused by overexertion or repetitive motion are 63% of disabling injuries in assembly facilities and about half the injuries in other process types. The chief preventive measures are ergonomics programmes based on risk factor analysis and structured reduction in force, frequency and postural stresses of high-risk jobs.
Production service occupations and skilled trades face the majority of acute and high-level chemical hazards. Typically these exposures occur during routine cleaning, response to spills and process upsets and in confined space entry during maintenance and service activities. Solvent exposures are prominent among these hazardous situations. The long-term health consequences of these intermittent high exposures are not known. High exposures to carcinogenic coal tar pitch volatiles are experienced by employees tarring wood block floors in many facilities or torching floor bolts in stamping plants. Excess mortality from lung cancer has been observed in such groups. Preventive measures focus on confined space entry and hazardous waste and emergency response programmes, although long-term prevention depends on process change to eliminate exposure.
Effects of chronic exposure to chemicals and some physical agents are most evident among fixed production workers, principally because these groups can more feasibly be studied. Virtually all the process-specific adverse effects described above arise from exposures in compliance with existing occupational exposure limits, so protection will depend on reduction of allowable limits. In the near term, best practices including well designed and maintained exhaust systems serve to reduce exposures and risks.
Noise-induced hearing loss is pervasive in all segments of the industry.
All sectors of the workforce are subject to psychosocial stress, although these are more apparent in the clerical, technical, administrative support, managerial and professional occupations because of their generally less intense exposure to other hazards. Nevertheless, job stress is likely more intense among production and maintenance employees, and stress effects are likely greater. No effective means of reducing stresses from night work and rotating shift work have been implemented, although shift preference agreements allow for some self selection, and shift premiums compensate those employees assigned to off shifts. Acceptance of rotating shifts by the workforce is historical and cultural. Skilled trades and maintenance employees work substantially more overtime and during holidays, vacations and shutdowns, compared to production employees. Typical work schedules include two production shifts and a shorter maintenance shift; this provides flexibility for overtime in periods of increased production.
The discussion which follows groups chemical and some specific physical hazards by production type and addresses injury and ergonomic hazards by job classification.
Foundries
Foundries stand out among auto industry processes with a higher fatality rate, arising from molten metal spills and explosions, cupola maintenance, including bottom drop, and carbon monoxide hazards during relining. Foundries report a higher fraction of foreign body, contusion and burn injuries and a lower fraction of musculoskeletal disorders than other facilities. Foundries also have the highest noise exposure levels (Andjelkovich et al. 1990; Andjelkovich et al. 1995; Koskela 1994; Koskela et al. 1976; Silverstein et al. 1986; Virtamo and Tossavainen 1976).
A recent review of mortality studies including the American auto industry showed that foundry workers experienced increased rates of deaths from lung cancer in 14 of 15 studies (Egan-Baum, Miller and Waxweiller 1981; Mirer et al. 1985). Because high lung cancer rates are found among cleaning room workers where the primary exposure is silica, it is likely that mixed silica-containing dust exposure is a major cause (IARC 1987, 1996), although polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon exposures are also found. Increased mortality from non-malignant respiratory disease was found in 8 of 11 studies. Silicosis deaths were recorded as well. Clinical studies find x-ray changes characteristic of pneumoconiosis, lung function deficits characteristic of obstruction and increased respiratory symptoms in modern production foundries with the highest levels of controls. These effects arose from exposure conditions which prevailed from the 1960s onward and strongly indicate that health risks persist under current conditions as well.
Asbestos effects are found on x ray among foundry workers; victims include production as well as maintenance workers with identifiable asbestos exposures.
Machining operations
A recent review of mortality studies among workers in machining operations found apparent exposure-related increased stomach, oesophageal, rectal, pancreatic and laryngeal cancer in multiple studies (Silverstein et al. 1988; Eisen et al. 1992). Known carcinogenic agents historically present in coolants include polynuclear aromatic compounds, nitrosamines, chlorinated paraffins and formaldehyde. Present formulations contain reduced amounts of these agents, and exposures to coolant particulate are reduced, but cancer risk may still occur with present exposures. Clinical studies have documented occupational asthma, increased respiratory symptoms, cross-shift lung function drop and, in one case, legionnaire’s disease associated with coolant mist exposure (DeCoufle 1978; Vena et al. 1985; Mallin, Berkeley and Young 1986; Park et al. 1988; Delzell et al. 1993). Respiratory effects are more prominent with synthetics and soluble oils, which contain chemical irritants such as petroleum sulphonates, tall oils, ethanolamines, formaldehyde and formaldehyde donor biocides, as well as bacterial products such as endotoxin. Skin disorders are still common among machining workers, with greater problems reported for those exposed to synthetic fluids.
Pressed metal operations
The characteristic injury hazards in mechanical power presswork are crushing and amputation injuries, especially of the hands, due to trapping in the press, and hand, foot and leg injuries, caused by scrap metal from the press.
Pressed metal facilities have twice the proportion of laceration injuries of auto industry facilities generally. Such operations have a higher proportion of skilled workers than typical for the industry, especially if die construction is pursued onsite. Die change is an especially hazardous activity.
Mortality studies in the metal-stamping industry are limited. One such study found increased mortality from stomach cancer; another found increased mortality from lung cancer among maintenance welders and millwrights exposed to coal tar pitch volatiles.
Hardware and electroplating
A mortality study of employees at an automotive hardware plant found excess mortality from lung cancer among workers in departments which integrated zinc die-cast and electroplating. Chromic and sulphuric acid mist or die-cast smoke were likely causes.
Vehicle assembly
Injury rates, including cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs), are now the highest in assembly of all processes in the auto sector, due largely to the high rate of musculoskeletal disorders from repetitive work or overexertion. Musculoskeletal disorders account for more than 60% of disabling injuries in this sector.
Several mortality studies in assembly plants observed increased deaths from lung cancer. No specific process within the assembly sector has been shown responsible, so this issue remains under investigation.
Testing of prototypes
Fatal vehicle accidents occur in this occupation.
Design work
The design staffs of auto companies have been the subject of health and safety concern. Prototype dies are made by first constructing the pattern of wood, using extremely hard wood, laminates and particleboard. Plastic models are made by fibrous glass lay-up with polyester-polystyrene resins. Metal models are essentially dies constructed by precision machining. Wood, plastic and metal model and pattern makers have been shown to suffer excess incidence and mortality from colon and rectal cancer in repeated studies. A specific agent has not been identified.
Environmental and Public Health Issues
Environmental regulation aimed at stationary sources in the auto industry principally addresses volatile organic compounds from spray painting and other surface coatings. Pressure to reduce solvent content of paints has actually changed the nature of the coatings used. These rules affect supplier and parts plants as well as vehicle assembly. Foundries are regulated for air emissions of particulates and sulphur dioxide, while spent sand is treated as hazardous waste.
Vehicle emissions and vehicle safety are critical public health and safety issues regulated outside the occupational arena.
" DISCLAIMER: The ILO does not take responsibility for content presented on this web portal that is presented in any language other than English, which is the language used for the initial production and peer-review of original content. Certain statistics have not been updated since the production of the 4th edition of the Encyclopaedia (1998)."