Primary Fibromyalgia
The cause of fibromyalgia is not known. Some patients associate trauma and infections with the development of symptoms, but there is no hard evidence in favour of such triggering events. However, many factors are known to aggravate the existing symptoms. Cold, damp weather, mental disturbance, physical or mental stress, and also physical inactivity have all been associated with fibromyalgia (Wolfe 1986).
A major feature is patients waking up in the morning feeling tired. Abnormal serotonin metabolism is associated with both the sleep disturbance and decreased pain threshold typical in these patients (Goldberg 1987).
The symptoms of fibromyalgia start insidiously with persisting widespread musculoskeletal pains, multiple general symptoms such as fatigue, stiffness, subjective swelling of the fingers not observed by the examining physician, non-refreshing sleep and muscular pain after exertion. About one-third of the patients have additional symptoms, such as irritable bowel syndrome, tension headaches, premenstrual syndrome, numbness and tingling in the extremities, dryness of mouth and eyes and constriction of the blood vessels in the fingers when exposed to cold (Raynaud’s phenomenon).
Typically, a patient with fibromyalgia has a large variety of symptoms, which, with the exception of tender points, have no objective counterparts. Fibromyalgia runs a chronic course. Most of the patients continue to have symptoms with varying intensity. Complete remission is an exception. In primary fibromyalgia, no laboratory signs referring to inflammatory arthritis are present. Patients with inflammatory arthritis (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis) can also have fibromyalgic symptoms, in which case the term secondary fibromyalgia is applied.
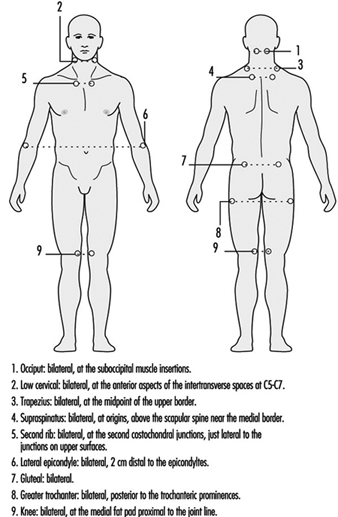
There is no one test for fibromyalgia. The diagnosis of fibro- myalgia is based on the history of the patient and on the clinical observation of tender points (figure 1). The prevalence of fibro-myalgia in the general population is 0.5 to 1%. Most (75 to 90%) of the patients are women, usually between 25 and 45 years of age; children are rarely affected.
Figure 1. Tender point sites in fibromyalgia.
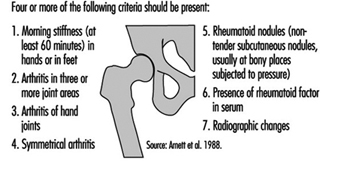
The American College of Rheumatology has set criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia (figure 2).
Figure 2. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
Diagnosis
Other ailments with similar symptoms must be excluded. Widespread pain must be present for at least three months. In addition there must be pain in 11 of the 18 tender point sites shown in figure 1 when pressed by an examiner’s finger.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
About 1% of the adult population has rheumatoid arthritis. The onset of the disease is usually at 30 to 50 years of age, with females having a threefold higher risk than males. The prevalence of the disease increases in older populations.
The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not known. It is not inherited, but genetic factors increase the risk for the development of the disease. In addition to one or multiple genetic factors, some environmental triggering factors are thought to play a role in its pathogenesis, and viral or bacterial infections are heavily suspected.
Rheumatoid arthritis usually starts gradually. Typically, the patient has mild swelling of the small joints of fingers, and tenderness of the feet that manifests in a symmetrical fashion. If joints on one hand, for example, are involved it is likely that the same joints on the other hand will be affected. Stiffness of hands and feet in the morning is a major symptom. The patient often has fatigue and can have mild fever. Laboratory features include evidence of inflammation (elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level) and often mild anaemia. About 70% of the patients have circulating rheumatoid factor (autoantibody against IgG-class immunoglobulin). In early cases, radiological examination of hands and feet is often normal, but later on, most patients develop radiological evidence of joint destruction (erosions). The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is based on a mixture of clinical, laboratory and radiological findings (see figure 3).
Figure 3. Criteris for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
The diseases which most often cause differential diagnostic problems are degenerative joint diseases of the hands, arthritis following infections, spondylarthropathies, and some rare connective tissue diseases (Guidelines 1992).
Patient education to diminish the work-load of the joints, use of ergonomic appliances, good footwear, and proper treatment of infections form the basis of preventive measures. Treatment guidelines are given in table 1.
Table 1. Guidelines for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
|
1. |
Treatment of joint pain |
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Acetaminophen (Dextropropoxyphen) |
|
2. |
Treatment of joint inflammation (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) |
Intramuscular gold Sulfasalazine Auranofin Antimalarials D-penicillamine Methotrexate Azathioprine Cyclosporine (Cyclophosphamide) Glucocorticosteroid therapy |
|
3. |
Local injections |
Glucocorticosteroid Chemical synovectomy osmium tetroxide Injection of radioactive isotopes |
|
4. |
Surgery |
Early reparative surgery (synovectomy, tenosynovectomy) Reconstructive surgery |
|
5. |
Rehabilitation |
Occupational therapy Physiotherapy Education Evaluation of needs of aids and appliances |
Spondylarthropathies
Epidemiology and aetiology
Spondylarthropathies include typical clinical entities such as ankylosing spondylitis and some forms of arthritides associated with psoriasis, with chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, or with bacterial infections in the urogenital tract or in the gut (so called reactive arthritis). The diseases are common. The prevalence of the most chronic form, ankylosing spondylitis, in Western populations varies between 0.1 and 1.8% (Gran and Husby 1993). Three new cases of transient arthritis such as reactive arthritis compared to one patient with ankylosing spondylitis are estimated to occur annually in a population of 10,000. Most of the patients who develop spondylarthropathy are young adults, between 20 and 40 years of age. There is evidence that the mean onset of symptoms for patients with ankylosing spondylitis is increasing (Calin et al. 1988).
Spondylarthropathies have a strong genetic component since a majority of the patients have an inherited genetic marker, HLA-B27. The frequency of this marker is about 7 to 15% in Western populations; 90 to 100% of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and 70 to 90% of patients with reactive arthritis are HLA-B27 positive. However, at population levels, most of the subjects with this marker are healthy. Therefore, it is thought that exogenous factors, in addition to the genetic susceptibility, are needed for the development of the disease. Such triggering factors include bacterial infections in the urogenital tract or in the gut (table 2) skin lesions, and chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. The evidence in favour of infections is most direct in the case of reactive arthritis. Salmonella infections are widely increasing, as a sequel of which an increase in the cases with joint complications can be expected. Agriculture and poultry can be the sources of these infections. As to yersinia infections, pigs harbour yersinia bacteria in their tonsils. Slaughtering followed by storage of the meat products in the cold has been suggested to contribute to the dispersion of infections in humans. In patients with ankylosing spondylitis, however, usually no preceding infections can be traced as an initiating event. Recent results have, however, focused on the finding that patients with ankylosing spondylitis often have asymptomatic chronic gut inflammation, which could serve as a triggering factor or as a contributing inflammatory focus in the chronicity of the disease.
Table 2. Infections known to trigger reactive arthritis
|
Focus |
Bacteria |
|
Upper respiratory tract |
Chlamydia pneumoniae Beta-haemolytic streptococcus (usually causes rheumatic fever) |
|
Gut |
Salmonella Shigella Yersinia enterocolitica Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Campylobacter jejuni |
|
Urogenital tract |
Chlamydia trachomatis Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
Signs and symptoms
Peripheral arthritis is asymmetric, affects large joints, and has a predilection to low extremities. The patients often also have inflammatory low back pain, worse by night and relieved by movement, not by rest. A typical feature is a tendency to inflammation of the junction between tendons and bones (enthesopathy), which can manifest itself as pain under the heel or in calcaneus at the insertion of Achilles tendon. In addition to inflammation in the joints and at ligamentous insertions, patients also can have inflammatory symptoms in eyes (iritis or conjunctivitis), skin (psoriasis, skin lesions in palms, soles, or leg induration) and sometimes in the heart.
The following are the diagnostic criteria for spondylarthro- pathy (Dougados et al. 1991).
Inflammatory low back pain
or
Joint inflammation (synovitis):
- asymmetric
- predilection to low extremities
and
at least one of the following:
- positive family history for spondylarthropathy
- psoriasis
- inflammatory bowel disease
- buttock pain changing from side to side
- pain at the junction between tendon and bone (enthesopathy).
Patients with ankylosing spondylitis have low-back pain, worse by night, and tenderness between the spine and the pelvis at the sacroiliac joints. They can have limited mobility of the spine with chest tenderness. A third of the patients have peripheral arthritis and enthesopathy. The cornerstone of the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis is the presence of radiological changes in the sacroiliac joints; there is a loss of space between the joints, and bony outgrowths. Such changes add to the diagnostic accuracy of patients with spondylarthropathy but are necessary only in the case of ankylosing spondylitis.
Gout
Epidemiology and aetiology
Gout is a metabolic disorder that is the most common cause of inflammatory arthritis in men. Its prevalence among adults varies from 0.2 to 0.3 per 1000, and is 1.5% in adult males. The prevalence of gout increases with age and with increasing serum urate levels.
Hyperuricemia (high level of uric acid in serum) is a risk factor. Contributing factors are chronic kidney diseases which lead to renal insufficiency, hypertension, use of diuretic drugs, high alcohol intake, lead exposure and obesity. Gouty attacks are precipitated by hypersaturation of joint fluid with uric acid; the precipitated crystals irritate the joint, with the development of acute arthritis.
Signs and symptoms
The natural course of gout runs through several stages from a- symptomatic hyperuricemia to acute gouty arthritis, asymptomatic periods, and to chronic tophaceous gout (gout with nodules).
Acute gouty arthritis often manifests itself as an acute inflammation in one joint, usually at the base of the big toe. The joint is very tender, swollen and highly painful; it is often red. The acute attack can subside spontaneously within days. If untreated, repeated attacks can occur, and in some patients these continue (during the subsequent years) so that the patient develops chronic arthritis. In these patients, urate deposits can be observed in the ear helices, at the elbows, or at the Achilles tendons, where they form non-tender subcutaneous palpable masses (tophi).
Infectious Arthritis
Epidemiology and aetiology
In children, infectious arthritis often develops in a previously healthy child, but adults often have some predisposing factor, such as diabetes, chronic arthritis, use of glucocorticosteroid or immunosuppressive therapy, previous injections or trauma in the joint. Patients with endoprosthesis are also susceptible to infections in the operated joint.
Bacteria are most often the cause of infectious arthritis. In immunosuppressed patients, fungi can be found. Although bacterial infection in the joint is rare, it is very important to recognize, because, if untreated, the infection rapidly destroys the joint. The microbes can reach the joint by circulation (septic infection), by direct penetrating wound or during a joint injection, or from an adjacent infectious focus.
Signs and symptoms
In a typical case, a patient has acute joint inflammation, usually in one single joint, which is painful, hot, red and tender to movement. There are general symptoms of infection (fever, chills) and laboratory evidence of acute inflammation. The joint aspiration is turbid, and in microscopic examination a high number of white blood cells are seen, with positive stain and cultures for bacteria. The patient can have signs of a focus of infection elsewhere, such as pneumonia.
Osteoporosis
Epidemiology and aetiology
Bone mass increases from childhood until adolescence. Women gain 15% less bone density than men. It is at its highest between 20 and 40 years, after which there is a constant decrease. Osteoporosis is a condition in which bone mass decreases and bones become susceptible to fracture. Osteoporosis is a major cause of morbidity in the elderly. The most important manifestation is lumbar and hip fractures. About 40% of women who have reached 70 years have suffered from fractures.
Peak bone mass is influenced by genetic factors. In women, bone mass decreases after menopause. The decrease of bone mass in men is less distinct than in women. In addition to lack of oestrogen, other factors influence the rate of bone loss and the development of osteoporosis. These include physical inactivity, low amount of calcium in the diet, smoking, coffee consumption and low body weight. Use of systemic corticosteroid therapy is also associated with enhanced risk for osteoporosis.
Signs and symptoms
Osteoporosis can be asymptomatic. On the other hand, the most distinct manifestation of osteoporosis is bone fracture, typically that of the hip, vertebrae (spine) and wrist. Hip and wrist fractures usually are a result of falling, but vertebral fractures can develop insidiously after a trivial trauma. The patient has back pain, kyphosis and loss of height.
Bone Cancer
Epidemiology and aetiology
Primary malignant bone tumours are uncommon. They occur most often in children and young adults. Osteosarcoma is the most frequent of the malignant bone tumours. It is most frequently observed in the second decade of life, and in older adults it can result secondary to a bone disease (Paget’s disease). Ewing’s sarcoma is also mostly observed in children, who present with destructive changes in the pelvis or in the long bones. Malignant tumours originating from the cartilage (chondrosarcoma) can occur in many cartilage areas. In adults, malignant bone lesions are often metastatic (i.e., the primary malignant disease is somewhere else in the body).
Most malignant primary tumours have no known aetiology. However, Paget’s disease of bone, osteomyelitis, osteonecrosis and radiation injury have been associated with malignant transformation. Bone metastases are frequent in primary cancers of the breast, lung, prostate, kidney or thyroid gland.
Signs and symptoms
Pain, limitation of movement and swelling are present in patients with osteosarcoma. In addition to bone pain, patients with Ewing’s sarcoma often have systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise and chills. Chondrosarcomas can cause varying symptoms depending on the site of the tumour and its histologic details.
Osteomyelitis
Epidemiology and aetiology
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection that is usually bacterial, but can be fungal or viral. In an otherwise healthy person, osteomyelitis is a rare event, but in patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, infection in the body can spread by the bloodstream or by direct invasion to bones. In children, the most favoured site for the spreading is the shaft of long bone, but in adults the infection is often in the spine. A focal point from which an infection can spread by bloodstream or by direct invasion, penetrating or blunt trauma, prior orthopaedic surgery (insertion of prosthesis) can all be complicated by osteomyelitis.
Signs and symptoms
Acute bone infection of the long bones is associated with fever, chills and bone pain. Spinal osteomyelitis can cause more vague symptoms with progressive pain and low-grade fever. Infections around a prosthesis cause pain and tenderness when moving the operated joint.