34. Psychosocial and Organizational Factors
Chapter Editors: Steven L. Sauter, Lawrence R. Murphy, Joseph J. Hurrell and Lennart Levi
Table of Contents
Tables and Figures
Psychosocial and Organizational Factors
Steven L. Sauter, Joseph J. Hurrell Jr., Lawrence R. Murphy and Lennart Levi
Theories of Job Stress
Psychosocial Factors, Stress and Health
Lennart Levi
Demand/Control Model: A Social, Emotional, and Physiological Approach to Stress Risk and Active Behaviour Development
Robert Karasek
Social Support: An Interactive Stress Model
Kristina Orth-Gomér
Factors Intrinsic to the Job
Person - Environment Fit
Robert D. Caplan
Workload
Marianne Frankenhaeuser
Hours of Work
Timothy H. Monk
Environmental Design
Daniel Stokols
Ergonomic Factors
Michael J. Smith
Autonomy and Control
Daniel Ganster
Work Pacing
Gavriel Salvendy
Electronic Work Monitoring
Lawrence M. Schleifer
Role Clarity and Role Overload
Steve M. Jex
Interpersonal Factors
Sexual Harassment
Chaya S. Piotrkowski
Workplace Violence
Julian Barling
Job Security
Job Future Ambiguity
John M. Ivancevich
Unemployment
Amiram D. Vinokur
Macro-Organizational Factors
Total Quality Management
Dennis Tolsma
Managerial Style
Cary L. Cooper and Mike Smith
Organizational Structure
Lois E. Tetrick
Organizational Climate and Culture
Denise M. Rousseau
Performance Measures and Compensation
Richard L. Shell
Staffing Issues
Marilyn K. Gowing
Career Development
Socialization
Debra L. Nelson and James Campbell Quick
Career Stages
Kari Lindström
Individual Factors
Type A/B Behaviour Pattern
C. David Jenkins
Hardiness
Suzanne C. Ouellette
Self-Esteem
John M. Schaubroeck
Locus of Control
Lawrence R. Murphy and Joseph J. Hurrell, Jr.
Coping Styles
Ronald J. Burke
Social Support
D. Wayne Corneil
Gender, Job Stress and Illness
Rosalind C. Barnett
Ethnicity
Gwendolyn Puryear Keita
Stress Reactions
Selected Acute Physiological Outcomes
Andrew Steptoe and Tessa M. Pollard
Behavioural Outcomes
Arie Shirom
Well-Being Outcomes
Peter Warr
Immunological Reactions
Holger Ursin
Chronic Health Effects
Cardiovascular Diseases
Töres Theorell and Jeffrey V. Johnson
Gastrointestinal Problems
Jerry Suls
Cancer
Bernard H. Fox
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Soo-Yee Lim, Steven L. Sauter and Naomi G. Swanson
Mental Illness
Carles Muntaner and William W. Eaton
Burnout
Christina Maslach
Prevention
Summary of Generic Prevention and Control Strategies
Cary L. Cooper and Sue Cartwright
Tables
Click a link below to view table in the article context.
Figures
Point to a thumbnail to see figure caption, click to see figure in article context.
Children categories
Psychosocial and Organizational Factors
In 1966, long before job stress and psychosocial factors became household expressions, a special report entitled “Protecting the Health of Eighty Million Workers—A National Goal for Occupational Health” was issued to the Surgeon General of the United States (US Department of Health and Human Services 1966). The report was prepared under the auspices of the National Advisory Environmental Health Committee to provide direction to Federal programmes in occupational health. Among its many observations, the report noted that psychological stress was increasingly apparent in the workplace, presenting “... new and subtle threats to mental health,” and possible risk of somatic disorders such as cardiovascular disease. Technological change and the increasing psychological demands of the workplace were listed as contributing factors. The report concluded with a list of two dozen “urgent problems” requiring priority attention, including occupational mental health and contributing workplace factors.
Thirty years later, this report has proven remarkably prophetic. Job stress has become a leading source of worker disability in North America and Europe. In 1990, 13% of all worker disability cases handled by Northwestern National Life, a major US underwriter of worker compensation claims, were due to disorders with a suspected link to job stress (Northwestern National Life 1991). A 1985 study by the National Council on Compensation Insurance found that one type of claim, involving psychological disability due to “gradual mental stress” at work, had grown to 11% of all occupational disease claims (National Council on Compensation Insurance 1985)
* In the United States, occupational disease claims are distinct from injury claims, which tend to greatly outnumber disease claims.
These developments are understandable considering the demands of modern work. A 1991 survey of European Union members found that “The proportion of workers who complain from organizational constraints, which are in particular conducive to stress, is higher than the proportion of workers complaining from physical constraints” (European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions 1992). Similarly, a more recent study of the Dutch working population found that one-half of the sample reported a high work pace, three-fourths of the sample reported poor possibilities of promotion, and one-third reported a poor fit between their education and their jobs (Houtman and Kompier 1995). On the American side, data on the prevalence of job stress risk factors in the workplace are less available. However, in a recent survey of several thousand US workers, over 40% of the workers reported excessive workloads and said they were “used up” and “emotionally drained” at the end of the day (Galinsky, Bond and Friedman 1993).
The impact of this problem in terms of lost productivity, disease and reduced quality of life is undoubtedly formidable, although difficult to estimate reliably. However, recent analyses of data from over 28,000 workers by the Saint Paul Fire and Marine Insurance company are of interest and relevance. This study found that time pressure and other emotional and personal problems at work were more strongly associated with reported health problems than any other personal life stressor; more so than even financial or family problems, or death of a loved one (St. Paul Fire and Marine Insurance Company 1992).
Looking to the future, rapid changes in the fabric of work and the workforce pose unknown, and possibly increased, risks of job stress. For example, in many countries the workforce is rapidly ageing at a time when job security is decreasing. In the United States, corporate downsizing continues almost unabated into the last half of the decade at a rate of over 30,000 jobs lost per month (Roy 1995). In the above-cited study by Galinsky, Bond and Friedman (1993) nearly one-fifth of the workers thought it likely they would lose their jobs in the forthcoming year. At the same time the number of contingent workers, who are generally without health benefits and other safety nets, continues to grow and now comprises about 5% of the workforce (USBLS 1995).
The aim of this chapter is to provide an overview of current knowledge on conditions which lead to stress at work and associated health and safety problems. These conditions, which are commonly referred to as psychosocial factors, include aspects of the job and work environment such as organizational climate or culture, work roles, interpersonal relationships at work, and the design and content of tasks (e.g., variety, meaning, scope, repetitiveness, etc.). The concept of psychosocial factors extends also to the extra-organizational environment (e.g., domestic demands) and aspects of the individual (e.g., personality and attitudes) which may influence the development of stress at work. Frequently, the expressions work organization or organizational factors are used interchangeably with psychosocial factors in reference to working conditions which may lead to stress.
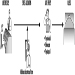
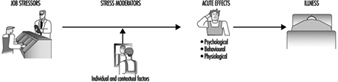
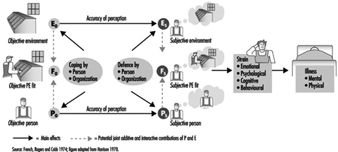
This section of the Encyclopaedia begins with descriptions of several models of job stress which are of current scientific interest, including the job demands-job control model, the person- environment (P-E) fit model, and other theoretical approaches to stress at work. Like all contemporary notions of job stress, these models have a common theme: job stress is conceptualized in terms of the relationship between the job and the person. According to this view, job stress and the potential for ill health develop when job demands are at variance with the needs, expectations or capacities of the worker. This core feature is implicit in figure 1, which shows the basic elements of a stress model favoured by researchers at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). In this model, work-related psychosocial factors (termed stressors) result in psychological, behavioural and physical reactions which may ultimately influence health. However, as illustrated in figure 1, individual and contextual factors (termed stress moderators) intervene to influence the effects of job stressors on health and well-being. (See Hurrell and Murphy 1992 for a more elaborate description of the NIOSH stress model.)
Figure 1. The Job Stress Model of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
But putting aside this conceptual similarity, there are also non-trivial theoretical differences among these models. For example, unlike the NIOSH and P-E fit models of job stress, which acknowledge a host of potential psychosocial risk factors in the workplace, the job demands-job control model focuses most intensely on a more limited range of psychosocial dimensions pertaining to psychological workload and opportunity for workers to exercise control (termed decision latitude) over aspects of their jobs. Further, both the demand-control and the NIOSH models can be distinguished from the P-E fit models in terms of the focus placed on the individual. In the P-E fit model, emphasis is placed on individuals’ perceptions of the balance between features of the job and individual attributes. This focus on perceptions provides a bridge between P-E fit theory and another variant of stress theory attributed to Lazarus (1966), in which individual differences in appraisal of psychosocial stressors and in coping strategies become critically important in determining stress outcomes. In contrast, while not denying the importance of individual differences, the NIOSH stress model gives primacy to environmental factors in determining stress outcomes as suggested by the geometry of the model illustrated in figure 1. In essence, the model suggests that most stressors will be threatening to most of the people most of the time, regardless of circumstances. A similar emphasis can be seen in other models of stress and job stress (e.g., Cooper and Marshall 1976; Kagan and Levi 1971; Matteson and Ivancevich 1987).
These differences have important implications for both guiding job stress research and intervention strategies at the workplace. The NIOSH model, for example, argues for primary prevention of job stress via attention first to psychosocial stressors in the workplace and, in this regard, is consistent with a public health model of prevention. Although a public health approach recognizes the importance of host factors or resistance in the aetiology of disease, the first line of defence in this approach is to eradicate or reduce exposure to environmental pathogens.
The NIOSH stress model illustrated in figure 1 provides an organizing framework for the remainder of this section. Following the discussions of job stress models are short articles containing summaries of current knowledge on workplace psychosocial stressors and on stress moderators. These subsections address conditions which have received wide attention in the literature as stressors and stress moderators, as well as topics of emerging interest such as organizational climate and career stage. Prepared by leading authorities in the field, each summary provides a definition and brief overview of relevant literature on the topic. Further, to maximize the utility of these summaries, each contributor has been asked to include information on measurement or assessment methods and on prevention practices.
The final subsection of the chapter reviews current knowledge on a wide range of potential health risks of job stress and underlying mechanisms for these effects. Discussion ranges from traditional concerns, such as psychological and cardiovascular disorders, to emerging topics such as depressed immune function and musculoskeletal disease.
In summary, recent years have witnessed unprecedented changes in the design and demands of work, and the emergence of job stress as a major concern in occupational health. This section of the Encyclopaedia tries to promote understanding of psychosocial risks posed by the evolving work environment, and thus better protect the well-being of workers.
Psychosocial Factors, Stress and Health
In the language of engineering, stress is “a force which deforms bodies”. In biology and medicine, the term usually refers to a process in the body, to the body’s general plan for adapting to all the influences, changes, demands and strains to which it is exposed. This plan swings into action, for example, when a person is assaulted on the street, but also when someone is exposed to toxic substances or to extreme heat or cold. It is not just physical exposures which activate this plan however; mental and social ones do so as well. For instance, if we are insulted by our supervisor, reminded of an unpleasant experience, expected to achieve something of which we do not believe we are capable, or if, with or without cause, we worry about our job or marriage.
There is something common to all these cases in the way the body attempts to adapt. This common denominator—a kind of “revving up” or “stepping on the gas”—is stress. Stress is, then, a stereotype in the body’s responses to influences, demands or strains. Some level of stress is always to be found in the body, just as, to draw a rough parallel, a country maintains a certain state of military preparedness, even in peacetime. Occasionally this preparedness is intensified, sometimes with good cause and at other times without.
In this way the stress level affects the rate at which processes of wear and tear on the body take place. The more “gas” given, the higher the rate at which the body’s engine is driven, and hence the more quickly the “fuel” is used up and the “engine” wears out. Another metaphor also applies: if you burn a candle with a high flame, at both ends, it will give off brighter light but will also burn down more quickly. A certain amount of fuel is necessary otherwise the engine will stand still, the candle will go out; that is, the organism would be dead. Thus, the problem is not that the body has a stress response, but that the degree of stress—the rate of wear and tear—to which it is subject may be too great. This stress response varies from one minute to another even in one individual, the variation depending in part on the nature and state of the body and in part on the external influences and demands—the stressors—to which the body is exposed. (A stressor is thus something that produces stress.)
Sometimes it is difficult to determine whether stress in a particular situation is good or bad. Take, for instance, the exhausted athlete on the winner’s stand, or the newly appointed but stress-racked executive. Both have achieved their goals. In terms of pure accomplishment, one would have to say that their results were well worth the effort. In psychological terms, however, such a conclusion is more doubtful. A good deal of torment may have been necessary to get so far, involving long years of training or never-ending overtime, usually at the expense of family life. From the medical viewpoint such achievers may be considered to have burnt their candles at both ends. The result could be physiological; the athlete may rupture a muscle or two and the executive develop high blood pressure or have a heart attack.
Stress in relation to work
An example may clarify how stress reactions can arise at work and what they might lead to in terms of health and quality of life. Let us imagine the following situation for a hypothetical male worker. Based on economic and technical considerations, management has decided to break up a production process into very simple and primitive elements which are to be performed on an assembly line. Through this decision, a social structure is created and a process set into motion which can constitute the starting point in a stress- and disease-producing sequence of events. The new situation becomes a psychosocial stimulus for the worker, when he first perceives it. These perceptions may be further influenced by the fact that the worker may have previously received extensive training, and thus was consequently expecting a work assignment which required higher qualifications, not reduced skill levels. In addition, past experience of work on an assembly line was strongly negative (that is, earlier environmental experiences will influence the reaction to the new situation). Furthermore, the worker’s hereditary factors make him more prone to react to stressors with an increase in blood pressure. Because he is more irritable, perhaps his wife criticizes him for accepting his new assignment and bringing his problems home. As a result of all these factors, the worker reacts to the feelings of distress, perhaps with an increase in alcohol consumption or by experiencing undesirable physiological reactions, such as the elevation in blood pressure. The troubles at work and in the family continue, and his reactions, originally of a transient type, become sustained. Eventually, he may enter a chronic anxiety state or develop alcoholism or chronic hypertensive disease. These problems, in turn, increase his difficulties at work and with his family, and may also increase his physiological vulnerability. A vicious cycle may set in which may end in a stroke, a workplace accident or even suicide. This example illustrates the environmental programming involved in the way a worker reacts behaviourally, physiologically and socially, leading to increased vulnerability, impaired health and even death.
Psychosocial conditions in present working life
According to an important International Labour Organization (ILO) (1975) resolution, work should not only respect workers’ lives and health and leave them free time for rest and leisure, but also allow them to serve society and achieve self-fulfilment by developing their personal capabilities. These principles were also set down as early as 1963, in a report from the London Tavistock Institute (Document No. T813) which provided the following general guidelines for job design:
- The job should be reasonably demanding in terms other than sheer endurance and provide at least a minimum of variety.
- The worker should be able to learn on the job and go on learning.
- The job should comprise some area of decision-making that the individual can call his or her own.
- There should be some degree of social support and recognition in the workplace.
- The worker should be able to relate what he or she does or produces to social life.
- The worker should feel that the job leads to some sort of desirable future.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), however, draws a less hopeful picture of the reality of working life, pointing out that:
- Work has been accepted as a duty and a necessity for most adults.
- Work and workplaces have been designed almost exclusively with reference to criteria of efficiency and cost.
- Technological and capital resources have been accepted as the imperative determinants of the optimum nature of jobs and work systems.
- Changes have been motivated largely by aspirations to unlimited economic growth.
- The judgement of the optimum designs of jobs and choice of work objectives has resided almost wholly with managers and technologists, with only a slight intrusion from collective bargaining and protective legislation.
- Other societal institutions have taken on forms that serve to sustain this type of work system.
In the short run, benefits of the developments which have proceeded according to this OECD list have brought more productivity at lesser cost, as well as an increase in wealth. However, the long-term disadvantages of such developments are often more worker dissatisfaction, alienation and possibly ill health which, when considering society in general, in turn, may affect the economic sphere, although the economic costs of these effects have only recently been taken into consideration (Cooper, Luikkonen and Cartwright 1996; Levi and Lunde-Jensen 1996).
We also tend to forget that, biologically, humankind has not changed much during the last 100,000 years, whereas the environment—and in particular the work environment—has changed dramatically, particularly during the past century and decades. This change has been partly for the better; however, some of these “improvements” have been accompanied by unexpected side effects. For example, data collected by the National Swedish Central Bureau of Statistics during the 1980s showed that:
- 11% of all Swedish employees are continuously exposed to deafening noise.
- 15% have work which makes them very dirty (oil, paint, etc.).
- 17% have inconvenient working hours, i.e., not only daytime work but also early or late night work, shift work or other irregular working hours.
- 9% have gross working hours exceeding 11 per day (this concept includes hours of work, breaks, travelling time, overtime, etc.; in other words, that part of the day which is set aside for work).
- 11% have work that is considered both “hectic” and “monotonous”.
- 34% consider their work “mentally exacting”.
- 40% consider themselves “without influence on the arrangement of time for breaks”.
- 45% consider themselves without “opportunities to learn new things” at their work.
- 26% have an instrumental attitude to their work. They consider “their work to yield nothing except the pay—i.e. no feeling of personal satisfaction”. Work is regarded purely as an instrument for acquiring an income.
In its major study of conditions of work in the 12 member States of the European Union at that time (1991/92), the European Foundation (Paoli 1992) found that 30% of the workforce regarded their work to risk their health, 23 million to have night work more than 25% of total hours worked, each third to report highly repetitive, monotonous work, each fifth male and each sixth female to work under “continuous time pressure”, and each fourth worker to carry heavy loads or to work in a twisted or painful position more than 50% of his or her working time.
Main psychosocial stressors at work
As already indicated, stress is caused by a bad “person- environment fit”, objectively, subjectively, or both, at work or elsewhere and in an interaction with genetic factors. It is like a badly fitting shoe: environmental demands are not matched to individual ability, or environmental opportunities do not measure up to individual needs and expectations. For example, the individual is able to perform a certain amount of work, but much more is required, or on the other hand no work at all is offered. Another example would be that the worker needs to be part of a social network, to experience a sense of belonging, a sense that life has meaning, but there may be no opportunity to meet these needs in the existing environment and the “fit” becomes bad.
Any fit will depend on the “shoe” as well as on the “foot”, on situational factors as well as on individual and group characteristics. The most important situational factors that give rise to “misfit” can be categorized as follows:
Quantitative overload. Too much to do, time pressure and repetitive work-flow. This is to a great extent the typical feature of mass production technology and routinized office work.
Qualitative underload. Too narrow and one-sided job content, lack of stimulus variation, no demands on creativity or problem- solving, or low opportunities for social interaction. These jobs seem to become more common with suboptimally designed automation and increased use of computers in both offices and manufacturing even though there may be instances of the opposite.
Role conflicts. Everybody occupies several roles concurrently. We are the superiors of some people and the subordinates of others. We are children, parents, marital partners, friends and members of clubs or trade unions. Conflicts easily arise among our various roles and are often stress evoking, as when, for instance, demands at work clash with those from a sick parent or child or when a supervisor is divided between loyalty to superiors and to fellow workers and subordinates.
Lack of control over one’s own situation. When someone else decides what to do, when and how; for example, in relation to work pace and working methods, when the worker has no influence, no control, no say. Or when there is uncertainty or lack of any obvious structure in the work situation.
Lack of social support at home and from your boss or fellow workers.
Physical stressors. Such factors can influence the worker both physically and chemically, for example, direct effects on the brain of organic solvents. Secondary psychosocial effects can also originate from the distress caused by, say, odours, glare, noise, extremes of air temperature or humidity and so on. These effects can also be due to the worker’s awareness, suspicion or fear that he is exposed to life-threatening chemical hazards or to accident risks.
Finally, real life conditions at work and outside work usually imply a combination of many exposures. These might become superimposed on each other in an additive or synergistic way. The straw which breaks the camel’s back may therefore be a rather trivial environmental factor, but one that comes on top of a very considerable, pre-existing environmental load.
Some of the specific stressors in industry merit special discussion, namely those characteristic of:
- mass production technology
- highly automated work processes
- shift work
Mass production technology. Over the past century work has become fragmented in many workplaces, changing from a well defined job activity with a distinct and recognized end-product, into numerous narrow and highly specified subunits which bear little apparent relation to the end-product. The growing size of many factory units has tended to result in a long chain of command between management and the individual workers, accentuating remoteness between the two groups. The worker also becomes remote from the consumer, since rapid elaborations for marketing, distribution and selling interpose many steps between the producer and the consumer.
Mass production, thus, normally involves not just a pronounced fragmentation of the work process but also a decrease in worker control of the process. This is partly because work organization, work content and work pace are determined by the machine system. All these factors usually result in monotony, social isolation, lack of freedom and time pressure, with possible long-term effects on health and well-being.
Mass production, moreover, favours the introduction of piece rates. In this regard, it can be assumed that the desire—or necessity—to earn more can, for a time, induce the individual to work harder than is good for the organism and to ignore mental and physical “warnings”, such as a feeling of tiredness, nervous problems and functional disturbances in various organs or organ systems. Another possible effect is that the employee, bent on raising output and earnings, infringes safety regulations thereby increasing the risk of occupational disease and of accidents to oneself and others (e.g., lorry drivers on piece rates).
Highly automated work processes. In automated work the repetitive, manual elements are taken over by machines, and the workers are left with mainly supervisory, monitoring and controlling functions. This kind of work is generally rather skilled, not regulated in detail and the worker is free to move about. Accordingly, the introduction of automation eliminates many of the disadvantages of the mass-production technology. However, this holds true mainly for those stages of automation where the operator is indeed assisted by the computer and maintains some control over its services. If, however, operator skills and knowledge are gradually taken over by the computer—a likely development if decision making is left to economists and technologists—a new impoverishment of work may result, with a re-introduction of monotony, social isolation and lack of control.
Monitoring a process usually calls for sustained attention and readiness to act throughout a monotonous term of duty, a requirement that does not match the brain’s need for a reasonably varied flow of stimuli in order to maintain optimal alertness. It is well documented that the ability to detect critical signals declines rapidly even during the first half-hour in a monotonous environment. This may add to the strain inherent in the awareness that temporary inattention and even a slight error could have extensive economic and other disastrous consequences.
Other critical aspects of process control are associated with very special demands on mental skill. The operators are concerned with symbols, abstract signals on instrument arrays and are not in touch with the actual product of their work.
Shift work. In the case of shift work, rhythmical biological changes do not necessarily coincide with corresponding environmental demands. Here, the organism may “step on the gas” and activation occurs at a time when the worker needs to sleep (for example, during the day after a night shift), and deactivation correspondingly occurs at night, when the worker may need to work and be alert.
A further complication arises because workers usually live in a social environment which is not designed for the needs of shift workers. Last but not least, shift workers must often adapt to regular or irregular changes in environmental demands, as in the case of rotating shifts.
In summary, the psychosocial demands of the modern workplace are often at variance with the workers’ needs and capabilities, leading to stress and ill health. This discussion provides only a snapshot of psychosocial stressors at work, and how these unhealthy conditions can arise in today’s workplace. In the sections that follow, psychosocial stressors are analysed in greater detail with respect to their sources in modern work systems and technologies, and with respect to their assessment and control.
Social Support: an Interactive Stress Model
The stress concept
Various definitions of stress have been formulated since the concept was first named and described by Hans Selye (Selye 1960). Almost invariably these definitions have failed to capture what is perceived as the essence of the concept by a major proportion of stress researchers.
The failure to reach a common and generally acceptable definition may have several explanations; one of them may be that the concept has become so widespread and has been used in so many different situations and settings and by so many researchers, professionals and lay persons that to agree on a common definition is no longer possible. Another explanation is that there really is no empirical basis for a single common definition. The concept may be so diverse that one single process simply does not explain the whole phenomenon. One thing is clear—in order to examine the health effects of stress, the concept needs to include more than one component. Selye’s definition was concerned with the physiological fight or flight reaction in response to a threat or a challenge from the environment. Thus his definition involved only the individual physiological response. In the 1960s a strong interest arose in so-called life events, that is, major stressful experiences that occur in an individual’s life. The work by Holmes and Rahe (1967) nicely demonstrated that an accumulation of life events was harmful to health. These effects were found mostly in retrospective studies. To confirm the findings prospectively proved to be more difficult (Rahe 1988).
In the 1970s another concept was introduced into the theoretical framework, that of the vulnerability or resistance of the individual who was exposed to stressful stimuli. Cassel (1976) hypothesized that host resistance was a crucial factor in the outcome of stress or the impact of stress on health. The fact that host resistance had not been taken into account in many studies might explain why so many inconsistent and contradictory results had been obtained on the health effect of stress. According to Cassel, two factors were essential in determining the degree of a person’s host resistance: his or her capacity for coping and his or her social supports.
Today’s definition has come to include considerably more than the physiological “Selye stress” reactions. Both social environ-mental effects as represented by (for instance) life events and the resistance or vulnerability of the individual exposed to the life events are included.
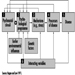
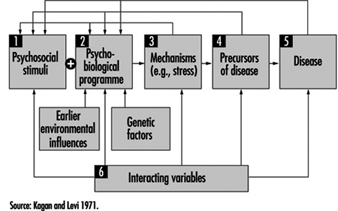
Figure 1. Components of stress in the stress-disease model of Kagan and Levi (1971)
In the stress-disease model proposed by Kagan and Levi (1971), several distinctions between different components are made (figure 1). These components are:
- stressful factors or stressors in the environment— social or psychological stimuli that evoke certain harmful reactions
- the individual psychobiological programme, predetermined both by genetic factors and early experiences and learning
- individual physiological stress reactions (“Selye Stress” reactions). A combination of these three factors may lead to
- precursors which may eventually provoke the final outcome, namely
- manifest physical illness.
It is important to note, that—contrary to Selye’s beliefs—several different physiological pathways have been identified that mediate the effects of stressors on physical health outcomes. These include not only the originally described sympatho-adreno-medullary reaction but also the action of the sympatho-adreno-cortical axis, which may be of equal importance, and the counterbalance provided by parasympathetic gastrointestinal neurohormonal regulation, which has been observed to dampen and buffer the harmful effects of stress. In order for a stressor to evoke such reactions, a harmful influence of the psychobiological programme is required— in other words, an individual propensity to react to stressors has to be present. This individual propensity is both genetically determined and based on early childhood experiences and learning.
If the physiological stress reactions are severe and long-standing enough, they may eventually lead to chronic states, or become precursors of illness. An example of such a precursor is hypertension, which is often stress-related and may lead to manifest somatic disease, such as stroke or heart disease.
Another important feature of the model is that the interaction effects of intervening variables are anticipated at each step, further increasing the complexity of the model. This complexity is illustrated by feed-back loops from all stages and factors in the model to every other stage or factor. Thus the model is complex—but so is nature.
Our empirical knowledge about the accuracy of this model is still insufficient and unclear at this stage, but further insight will be gained by applying the interactive model to stress research. For example, our ability to predict disease may increase if the attempt is made to apply the model.
Empirical evidence on host resistance
In our group of investigators at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, recent research has been focused on factors that promote host resistance. We have hypothesized that one such powerful factor is the health-promoting effects of well-functioning social networks and social support.
Our first endeavour to investigate the effects of social networks on health were focused on the entire Swedish population from a “macroscopic” level. In cooperation with the Central Swedish Bureau of Statistics we were able to evaluate the effects of self-assessed social network interactions on health outcome, in this case on survival (Orth-Gomér and Johnson 1987).
Representing a random sample of the adult Swedish population, 17,433 men and women responded to a questionnaire about their social ties and social networks. The questionnaire was included in two of the annual Surveys of Living Conditions in Sweden, which were designed to assess and measure the welfare of the nation in material as well as in social and psychological terms. Based on the questionnaire, we created a comprehensive social network interaction index which included the number of members in the network and the frequency of contacts with each member. Seven sources of contacts were identified by means of factor analysis: parents, siblings, nuclear family (spouse and children), close relatives, co-workers, neighbours, distant relatives and friends. The contacts with each source were calculated and added up to a total index score, which ranged from zero to 106.
By linking the Surveys of Living Conditions with the national death register, we were able to investigate the impact of the social network interaction index on mortality. Dividing the study population into tertiles according to their index score, we found that those men and women who were in the lower tertile had an invariably higher mortality risk than those who were in the middle and upper tertiles of the index score.
The risk of dying if one was in the lower tertile was four to five times higher than in the other tertiles, although many other factors might explain this association such as the fact that increasing age is associated with higher risk of dying. Also, as one ages the number of social contacts decrease. If one is sick and disabled, mortality risk increases and it is likely that the extent of the social network decreases. Morbidity and mortality are also higher in lower social classes, and social networks are also smaller and social contacts less abundant. Thus, controlling for these and other mortality risk factors is necessary in any analysis. Even when these factors were taken into account, a statistically significant 40% increase in risk was found to be associated with a sparse social network among those in the lowest third of the population. It is interesting to note that there was no additional health-promoting effect of being in the highest as compared to the middle tertile. Possibly, a great number of contacts can represent a strain on the individual as well as protection against harmful health effects.
Thus, without even knowing anything further about the stressors in the lives of these men and women we were able to confirm a health-promoting effect of social networks.
Social networks alone cannot explain the health effects observed. It is probable that the way in which a social network functions and the basis of support the network members provide are more important than the actual number of people included in the network. In addition, an interactive effect of different stressors is possible. For example the effects of work-related stress have been found to worsen when there is also a lack of social support and social interaction at work (Karasek and Theorell 1990).
In order to explore the issues of interaction, research studies have been carried out using various measures for assessing both qualitative and quantitative aspects of social support. Several interesting results were obtained which are illustrative of the health effects that have been associated with social support. For example, one study of heart disease (myocardial infarct and sudden cardiac death) in a population of 776 fifty-year-old men born in Gothenburg, randomly selected from the general population and found healthy on initial examination, smoking and lack of social support were found to be the strongest predictors of disease (Orth-Gomér, Rosengren and Wilheemsen 1993). Other risk factors included elevated blood pressure, lipids, fibrinogen and a sedentary lifestyle.
In the same study it was shown that only in those men who lacked support, in particular emotional support from a spouse, close relatives or friends, were the effects of stressful life events harmful. Men who both lacked support and had experienced several serious life events had more than five times the mortality of men who enjoyed close and emotional support (Rosengren et al. 1993).
Another example of interactive effects was offered in a study of cardiac patients who were examined for psychosocial factors such as social integration and social isolation, as well as myocardial indicators of an unfavourable prognosis and then followed for a ten-year period. Personality and behaviour type, in particular the Type A behaviour pattern, was also assessed.
The behaviour type in itself had no impact on prognosis in these patients. Of Type A men, 24% died as compared to 22% of Type B men. But when considering the interactive effects with social isolation another picture emerged.
Using a diary of activities during a regular week, men partici-pating in the study were asked to describe anything they would do in the evenings and weekends of a normal week. Activities were then divided into those that involved physical exercise, those that were mainly involved with relaxation and performed at home and those that were performed for recreation together with others. Of these activity types, lack of social recreational activity was the strongest predictor of mortality. Men who never engaged in such activities—called socially isolated in the study—had about three times higher mortality risk than those who were socially active. In addition, Type A men who were socially isolated had an even higher mortality risk than those in any of the other categories (Orth-Gomér, Undén and Edwards 1988).
These studies demonstrate the need to consider several aspects of the psychosocial environment, individual factors as well as of course the physiological stress mechanisms. They also demonstrate that social support is one important factor in stress-related health outcomes.
Demand/Control Model: a Social, Emotional, and Physiological Approach to Stress Risk and Active Behaviour
Most previous stress theories were developed to describe reactions to “inevitable” acute stress in situations threatening biological survival (Cannon 1935; Selye 1936). However, the Demand/Control model was developed for work environments where “stressors” are chronic, not initially life threatening, and are the product of sophisticated human organizational decision making. Here, the controllability of the stressor is very important, and becomes more important as we develop ever more complex and integrated social organizations, with ever more complex limitations on individual behaviour. The Demand/Control model (Karasek 1976; Karasek 1979; Karasek and Theorell 1990), which is discussed below, is based on psychosocial characteristics of work: the psychological demands of work and a combined measure of task control and skill use (decision latitude). The model predicts, first, stress-related illness risk, and, secondly, active/passive behavioural correlates of jobs. It has mainly been used in epidemiological studies of chronic disease, such as coronary heart disease.
Pedagogically, it is a simple model which can help to demonstrate clearly several important issues relevant for social policy discussions of occupational health and safety:
- that the social organizational characteristics of work, and not just physical hazards, lead to illness and injury
- that stress-related consequences are related to the social organization of work activity and not just its demands
- that work’s social activity affects stress-related risks, not just person-based characteristics
- that the possibility of both “positive stress” and “negative stress” can be explained in terms of combinations of demands and control
- that can provide the simple model—with basic face validity—to begin discussions on personal stress response for shop-floor workers, clerical staff and other lay people for whom this is a sensitive topic.
Beyond the health consequences of work, the model also captures the perspectives of the work’s organizers who are concerned with productivity results. The psychological demand dimension relates to “how hard workers work”; the decision latitude dimension reflects work organization issues of who makes decisions and who does what tasks. The model’s active learning hypothesis describes the motivation processes of high performance work. The economic logic of extreme labour specialization, the past conventional wisdom about productive job design is contradicted by adverse health consequences in the Demand/Control model. The model implies alternative, health-promoting perspectives on work organization which emphasize broad skills and participation for workers, and which may also bring economic advantages for innovative manufacturing and in service industries because of the increased possibilities for learning and participation.
Hypotheses of the Demand/Control Model
Psychosocial functioning at the workplace, based on psychological demands and decision latitude
Job strain hypothesis
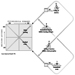
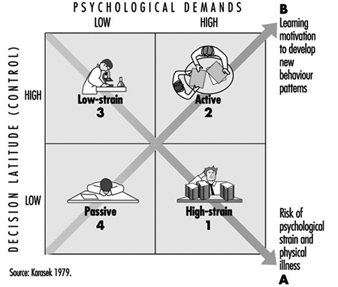
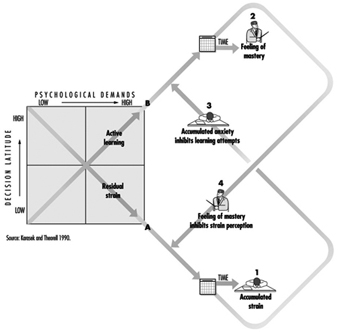
The first hypothesis is that the most adverse reactions of psychological strain occur (fatigue, anxiety, depression and physical illness) when the psychological demands of the job are high and the worker’s decision latitude in the task is low (figure 1, lower right cell). These undesirable stress-like reactions, which result when arousal is combined with restricted opportunities for action or coping with the stressor, are referred to as psychological strain (the term stress is not used at this point as it is defined differently by many groups).
Figure 1. Psychological demand/decision latitude model
For example, the assembly-line worker has almost every behaviour rigidly constrained. In a situation of increased demands (“speed-up”), more than just the constructive response of arousal, the often helpless, long-lasting, and negatively experienced response of residual psychological strain occurs. When the lunch-time rush occurs (Whyte 1948), it is the restaurant worker who does not know how to “control” her customers’ behaviour (“get the jump on the customer”) who experiences the greatest strain on the job. Kerckhoff and Back (1968) describe garment workers under heavy deadline pressure and the subsequent threat of layoff. They conclude that when the actions normally needed to cope with job pressures cannot be taken, the most severe behavioural symptoms of strain occur (fainting, hysteria, social contagion). It is not only the freedom of action as to how to accomplish the formal work task that relieves strain, it may also be the freedom to engage in the informal “rituals”, the coffee break, smoke break or fidgeting, which serve as supplementary “tension release” mechanisms during the work day (Csikszentmihalyi 1975).These are often social activities with other workers— precisely those activities eliminated as “wasted motions” and “soldiering” by Frederick Taylor’s methods (1911 (1967)). This implies a needed expansion of the model to include social relations and social support.
In the model, decision latitude refers to the worker’s ability to control his or her own activities and skill usage, not to control others. Decision latitude scales have two components: task authority—a socially predetermined control over detailed aspects of task performance (also called autonomy); and skill discretion— control over use of skills by the individual, also socially determined at work (and often called variety or “substantive complexity” (Hackman and Lawler 1971; Kohn and Schooler 1973)). In modern organizational hierarchies, the highest levels of knowledge legitimate the exercise of the highest levels of authority, and workers with limited-breadth, specialized tasks are coordinated by managers with higher authority levels. Skill discretion and authority over decisions are so closely related theoretically and empirically that they are often combined.
Examples of work’s psychological demands—“how hard you work”—include the presence of deadlines, the mental arousal or stimulation necessary to accomplish the task, or coordination burdens. The physical demands of work are not included (although psychological arousal comes with physical exertion). Other components of psychological job demands are stressors arising from personal conflicts. Fear of losing a job or skill obsolescence may obviously be a contributor. Overall, Buck (1972) notes that “task requirements” (workload) are the central component of psychological job demands for most workers in spite of the above diversity. While simple measures of working hours, in moderate ranges, do not seem to strongly predict illness, one such measure, shiftwork—especially rotating shiftwork, is associated with substantial social problems as well as increased illness.
While some level of “demands” is necessary to achieve new learning and effective performance on the job (i.e., interest), too high a level is obviously harmful. This has implied the inverted “U-shaped” curve of “optimal” level of demands in the well known General Adaptation Syndrome of Selye (1936) and related, classic theories by Yerkes and Dodson (1908) and Wundt (1922) on stress and performance.* However, our findings show that most work situations have an overload, rather than an underload, problem.
* Although Selye’s “U-shaped” association between demands and stress purported to be unidimensional along a stressor axis, it probably also included a second dimension of constraint in his animal experiments - and thus was really a composite model of stress-related physiological deterioration - potentially similar to the high demand, low control situation, as other researchers have found (Weiss 1971).
Active learning hypothesis
When control on the job is high, and psychological demands are also high, but not overwhelming (fig. 34.2 upper right cell) learning and growth are the predicted behavioural outcomes (i.e., the active learning hypothesis). Such a job is termed the “active job”, since research in both the Swedish and American populations has shown this to be the most active group outside of work in leisure and political activity, in spite of heavy work demands (Karasek and Theorell 1990). Only average psychological strain is predicted for the ‘active job’ because much of the energy aroused by the job’s many stressors (“challenges”) are translated into direct action—effective problem solving—with little residual strain to cause disturbance. This hypothesis parallels White’s “concept of competence” (1959): the psychological state of individuals in challenging circumstances is enhanced by increasing “demands”, an environment-based theory of motivation. The model also predicts that the growth and learning stimuli of these settings, when they occur in a job context, are conducive to high productivity.
In the Demand/Control model, learning occurs in situations which require both individual psychological energy expenditure (demands or challenges) and the exercise of decision-making capability. As the individual with decision-making latitude makes a “choice” as to how to best cope with a new stressor, that new behaviour response, if effective, will be incorporated into the individual’s repertoire of coping strategies (i.e., it will be “learned”). The potential activity level in the future will be raised because of the expanded range of solutions to environmental challenges, yielding an increase in motivation. Opportunities for constructive reinforcement of behaviour patterns are optimal when the challenges in the situation are matched by the individual’s control over alternatives or skill in dealing with those challenges (Csikszentmihalyi 1975). The situation will not be unchallengingly simple (thus, unimportant) nor so demanding that appropriate actions can not be taken because of high anxiety level (the psychological “strain” situation).
The Demand/Control model predicts that situations of low demand and low control (Figure 1 opposite end of diagonal B) cause a very “unmotivating” job setting which leads to “negative learning” or gradual loss of previously acquired skills. Evidence shows that disengagement from leisure and political activity outside the job appear to increase over time in such jobs (Karasek and Theorell 1990). These “passive” job, may be the result of “learned helplessness”, discussed by Seligman (1975) from a sequence of job situations which reject worker’s initiatives.
The fact that environmental demands can thus be conceptualized in both positive and negative terms is congruent with the common understanding that there is both “good” and “bad” stress. Evidence that at least two separable mechanisms must be used to describe “psychological functioning” on the job is one of the primary validations of the multidimensional “Demand/ Control” model structure. The “active”-“passive” diagonal B implies that learning mechanisms are independent of (i.e., orthogonal to) psychological strain mechanisms. This yields a parsimonious model with two broad dimensions of work activity and two major psychological mechanisms (the primary reason for calling it an “interaction” model (Southwood 1978)). (Multiplicative interactions for the axes is too restrictive a test for most sample sizes.)
Clarifying Demand and Control definitions
The Demand/Control model has sometimes been assumed to be congruent with a model of “demands and resources”, allowing a simple fit with currently common “cost/benefit” thinking—where the positive “benefits” of resources are subtracted from the negative “costs” of demands. “Resources” allows inclusion of many factors outside the worker’s immediate task experience of obvious importance. However, the logic of the Demand/ Control model hypotheses cannot be collapsed into a unidimensional form. The distinction between decision latitude and psychological stressors must be retained because the model predicts both learning and job strain—from two different combinations of demands and control which are not simply mathematically additive. Job “control” is not merely a negative stressor, and “demands and challenges” associated with lack of control are not associated with increased learning. Having decision latitude over the work process will reduce a worker’s stress, but increase his learning, while psychological demands would increase both learning and stress. This distinction between demands and control allows understanding of the otherwise unclear prediction of the effects of: (a) “responsibility”, which actually combines high demands and high decision latitude; (b) “qualitative job demands”, which also measures the possibility of decision making about what skills to employ; and (c) “piece work”, where the decision latitude to work faster almost directly brings with it increased demands.
Expanding the Model
Social support hypotheses
The Demand/Control model has been usefully expanded by Johnson by the addition of social support as a third dimension (Johnson 1986; Kristensen 1995). The primary hypothesis, that jobs which are high in demands, low in control—and also low in social support at work (high “iso-strain”) carry the highest risks of illness, has been empirically successful in a number of chronic disease studies. The addition clearly acknowledges the need of any theory of job stress to assess social relations at the workplace (Karasek and Theorell 1990; Johnson and Hall 1988). Social support “buffering” of psychological strain may depend on the degree of social and emotion integration and trust between co-workers, supervisors, etc.—“socio-emotional support” (Israel and Antonnuci 1987). Addition of social support also makes the Demand/Control perspective more useful in job redesigning. Changes in social relations between workers (i.e., autonomous work groups) and changes in decision latitude are almost inseparable in job redesign processes, particularly “participatory” processes (House 1981).
However, a full theoretical treatment of the impact of social relations on both job stress and behaviour is a very complex problem which needs further work. The associations with measures of co-worker and supervisor interactions and chronic disease are less consistent than for decision latitude, and social relations can strongly increase, as well as decrease, the nervous system arousal that may be the risk-inducing link between social situation and illness. The dimensions of work experience that reduce job stress would not necessarily be the same dimensions that are relevant for active behaviour in the Demand/Control model. Facilitating collective forms of active behaviour would likely focus on the distribution of and ability to use competences, communication structure and skills, coordination possibilities, “emotional intelligence skills” (Goleman 1995)—as well as the trust important for social support.
Occupation and psychosocial job characteristics
Job characteristics can be displayed in a four quadrant diagram using the average job characteristics of occupations in the US Census occupation codes (Karasek and Theorell 1990). The “active” job quadrant, with high demand and high control, has high-prestige occupations: lawyers, judges, physicians, professors, engineers, nurses and managers of all kinds. The “passive” job quadrant, with low demands and low control, has clerical workers such as stock and billing clerks, transport operatives and low status service personnel such as janitors. The “high strain” quadrant, with high demands and low control, has machine-paced operatives such as assemblers, cutting operatives, inspectors and freight handlers, as well as other low-status service operatives such as waiters or cooks. Female-dominated occupations are frequent (garment stitchers, waitresses, telephone operators and other office automation workers). “Low strain” self-paced occupations, such as repairmen, sales clerks, foresters, linemen and natural scientists, often involve significant training and self-pacing.
Thus, executives and professionals have a moderate level of stress, and not the highest level of stress, as popular belief often holds. While “managerial stress” certainly exists because of the high psychological demands that come with these jobs, it appears that the frequent occasions for decision-making and deciding how to do the job are a significant stress moderator. Of course, at the highest status levels, executive jobs consist of decision-making as the primary psychological demand, and then the Demand/ Control model fails. However, the implication here is that executives could reduce their stress if they made fewer decisions, and lower status workers would be better off with more decision opportunities, so that all groups could be better off with a more equal share of decision power.
Men are more likely than women to have high control over their work process at the task level, with a difference as great as wage differentials (Karasek and Theorell 1990). Another major gender difference is the negative correlation between decision latitude and demands for women: women with low control also have higher job demands. This means that women are several times as likely to hold high strain jobs in the full working population. By contrast, men’s high demand jobs are generally accompanied by somewhat higher decision latitude (“authority commensurate with responsibility”)
Theoretical linkages between the Demand/Control model and other theoretical perspectives
The Demand/Control models arises out of theoretical integration of several disparate scientific directions. Thus, it falls outside the boundaries of a number of established scientific traditions from which it has gained contributions or with which it is often contrasted: mental health epidemiology and sociology, and stress physiology, cognitive psychology and personality psychology. Some of these previous stress theories have focused on a person-based causal explanation, while the Demand/Control model predicts a stress response to social and psychological environments. However, the Demand/Control model has attempted to provide a set of interfacing hypotheses with person-based perspectives. In addition, linkage to macro social organizational and political economic issues, such as social class, have also been proposed. These theoretical integrations and contrasts with other theories are discussed below at several levels. The linkages below provide the background for an extended set of scientific hypotheses.
Contrast between the Demand/Control model and the cognitive psychological model
One area of stress theory grows out of the currently popular field of cognitive psychology. The central tenet of the cognitive model of human psychological functioning is that it is the processes of perception and interpretation of the external world that determine the development of psychological states in the individual. Mental workload is defined as the total information load that the worker is required to perceive and interpret while performing job tasks (Sanders and McCormick 1993; Wickens 1984). “Overload” and stress occur when this human information processing load is too large for the individual’s information processing capabilities. This model has enjoyed great currency since modelling human mental functions in the same rough conceptual model as modern computers utilize, and thus fits an engineering conception of work design. This model makes us aware of the importance of information overloads, communication difficulties and memory problems. It does well in the design of some aspects of human/computer interfaces and human monitoring of complex processes.
However, the cognitive psychological perspective tends to downplay the importance of “objective” workplace stressors, for example, and emphasize instead the importance of the stressed individuals’ interpretation of the situation. In the cognitive-based “coping approach”, Lazarus and Folkman (1986) advocate that the individual “cognitively reinterpret” the situation in a way that makes it appear less threatening, thus reducing experienced stress. However, this approach could be harmful to workers in situations where the environmental stressors are “objectively” real and must be modified. Another variant of the cognitive approach, more consistent with worker empowerment, is Bandura’s (1977) “self-efficacy /motivation” theory which emphasizes the increases in self-esteem which occur when individuals: (a) define a goal for a change process; (b) receive feedback on the positive results from the environment; and (c) successfully achieve incremental progress.
Several omissions in the cognitive model are problematic for an occupational health perspective on stress and conflict with the Demand/Control model:
- There is no role for the social and mental “demands” of work that do not translate into information loads (i.e., no role for tasks which require social organizational demands, conflicts and many non-intellectual time deadlines).
- The cognitive model predicts that situations which require taking a lot of decisions are stressful because they can overload the individual’s information-processing capacity. This directly contradicts the Demand/Control model which predicts lower strain in demanding situations that allow freedom of decision making. The majority of epidemiological evidence from field studies supports the Demand/Control model, but laboratory tests can generate decision-based cognitive overload effect also.
- The cognitive model also omits physiological drives and primitive emotions, which often dominate cognitive response in challenging situations. There is little discussion of how either negative emotions, nor learning-based behaviour (except for Bandura, above) arise in common adult social situations.
Although overlooked in the cognitive model, emotional response is central to the notion of “stress”, since the initial stress problem is often what leads to unpleasant emotional states such as anxiety, fear and depression. “Drives” and emotions are most centrally affected by the limbic regions of the brain—a different and more primitive brain region than the cerebral cortex addressed by most of the processes described by cognitive psychology. Possibly, the failure to develop an integrated perspective on psychological functioning reflects the difficulty of integrating different research specializations focusing on two different neurological systems in the brain. However, recently, evidence has begun to accumulate about the joint effects of emotion and cognition. The conclusion seems to be that emotion is an underlying determinant of strength of behaviour pattern memory and cognition (Damasio 1994; Goleman 1995).
Integrating Sociological and Emotional Stress Perspectives
Development of the Demand/Control model
The goal of the Demand/Control model has been to integrate understanding of the social situation with evidence of emotional response, psychosomatic illness symptoms and active behaviour development in major spheres of adult life activity, particularly in the highly socially structured work situation. However, when the model was being developed, one likely platform for this work, sociological research exploring illness in large population studies, often omitted the detailed level of social or personal response data of stress research, and thus much integrating work was needed to develop the model.
The first Demand/Control integrating idea—for social situation and emotional response—involved stress symptoms, and linked two relatively unidimensional sociological and social psychological research traditions. First, the life stress/illness tradition (Holmes and Rahe 1967; Dohrenwend and Dohrenwend 1974) predicted that illness was based on social and psychological demands alone, without mention of control over stressors. Second, the importance of control at the workplace had been clearly recognized in the job satisfaction literature (Kornhauser 1965): task autonomy and skill variety were used to predict job satisfaction, absenteeism or productivity, with limited additions reflecting the workers’ social relationship to the job—but there was little mention of job workloads. Integrating studies helped bridge the gaps in the area of illness and mental strain. Sundbom (1971) observed symptoms of psychological strain in “mentally heavy work”—which was actually measured by questions relating to both heavy mental pressures and monotonous work (presumably also representing restricted control). The combined insight of these two studies and research traditions was that a two-dimensional model was needed to predict illness: the level of psychological demands determined whether low control could lead to two significantly different types of problem: psychological strain, or passive withdrawal.
The second Demand/Control integration predicted behaviour patterns related to work experience. Behavioural outcomes of work activity also appeared to be affected by the same two broad job characteristics—but in a different combination. Kohn and Schooler (1973) had observed that active orientations to the job were the consequence of both high skill and autonomy levels, plus psychologically demanding work. Social class measures were important correlates here. Meissner (1971) had also found that leisure behaviour was positively associated with opportunities both to take decisions on the job and to perform mentally challenging work. The combined insight of these studies was that “challenge” or mental arousal was necessary, on the one hand, for effective learning and, on the other, could contribute to psychological strain. “Control” was the crucial moderating variable that determined whether environmental demands would lead to “positive” learning consequences, or “negative” strain consequences.
The combination of these two integrating hypotheses, predicting both health and behavioural outcomes, is the basis of the Demand/Control model. “Demand” levels are the contingent factor which determines whether low control leads to either passivity or psychological strain; and “control” levels are the contingent factor which determines whether demands lead to either active learning or psychological strain (Karasek 1976; 1979). The model was then tested on a representative national sample of Swedes (Karasek 1976) to predict both illness symptoms and leisure and political behavioural correlates of psychosocial working conditions. The hypotheses were confirmed in both areas, although many confounding factors obviously share in these results. Shortly after these empirical confirmations, two other conceptual formulations, consistent with the Demand/Control model, appeared, which confirmed the robustness of the general hypotheses. Seligman (1976) observed depression and learned helplessness in conditions of intense demand with restricted control. Simultaneously, Csikszentmihalyi (1975) found that an “active experience” (“flow”) resulted from situations which involved both psychological challenges and high levels of competence. Use of this integrated model was able to resolve some paradoxes in job satisfaction and mental strain research (Karasek 1979): for example, that qualitative workloads were often negatively associated with strain (because they also reflected the individual’s control over his or her use of skills). The most extensive acceptance of the model by other researchers came in 1979 after the expansion of empirical prediction to coronary heart disease, with the assistance of colleague Tores Theorell, a physician with significant background in cardiovascular epidemiology.
A second Demand/Control model integration—physiological response
Additional research has allowed a second level of integration linking the Demand/Control model to physiological response. The main research developments in physiological research had identified two patterns of an organism’s adaptation to its environment. Cannon’s (1914) fight-flight response is most associated with stimulation of the adrenal medulla—and adrenaline secretion. This pattern, occurring in conjunction with sympathetic arousal of the cardiovascular system, is clearly an active and energetic response mode where the human body is able to use maximum metabolic energy to support both mental and physical exertion necessary to escape major threats to its survival. In the second physiological response pattern, the adrenocortical response is a response to defeat or withdrawal in a situation with little possibility of victory. Selye’s research (1936) on stress dealt with the adrenocortical response to animals in a stressed but passive condition (i.e., his animal subjects were restrained while they were stressed, not a fight-flight situation). Henry and Stephens (1977) describe this behaviour as the defeat or loss of social attachments, which leads to a withdrawal and submissiveness in social interactions.
* A major stimulus for the development of the strain hypothesis of the Demand/Control model in 1974 were Dement’s observations (1969) that vital relaxation related to REM dreaming was inhibited if sleep-deprived cats were “constrained” by a treadmill (perhaps like an assembly line) after periods of extreme psychological stressor exposure. The combined actions of both environmental stressors and low environmental control were essential elements in producing these effects. The negative impacts, in terms of mental derangement, were catastrophic and led to inability to coordinate the most basic physiological processes.
In the early 1980s, Frankenhaeuser’s (1986) research demonstrated the congruence of these two patterns of physiological response with the main hypotheses of the Demand/ Control model—allowing linkage to be made between physiological response and social situation, and emotional response patterns. In high-strain situations, cortisol from the adrenal cortex, and adrenaline from the adrenal medulla, secretions are both elevated, whereas in a situation where the subject has a controllable and predictable stressor, adrenaline secretion alone is elevated (Frankenhaeuser, Lundberg and Forsman 1980). This demonstrated a significant differentiation of psychoendocrine response associated with different environmental situations. Frankenhaeuser used a two-dimension model with the same structure as the Demand/Control model, but with dimensions labelling personal emotional response. “Effort” describes adrenal-medullary stimulating activity (demands in the Demand/Control model) and “distress” describes adrenocortical stimulating activity (lack of decision latitude in the Demand/ Control model). Frankenhaeuser’s emotional response categories illuminate a clearer link between emotion and physiological response, but in this form the Demand/Control model fails to illuminate the association between work sociology and physiological response, which has been another strength of the model.
Integrating person-based stress theory: The dynamic version of the Demand/Control model
One of the challenges behind the development of the Demand/ Control model has been to develop an alternative to the socially conservative explanation that the worker’s perception or response orientations are primary responsible for stress—the claim of some person-based stress theories. For example, it is hard to accept the claims, extended by personality-based stress models, that the majority of stress reactions develop because common individual personality types habitually misinterpret real world stresses or are oversensitive to them, and that these types of personality can be identified on the basis of simple tests. Indeed, evidence for such personality effects has been mixed at best with even the most common measures (although a stress denial personality has been identified—alexithymia (Henry and Stephens 1977). The Type A behaviour pattern, for example, was originally interpreted as the individual’s proclivity to select stressful activities, but research in this area has now shifted to the “anger-prone” personality (Williams 1987). Of course, anger response could have a significant environment-response component. A more generalized version of the personality approach is found in the “person-environment fit” model (Harrison 1978), which postulates that a good match between the person and the environment is what reduces stress. Here also it has been difficult to specify the specific personality characteristics to be measured. Nevertheless, personal response/personality-based approaches addressed the obvious fact that: (a) person-based perceptions are an important part of the process in which environments affect individuals; and (b) there are long-term differences in personal responses to environments. Thus, a time dynamic, integrated environment and person-based version of the Demand/Control model was developed.
The dynamic version of the Demand/Control model (figure 2) integrates environment effects with person-based phenomena such as self-esteem development and long-term exhaustion. The dynamic version integrates person-based and environmental factors by building two combined hypotheses on the original strain and learning mechanisms: (a) that stress inhibits learning; and (b) that learning, in the long term, can inhibit stress. The first hypothesis is that high-strain levels may inhibit the normal capacity to accept a challenge, and thus inhibit new learning. These high-strain levels may be the result of long-lasting psychological strain accumulated over time—and reflected in person-based measures (figure 2, diagonal arrow B). The second hypothesis is that new learning may lead to feelings of mastery or confidence—a person-based measure. These feelings of mastery, in turn, can lead to reduced perceptions of events as stressful and increased coping success (figure 3, diagonal arrow A). Thus, environmental factors, over the long term, partly determine personality, and later, environmental effects are moderated by these previously developed personality orientations. This broad model could incorporate the following, more specific measures of personal response: feelings of mastery, denial, alexithymia, trait anxiety, trait anger, vital exhaustion, burnout, culmulative life-stressor implications, and possibly Type A behaviour components.
Figure 2. Dynamic associations linking environmental strain and learning to evolution of personality
The dynamic model yields the possibility of two long-term dynamic “spirals” of behaviour. The positive behavioural dynamic begins with the active job setting, the increased “feeling of mastery”, and the increased ability to cope with inevitable job stressors. These, in turn, reduce accumulated anxiety and thus increase the capacity to accept still more learning challenges —yielding still further positive personality change and improved well-being. The undesirable behavioural dynamic begins with the high-strain job, the high accumulated residual strain and the restricted capacity to accept learning challenges. These, in turn, lead to diminishing self-esteem and increased stress perceptions—yielding still further negative personality change and diminished well-being. Evidence for submechanisms is discussed in Karasek and Theorell (1990), although the complete model has not been tested. Two promising research directions which could easily integrate with Demand/Control research are “vital exhaustion” research integrated with changing responses to life demands (Appels 1990), and Bandura’s (1977) “self-efficacy” methods, which integrate skill development and self-esteem development.
The Demand/Control model and the system dynamics of physiological stress
One necessary next step for Demand/Control research is a more comprehensive specification of the physiological pathways of illness causation. Physiological response is increasingly being understood as a complex system response. The physiology of human stress response—to accomplish, for example, a fight or flight behaviour—is a highly integrated combination of changes in cardiovascular output, brain-stem regulation, respiratory interaction, limbic-system control of the endocrine response, general cortical activation and peripheral circulatory system changes. The concept of “stress” is very possibly most relevant for complex systems—which involve multiple, interacting subsystems and complex causality.* Accompanying this new perspective of systems dynamic principles in physiology, are definitions of many diseases as disorders of system regulation (Henry and Stephens 1977; Weiner 1977), and investigation of the results of time-dependent, multifactoral adjustments to system equilibrium, or alternatively, their absence in “chaos”.
* Instead of a single and unambiguous cause and effect linkage, as in the "hard sciences" (or hard science mythologically), in stress models causal associations are more complex: there may be many causes which "accumulate" to contribute to a single effect; a single cause ("stressor") may have many effects; or effects which occur only after significant time delays.
Interpreting such observations from the perspective of a “generalized” Demand/Control model, we could say that stress refers to a disequilibrium of the system as a whole, even when parts of the system are functioning. All organisms must have control mechanisms to integrate the actions of separate subsystems (i.e., the brain, the heart and the immune systems). Stress (or job strain) would be an overload condition experienced by the organism’s “control system” when it attempts to maintain integrated functioning in the face of too many environmental challenges (“high demands”), and when the system’s capability of integrated control of its submechanisms fails (“high strain”). To impose order on its chaotic environment, the individual’s internal physiological control systems must “do the work” of maintaining a coordinated physiological regularity (i.e., a constant heart rate) in the face of irregular environmental demands. When the organism’s control capacity is exhausted after too much “organizing” (a low entropy condition, by analogy from thermodynamics), further demands lead to excess fatigue or debilitating strain. Furthermore, all organisms must periodically return their control systems to the rest-state—sleep or relaxation periods (a state of relaxed disorder or high entropy)—to be capable of undertaking the next round of coordinating tasks. The system’s coordination processes or its relaxation attempts may be inhibited if it cannot follow its own optimal course of action, i.e., if it has no possibilities to control its situation or find a satisfactory internal equilibrium state. In general, “lack of control” may represent restriction of the organism’s ability to use all of its adaptive mechanisms to maintain physiological equilibrium in the face of demands, leading to increased long-term burdens and disease risk. This is a direction for future Demand/Control physiological research.
One potentially consistent finding is that while the Demand/Control model predicts cardiovascular mortality, no single conventional risk factor or physiological indicator seems to be the primary pathway of this risk. Future research may show whether “systems dynamic failures” are the pathway.
Macro-social implications of Demand/Control model
Models which integrate over several spheres of research allow broader predictions about the health consequences of human social institutions. For example, Henry and Stephens (1977) observe that in the animal world “psychological demands” result from the thoroughly “social” responsibilities of finding family food and shelter, and rearing and defending offspring; situations of enforced demands combined with social isolation would be hard to imagine. However, the human world of work is so organized that demands can occur without any social affiliation at all. Indeed, according to Frederick Taylor’s Principles of Scientific Management (1911 (1967)), increasing workers’ job demands often should be done in isolation, otherwise the workers would revolt against the process—and return to time-wasting socializing! In addition to showing the utility of an integrated model, this example shows the need to expand even further the social understanding of the human stress response (for example, by adding a social support dimension to the Demand/Control model).
An integrated, socially anchored, understanding of human stress response is particularly needed to understand future economic and political development. Less comprehensive models could be misleading. For example, according to the cognitive model which has dominated public dialogues about future social and industrial development (i.e., the direction for worker’s skills, life in the information society, etc.), an individual has freedom to interpret—i.e., reprogramme—his perception of real world events as stressful or non-stressful. The social implication is that, literally, we can design for ourselves any social arrangement—and we should take the responsibility for adapting to any stresses it may cause. However, many of the physiological consequences of stress relate to the “emotional brain” in the limbic system, which has a deterministic structure with clear limitations on overall demands. It is definitely not “infinitely” re-programmable, as studies of post traumatic stress syndrome clearly indicate (Goleman 1995). Overlooking the limbic system’s limits—and the integration of emotional response and social integration—can lead to a very modern set of basic conflicts for human development. We may be developing social systems on the basis of the extraordinary cognitive capabilities of our brain cortex that place impossible demands on the more basic limbic brain functions in terms of overloads: lost social bonds, lack of internal control possibilities, and restricted ability to see the “whole picture”. In short, we appear to be running the risk of developing work organizations for which we are sociobiologically misfit. These results are not just the consequence of scientific incomplete models, they also facilitate the wrong kinds of social process—processes where the interests of some groups with social power are served to the cost to others of previously inexperienced levels of social and personal dysfunction.
Social class and psychosocial job measures
In many cases, individual level stressors can be modelled as the causal outcome of larger-scale social, dynamic and political- economic processes. Thus, theoretical linkages to concepts such as social class are also needed. Assessment of associations between social situation and illness raise the question of the relation between psychosocial Demand/Control factors and broad measures of social circumstance such as social class. Job decision latitude measure is, indeed, clearly correlated with education and other measures of social class. However, social class conventionally measures effects of income and education which operate via different mechanisms than the psychosocial pathways of the Demand/Control model. Importantly, the job strain construct is almost orthogonal to most social class measures in national populations (however, the active/passive dimension is highly correlated with social class among high status workers (only)) (Karasek and Theorell 1990). The low-decision latitude aspects of low status jobs appear to be a more important contributor to psychological strain than the distinction between mental and physical workload, the conventional determinant of white/blue-collar status. Indeed, the physical exertion common in many blue-collar jobs may be protective for psychological strain in some circumstances. While job strain is indeed more common in low status jobs, psychosocial job dimensions define a strain-risk picture which is significantly independent of the conventional social class measures.
Although it has been suggested that the observed Demand/Control job/illness associations merely reflect social class differences (Ganster 1989; Spector 1986), a review of evidence rejects this view (Karasek and Theorell 1990). Most of the Demand/Control research has simultaneously controlled for social class, and Demand/Control associations persist within social class groups. However, blue-collar associations with the model are more consistently confirmed, and the strength of white-collar associations varies (see “Job strain and cardiovascular disease”, below) across studies, with white-collar single occupation studies being somewhat less robust. (Of course, for the very highest status managers and professionals decision making may become a significant demand in itself.)
The fact that conventional “social class” measures often find weaker associations with mental distress and illness outcomes than the Demand/Control model actually makes a case for new social class conceptions. Karasek and Theorell (1990) define a new set of psychosocially advantaged and disadvantaged workers, with job stress “losers” in routinized, commercialized and bureaucratized jobs, and “winners” in highly creative learning-focused intellectual work. Such a definition is consistent with a new, skill-based industrial output in the “information society”, and a new perspective on class politics.
Methodological Issues
Objectivity of psychosocial job measures
Self-report questionnaires administered to workers have been the most common method of gathering data on psychosocial characteristics of work since they are simple to administer and can be easily designed to tap core concepts in work redesign efforts also (Hackman and Oldham’s JDS 1975), Job Content Questionnaire (Karasek 1985), the Swedish Statshalsan questionnaire. While designed to measure the objective job, such questionnaire instruments inevitably measure job characteristics as perceived by the worker. Self-report bias of findings can occur with self-reported dependent variables such as depression, exhaustion and dissatisfaction. One remedy is to aggregate self-report responses by work groups with similar work situations—diluting individual biases (Kristensen 1995). This is the basis of extensively used systems linking psychosocial job characteristics to occupations (Johnson et al. 1996).
There is also evidence assessing the “objective” validity of self-reported psychosocial scales: correlations between self-report and expert observation data are typically 0.70 or higher for decision latitude, and lower (0.35) correlations for work demands (Frese and Zapf 1988). Also supporting objective validity is the high between-occupation variances of (40 to 45%) of decision latitude scales, which compare favourably with 21% for income and 25% for the physical exertion, which are acknowledged to vary dramatically by occupation (Karasek and Theorell 1990). However, only 7% and 4%, of psychological demands and social support scale variance, respectively, is between occupations, leaving the possibility of a large person-based component of self-reports of these measures.
More objective measurement strategies would be desirable. Some well-known objective assessment methods are congruent with the Demand/Control model (for decision latitude: VERA, Volpert et al. (1983)). However, expert observations have problems also: observations are costly, time consuming, and, in assessment of social interactions, obviously do not generate more accurate measures. There are also theoretical biases involved in the very concept of standard “expert” measures: it is much easier to “measure” the easily observed, repetitive quality of the low status assembly-line worker jobs, than the diverse tasks of high status managers or professionals. Thus, objectivity of the psychosocial measures is inversely related to the decision latitude of the subject.
Some reviews of empirical evidence for the Demand/Control model
Job strain and cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Job strain and heart disease associations represent the broadest base of empirical support for the model. Recent comprehensive reviews have been done by Schnall, Landsbergis and Baker (1994), Landsbergis et al. (1993) and Kristensen (1995). Summarizing Schnall, Landsbergis and Baker(1994) (updated by Landsbergis, personal communication, Fall 1995): 16 of 22 studies have confirmed a job strain association with cardiovascular mortality using a wide range of methodologies, including 7 of 11 cohort studies; 2 of 3 cross-sectional studies; 4 of 4 case control studies; and 3 of 3 studies utilizing disease symptom indicators. Most negative studies have been in older populations (mainly over age 55, some with much post-retirement time) and are mainly based upon aggregated occupation scores which, although they minimize self-report bias, are weak in statistical power. The job strain hypothesis appears to be somewhat more consistent when predicting blue-collar than white-collar CVD (Marmot and Theorell 1988). Conventional CVD risk factors such as serum cholesterol, smoking and even blood pressure, when measured in the conventional manner, have so far only shown inconsistent or weak job-strain effects. However, more sophisticated methods (ambulatory blood pressures) show substantial positive results (Theorell and Karasek 1996).
Job strain and psychological distress/behaviour, absenteeism
Psychological disorder findings are reviewed in Karasek and Theorell (1990). The majority of the studies confirm a job strain association and are from broadly representative or nationally representative populations in a number of countries. The common study limitations are cross-section design and the difficult-to-avoid problem of self-reported job and psychological strain questionnaires, although some studies also include objective observer assessment of work situations and there are also supportive longitudinal studies. While some have claimed that a person-based tendency towards negative affect inflates work-mental strain associations (Brief et al. 1988), this could not be true for several strong findings on absenteeism (North et al. 1996; Vahtera Uutela and Pentii 1996). Associations in some studies are very strong and, in a number of studies, are based on a linkage system which minimizes potential self-report bias (at the risk of loss of statistical power). These studies confirm associations for a broad range of psychological strain outcomes: moderately severe forms of depression, exhaustion, drug consumption, and life and job dissatisfaction, but findings also differ by outcome. There is also some differentiation of negative affect by Demand/Control model dimensions. Exhaustion, rushed tempo or simply reports of “feeling stressed” are more strongly related to psychological demands—and are higher for managers and professionals. More serious strain symptoms such as depression, loss of self-esteem, and physical illness seem to be more strongly associated with low decision latitude—a larger problem for low status workers.
Job strain and musculoskeletal disorders and other chronic diseases
Evidence of the utility of the Demand/Control model is accumulating in other areas (see Karasek and Theorell 1990). Prediction of occupational musculoskeletal illness is reviewed for 27 studies by Bongers et al. (1993) and other researchers (Leino and Häøninen 1995; Faucett and Rempel 1994). This work supports the predictive utility of the Demand/ Control/support model, particularly for upper extremity disorders. Recent studies of pregnancy disorders (Fenster et al. 1995; Brandt and Nielsen 1992) also show job strain associations.
Summary and Future Directions
The Demand/Control/support model has stimulated much research during recent years. The model has helped to document more specifically the importance of social and psychological factors in the structure of current occupations as a risk factor for industrial society’s most burdensome diseases and social conditions. Empirically, the model has been successful: a clear relationship between adverse job conditions (particularly low decision latitude) and coronary heart disease has been established.
However, it is still difficult to be precise about which aspects of psychological demands, or decision latitude, are most important in the model, and for what categories of workers. Answers to these questions require more depth of explanation of the physiological and micro-behavioural effects of psychological demands, decision latitude and social support than the model’s original formulation provided, and require simultaneous testing of the dynamic version of the model, including the active/passive hypotheses. Future utility of Demand/Control research could be enhanced by an expanded set of well-structured hypotheses, developed through integration with other intellectual areas, as outlined above (also in Karasek and Theorell 1990). The active/passive hypotheses, in particular, have received too little attention in health outcome research.
Other areas of progress are also needed, particularly new methodological approaches in the psychological demand area. Also, more longitudinal studies are needed, methodological advances are needed to address self-report bias and new physiological monitoring technologies must be introduced. At the macro level, macro social occupational factors, such as worker collective and organizational level decision influence and support, communication limitations and job and income insecurity, need to be more clearly integrated into the model. The linkages to social class concepts need to be further explored, and the strength of the model for women and the structure of work/family linkages need to be further investigated. Population groups in insecure employment arrangements, which have the highest stress levels, must be covered by new types of study designs—especially relevant as the global economy changes the nature of work relationships. As we are more exposed to the strains of the global economy, new measures at macro levels are needed to test the lack of local control and increased intensity of work activity— apparently making the general form of the Demand/Control model relevant in the future.
Person–Environment Fit
Person–environment fit (PE) theory offers a framework for assessing and predicting how characteristics of the employee and the work environment jointly determine worker well-being and, in the light of this knowledge, how a model for identifying points of preventive intervention may be elaborated. Several PE fit formulations have been proposed, the most widely known ones being those of Dawis and Lofquist (1984); French, Rodgers and Cobb (1974); Levi (1972); McGrath (1976); and Pervin (1967). The theory of French and colleagues, illustrated in figure 1, may be used to discuss the conceptual components of PE fit theory and their implications for research and application.
Figure 1. Schematic of French, Rogers and Cobb's theory of person-environment (PE) fit
Poor PE fit can be viewed from the perspectives of the employee’s needs (needs–supplies fit) as well as the job–environment’s demands (demands–abilities fit). The term needs–supplies fit refers to the degree to which employee needs, such as the need to use skills and abilities, are met by the work environment’s supplies and opportunities to satisfy those needs. Demands–abilities fit refers to the degree to which the job’s demands are met by the employee’s skills and abilities. These two types of fit can overlap. For example, work overload may leave the employer’s demands unmet as well as threaten the employee’s need to satisfy others.
Conceptualizing Person (P) and Environment (E)
Characteristics of the person (P) include needs as well as abilities. Characteristics of the environment (E) include supplies and opportunities for meeting the employee’s needs as well as demands which are made on the employee’s abilities. In order to assess the degree to which P equals (or fits), exceeds, or is less than E, the theory requires that P and E be measured along commensurate dimensions. Ideally, P and E should be measured on equal interval scales with true zero points. For example, one could assess PE fit on workload for a data-entry operator in terms of both the number of data-entry keystrokes per minute demanded by the job (E) and the employee’s keystroke speed (P). As a less ideal alternative, investigators often use Likert type scales. For example, one could assess how much the employee wants to control the work pace (P) and how much control is provided by the job’s technology (E) by using a rating scale, where a value of 1 corresponds to no control, or almost no control and a value of 5 corresponds to complete control.
Distinguishing Subjective from Objective Fit
Subjective fit (FS) refers to the employee’s perceptions of P and E, whereas objective fit (FO) refers to assessments that are, in theory, free of subjective bias and error. In practice, there is always measurement error, so that it is impossible to construct truly objective measures. Consequently, many researchers prefer to create a working distinction between subjective and objective fit, referring to measures of objective fit as ones which are relatively, rather than absolutely, immune to sources of bias and error. For example, one can assess objective PE fit on keystroke ability by examining the fit between a count of required keystrokes per minute in the actual workload assigned to the employee (EO) and the employee’s ability as assessed on an objective-type test of keystroke ability (PO). Subjective PE fit might be assessed by asking the employee to estimate per minute keystroke ability (PS) and the number of keystrokes per minute demanded by the job (ES).
Given the challenges of objective measurement, most tests of PE fit theory have used only subjective measures of P and E (for an exception, see Chatman 1991). These measures have tapped a variety of dimensions including fit on responsibility for the work and well-being of other persons, job complexity, quantitative workload and role ambiguity.
Dynamic Properties of the PE Fit Model
Figure 1 depicts objective fit influencing subjective fit which, in turn, has direct effects on well-being. Well-being is broken down into responses called strains, which serve as risk factors for subsequent illness. These strains can involve emotional (e.g., depression, anxiety), physiological (e.g., serum cholesterol, blood pressure), cognitive (e.g., low self-evaluation, attributions of blame to self or others), as well as behavioural responses (e.g., aggression, changes in lifestyle, drug and alcohol use).
According to the model, levels of and changes in objective fit, whether due to planned intervention or otherwise, are not always perceived accurately by the employee, so that discrepancies arise between objective and subjective fit. Thus, employees can perceive good fit as well as poor fit when, objectively, such is not the case.
Inaccurate employee perceptions can arise from two sources. One source is the organization, which, unintentionally or by design (Schlenker 1980), may provide the employee with inadequate information regarding the environment and the employee. The other source is the employee. The employee might fail to access available information or might defensively distort objective information about what the job requires or about his or her abilities and needs — Taylor (1991) cites such an example.
French, Rodgers and Cobb (1974) use the concept of defences to refer to employee processes for distorting the components of subjective fit, PS and ES, without changing the commensurate components of objective fit, PO and EO. By extension, the organization can also engage in defensive processes—for example, cover-ups, denial or exaggeration—aimed at modifying employee perceptions of subjective fit without concomitantly modifying objective fit.
The concept of coping is, by contrast, reserved for responses and processes that aim to alter and, in particular, improve objective fit. The employee can attempt to cope by improving objective skills (PO) or by changing objective job demands and resources (EO) such as through a change of jobs or assigned responsibilities. By extension, the organization can also apply coping strategies to improve objective PE fit. For example, organizations can make changes in selection and promotion strategies, in training and in job design to alter EO and PO.
The distinctions between coping and defence on the one hand and objective and subjective fit on the other can lead to an array of practical and scientific questions regarding the consequences of using coping and defence and the methods for distinguishing between effects of coping and effects of defence on PE fit. By derivation from the theory, sound answers to such questions require sound measures of objective as well as subjective PE fit.
Statistical Models
PE fit can have non-linear relations with psychological strain. Figure 2 presents a U-shaped curve as an illustration. The lowest level of psychological strain on the curve occurs when employee and job characteristics fit each other (P = E). Strain increases as the employee’s abilities or needs respectively fall short of the job’s demands or resources (P
Figure 2. Hypothetical U-shaped relation of person-environment fit to psychological strain
Efficacy of the Model
A variety of different approaches to the measurement of PE fit demonstrate the model’s potential for predicting well-being and performance. For example, careful statistical modelling found that PE fit explained about 6% more variance in job satisfaction than was explained by measures of P or E alone (Edwards and Harrison 1993). In a series of seven studies of accountants measuring PE fit using a card-sort method, high-performers had higher correlations between P and E (average r = 0.47) than low performers (average r = 0.26; Caldwell and O’Reilly 1990). P was assessed as the employee’s knowledge, skills and abilities (KSAs), and E was assessed as the commensurate KSAs required by the job. Poor PE fit between the accountant’s values and the firm’s also served to predict employee turnover (Chatman 1991).
Workload
Workload and Brain Function
Knowledge about human needs, abilities and constraints provides guidelines for shaping psychosocial work conditions so as to reduce stress and improve occupational health (Frankenhaeuser 1989). Brain research and behavioural research have identified the conditions under which people perform well and the conditions under which performance deteriorates. When the total inflow of impressions from the outside world falls below a critical level and work demands are too low, people tend to become inattentive and bored and to lose their initiative. Under conditions of excessive stimulus flow and too high demands, people lose their ability to integrate messages, thought processes become fragmented and judgement is impaired. This inverted U-relationship between workload and brain function is a fundamental biological principle with wide applications in working life. Stated in terms of efficiency at different workloads, it means that the optimal level of mental functioning is located at the midpoint of a scale ranging from very low to very high work demands. Within this middle zone the degree of challenge is “just right”, and the human brain functions efficiently. The location of the optimal zone varies among different people, but the crucial point is that large groups spend their lives outside the optimal zone that would provide opportunities for them to develop their full potential. Their abilities are constantly either underutilized or overtaxed.
A distinction should be made between quantitative overload, which means too much work within a given time period, and qualitative underload, which means that tasks are too repetitive, lacking variety and challenge (Levi, Frankenhaeuser and Gardell 1986).
Research has identified criteria for “healthy work” (Frankenhaeuser and Johansson 1986; Karasek and Theorell 1990). These criteria emphasize that workers should be given the opportunity to: (a) influence and control their work; (b) understand their contribution in a wider context; (c) experience a sense of togetherness and belonging at their place of work; and (d) develop their own abilities and vocational skill by continuous learning.
Monitoring Bodily Responses at Work
People are challenged by different work demands whose nature and strength are appraised via the brain. The appraisal process involves a weighing, as it were, of the severity of the demands against one’s own coping abilities. Any situation which is perceived as a threat or challenge requiring compensatory effort is accompanied by the transmission of signals from the brain to the adrenal medulla, which responds with an output of the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine. These stress hormones make us mentally alert and physically fit. In the event that the situation induces feelings of uncertainty and helplessness, the brain messages also travel to the adrenal cortex, which secretes cortisol, a hormone which plays an important part in the body’s immune defence (Frankenhaeuser 1986).
With the development of biochemical techniques that permit the determination of exceedingly small amounts of hormones in blood, urine and saliva, stress hormones have come to play an increasingly important role in research on working life. In the short term, a rise in stress hormones is often beneficial and seldom a threat to health. But in the longer term, the picture may include damaging effects (Henry and Stephens 1977; Steptoe 1981). Frequent or long-lasting elevations of stress-hormone levels in the course of daily life may result in structural changes in the blood vessels which, in turn, may lead to cardiovascular disease. In other words, consistently high levels of stress hormones should be regarded as warning signals, telling us that the person may be under excessive pressure.
Biomedical recording techniques permit the monitoring of bodily responses at the workplace without interfering with the worker’s activities. Using such ambulatory-monitoring techniques, one can find out what makes the blood pressure rise, the heart beat faster, the muscles tense up. These are important pieces of information which, together with stress-hormone assays, have helped in identifying both aversive and protective factors related to job content and work organization. Thus, when searching the work environment for harmful and protective factors, one can use the people themselves as “measuring rods”. This is one way in which the study of human stress and coping may contribute to intervention and prevention at the workplace (Frankenhaeuser et al. 1989; Frankenhaeuser 1991).
Personal Control as a “Buffer”
Data from both epidemiological and experimental studies support the notion that personal control and decision latitude are important “buffering” factors which help people to simultaneously work hard, enjoy their jobs and remain healthy (Karasek and Theorell 1990). The chance of exercising control may “buffer” stress in two ways: first, by increasing job satisfaction, thus reducing bodily stress responses, and secondly, by helping people develop an active, participatory work role. A job that allows the worker to use his or her skills to the full will increase self-esteem. Such jobs, while demanding and taxing, may help to develop competencies that aid in coping with heavy workloads.
The pattern of stress hormones varies with the interplay of positive versus negative emotional responses evoked by the situation. When demands are experienced as a positive and manageable challenge, the adrenaline output is typically high, whereas the cortisol-producing system is put to rest. When negative feelings and uncertainty dominate, both cortisol and adrenaline increase. This would imply that the total load on the body, the “cost of achievement”, will be lower during demanding, enjoyable work than during less demanding but tedious work, and it would seem that the fact that cortisol tends to be low in controllable situations could account for the positive health effects of personal control. Such a neuroendocrine mechanism could explain the epidemiological data obtained from national surveys in different countries which show that high job demands and work overload have adverse health consequences mainly when combined with low control over job-related decisions (Frankenhaeuser 1991; Karasek and Theorell 1990; Levi, Frankenhaeuser and Gardell 1986).
Total Workload of Women and Men
In order to assess the relative workloads associated with men’s and women’s different life situations, it is necessary to modify the concept of work so as to include the notion of total workload, that is, the combined load of demands related to paid and unpaid work. This includes all forms of productive activities defined as “all the things that people do that contribute to the goods and services that other people use and value” (Kahn 1991). Thus, a person’s total workload includes regular employment and overtime at work as well as housework, child care, care of elderly and sick relatives and work in voluntary organizations and unions. According to this definition, employed women have a higher workload than men at all ages and all occupational levels (Frankenhaeuser 1993a, 1993b and 1996; Kahn 1991).
The fact that the division of labour between spouses in the home has remained the same, while the employment situation of women has changed radically, has led to a heavy workload for women, with little opportunity for them to relax in the evenings (Frankenhaeuser et al. 1989). Until a better insight has been gained into the causal links between workload, stress and health, it will remain necessary to regard prolonged stress responses, displayed in particular by women at the managerial level, as warning signals of possible long-term health risks (Frankenhaeuser, Lundberg and Chesney 1991).
Hours of Work
Introduction
The patterning and duration of the hours a person works are a very important aspect of his or her experience of the work situation. Most workers feel that they are paid for their time rather than explicitly for their efforts, and thus the transaction between the worker and the employer is one of exchanging time for money. Thus, the quality of the time being exchanged is a very important part of the equation. Time that has high value because of its importance to the worker in terms of allowing sleep, interaction with family and friends and participation in community events may be more highly prized, and thus require extra financial compensation, as compared to normal “day work” time when many of the worker’s friends and family members are themselves at work or at school. The balance of the transaction can also be changed by making the time spent at work more congenial to the worker, for example, by improving working conditions. The commute to and from work is unavailable to the worker for recreation, so this time too must be considered as “grey time” (Knauth et al. 1983) and therefore a “cost” to the worker. Thus, measures such as compressed workweeks, which reduce the number of commuting trips taken per week, or flexitime, which reduces the commute time by allowing the worker to avoid the rush hour, are again likely to change the balance.
Background Literature
As Kogi (1991) has remarked, there is a general trend in both manufacturing and service industries towards greater flexibility in the temporal programming of work. There are a number of reasons for this trend, including the high cost of capital equipment, consumer demand for around-the-clock service, legislative pressure to reduce the length of the workweek and (in some societies such as the United States and Australia) taxation pressure on the employer to have as few different employees as possible. For many employees, the conventional “9 to 5” or “8 to 4”, Monday through Friday workweek is a thing of the past, either because of new work systems or because of the large amounts of excessive overtime required.
Kogi notes that while the benefits to the employer of such flexibility are quite clear in allowing extended business hours, accommodation of market demand and greater management flexibility, the benefits to the worker may be less certain. Unless the flexible schedule involves elements of choice for workers with respect to their particular hours of work, flexibility can often mean disruptions in their biological clocks and domestic situations. Extended work shifts may also lead to fatigue, compromising safety and productivity, as well as to increased exposure to chemical hazards.
Biological Disruptions due to Abnormal Work Hours
Human biology is specifically oriented towards wakefulness during daylight and sleep at night. Any work schedule which requires late evening or all-night wakefulness as a result of compressed workweeks, mandatory overtime or shiftwork will lead, therefore, to disruptions of the biological clock (Monk and Folkard 1992). These disruptions can be assessed by measuring workers’ “circadian rhythms”, which comprise regular fluctuations over the 24 hours in vital signs, blood and urine composition, mood and performance efficiency over the 24-hour period (Aschoff 1981). The measure used most often in shiftwork studies has been body temperature, which, under normal conditions, shows a clear rhythm with a peak at about 2000 hours, a trough at about 0500 hours and a difference of about 0.7°C. between the two. After an abrupt change in routine, the amplitude (size) of the rhythm diminishes and the phase (timing) of the rhythm is slow to adjust to the new schedule. Until the adjustment process is complete, sleep is disrupted and daytime mood and performance efficiency are impaired. These symptoms can be regarded as the shiftwork equivalent of jet-lag and can be extremely long lasting (Knauth and Rutenfranz 1976).
Abnormal work hours can also lead to poor health. Although it has proved difficult to precisely quantify the exact size of the effect, it appears that, in addition to sleep disorders, gastrointestinal disorders (including peptic ulcers) and cardiovascular disease can be more frequently found in shift workers (and former shift workers) than in day workers (Scott and LaDou 1990). There is also some preliminary evidence for increased incidence of psychiatric symptoms (Cole, Loving and Kripke 1990).
Social Disruptions due to Abnormal Work Hours
Not only human biology, but also human society, opposes those who work abnormal hours. Unlike the nocturnal sleep of the majority, which is carefully protected by strict taboos against loud noise and telephone use at night, the late wakening, day-sleeping and napping that are required by those working abnormal work hours is only grudgingly tolerated by society. Evening and weekend community events can also be denied to these people, leading to feelings of alienation.
It is with the family, however, that the social disruptions of abnormal work hours may be the most devastating. For the worker, the family roles of parent, caregiver, social companion and sexual partner can all be severely compromised by abnormal work hours, leading to marital disharmony and problems with children (Colligan and Rosa 1990). Moreover, the worker’s attempts to rectify, or to avoid, such social problems may result in a decrease in sleep time, thus leading to poor alertness and compromised safety and productivity.
Suggested Solutions
Just as the problems of abnormal work hours are multifaceted, so too must be the solutions to those problems. The primary areas to be addressed should include:
- selection and education of the worker
- selection of the most appropriate work schedule or roster
- improvement of the work environment.
Selection and education of the worker should involve identification and counselling of those persons likely to experience difficulties with abnormal or extended work hours (e.g., older workers and those with high sleep needs, extensive domestic workloads or long commutes). Education in circadian and sleep hygiene principles and family counselling should also be made available (Monk and Folkard 1992). Education is an extremely powerful tool in helping those with abnormal work hours to cope, and in reassuring them about why they may be experiencing problems. Selection of the most appropriate schedule should begin with a decision as to whether abnormal work hours are actually needed at all. For example, night work may in many cases be done better at a different time of day (Knauth and Rutenfranz 1982). Consideration should be also be given to the schedule best suited to the work situation, bearing in mind the nature of the work and the demographics of the workforce. Improvement of the work environment may involve raising illumination levels and providing adequate canteen facilities at night.
Conclusions
The particular pattern of work hours chosen for an employee can represent a significant challenge to his or her biology, domestic situation and role in the community. Informed decisions should be made, incorporating a study of the demands of the work situation and the demographics of the workforce. Any changes in hours of work should be preceded by detailed investigation and consultation with the employees and followed by evaluation studies.
Environmental Design
Overview
In this article, the links between the physical features of the workplace and occupational health are examined. Workplace design is concerned with a variety of physical conditions within work environments that can be objectively observed or recorded and modified through architectural, interior design and site planning interventions. For the purposes of this discussion, occupational health is broadly construed to encompass multiple facets of workers’ physical, mental and social well-being (World Health Organization 1984). Thus, a broad array of health outcomes is examined, including employee satisfaction and morale, work-group cohesion, stress reduction, illness and injury prevention, as well as environmental supports for health promotion at the worksite.
Empirical evidence for the links between workplace design and occupational health is reviewed below. This review, highlighting the health effects of specific design features, must be qualified in certain respects. First, from an ecological perspective, worksites function as complex systems comprised of multiple social and physical environmental conditions, which jointly influence employee well-being (Levi 1992; Moos 1986; Stokols 1992). Thus, the health consequences of environmental conditions are often cumulative and sometimes involve complex mediated and moderated relationships among the sociophysical environment, personal resources and dispositions (Oldham and Fried 1987; Smith 1987; Stellman and Henifin 1983). Moreover, enduring qualities of people-environment transaction, such as the degree to which employees perceive their work situation to be controllable, socially supportive and compatible with their particular needs and abilities, may have a more pervasive influence on occupational health than any single facet of workplace design (Caplan 1983; Karasek and Theorell 1990; Parkes 1989; Repetti 1993; Sauter, Hurrell and Cooper 1989). The research findings reviewed should be interpreted in light of these caveats.
Research Findings
The relationships between worksite design and occupational health can be considered at several levels of analysis, including the:
- physical arrangement of employees’ immediate work area
- ambient environmental qualities of the work area
- physical organization of buildings that comprise a particular workplace
- exterior amenities and site planning of those facilities.
Previous research has focused primarily on the first and second levels, while giving less attention to the third and fourth levels of workplace design.
Physical features of the immediate work area
The immediate work area extends from the core of an employee’s desk or workstation to the physical enclosure or imaginary boundary surrounding his or her work space. Several features of the immediate work area have been found to influence employee well-being. The degree of physical enclosure surrounding one’s desk or workstation, for example, has been shown in several studies to be positively related to the employee’s perception of privacy, satisfaction with the work environment and overall job satisfaction (Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Hedge 1986; Marans and Yan 1989; Oldham 1988; Sundstrom 1986; Wineman 1986). Moreover, “open-plan” (low enclosure) work areas have been linked to more negative social climates in work groups (Moos 1986) and more frequent reports of headaches among employees (Hedge 1986). It is important to note, however, that the potential health effects of workstation enclosure may depend on the type of work being performed (e.g., confidential versus non-confidential, team versus individualized tasks; see Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984), job status (Sundstrom 1986), levels of social density adjacent to one’s work area (Oldham and Fried 1987), and workers’ needs for privacy and stimulation screening (Oldham 1988).
A number of studies have shown that the presence of windows in the employees’ immediate work areas (especially windows that afford views of natural or landscaped settings), exposure to indoor natural elements (e.g., potted plants, pictures of wilderness settings), and opportunities to personalize the decor of one’s office or workstation are associated with higher levels of environmental and job satisfaction and lower levels of stress (Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Goodrich 1986; Kaplan and Kaplan 1989; Steele 1986; Sundstrom 1986). Providing employees with localized controls over acoustic, lighting and ventilation conditions within their work areas has been linked to higher levels of environmental satisfaction and lower levels of stress in some studies (Becker 1990; Hedge 1991; Vischer 1989). Finally, several research programmes have documented the health benefits associated with employees’ use of adjustable, ergonomically sound furniture and equipment; these benefits include reduced rates of eyestrain and of repetitive motion injuries and lower back pain (Dainoff and Dainoff 1986; Grandjean 1987; Smith 1987).
Ambient environmental qualities of the work area
Ambient environmental conditions originate from outside the worker’s immediate work area. These pervasive qualities of the worksite influence the comfort and well-being of employees whose work spaces are located within a common region (e.g., a suite of offices located on one floor of a building). Examples of ambient environmental qualities include levels of noise, speech privacy, social density, illumination and air quality—conditions that are typically present within a particular portion of the worksite. Several studies have documented the adverse health impacts of chronic noise disturbance and low levels of speech privacy in the workplace, including elevated levels of physiological and psychological stress and reduced levels of job satisfaction (Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Canter 1983; Klitzman and Stellman 1989; Stellman and Henifin 1983; Sundstrom 1986; Sutton and Rafaeli 1987). High levels of social density in the immediate vicinity of one’s work area have also been linked with elevated stress levels and reduced job satisfaction (Oldham 1988; Oldham and Fried 1987; Oldham and Rotchford 1983).
Health consequences of office lighting and ventilation systems have been observed as well. In one study, lensed indirect fluorescent uplighting was associated with higher levels of employee satisfaction and reduced eyestrain, in comparison with traditional fluorescent downlighting (Hedge 1991). Positive effects of natural lighting on employees’ satisfaction with the workplace also have been reported (Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Goodrich 1986; Vischer and Mees 1991). In another study, office workers exposed to chilled-air ventilation systems evidenced higher rates of upper-respiratory problems and physical symptoms of “sick building syndrome” than those whose buildings were equipped with natural or mechanical (non-chilled, non-humidified) ventilation systems (Burge et al. 1987; Hedge 1991).
Features of the ambient environment that have been found to enhance the social climate and cohesiveness of work groups include the provision of team-oriented spaces adjacent to individualized offices and workstations (Becker 1990; Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Steele 1986; Stone and Luchetti 1985) and visible symbols of corporate and team identity displayed within lobbies, corridors, conference rooms, lounges and other collectively used areas of the worksite (Becker 1990; Danko, Eshelman and Hedge 1990; Ornstein 1990; Steele 1986).
Overall organization of buildings and facilities
This level of design encompasses the interior physical features of work facilities that extend throughout an entire building, many of which are not immediately experienced within an employee’s own work space or within those adjacent to it. For example, enhancing the structural integrity and fire-resistance of buildings, and designing stairwells, corridors and factories to prevent injuries, are essential strategies for promoting worksite safety and health (Archea and Connell 1986; Danko, Eshelman and Hedge 1990). Building layouts that are consistent with the adjacency needs of closely interacting units within an organization can improve coordination and cohesion among work groups (Becker 1990; Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Sundstrom and Altman 1989). The provision of physical fitness facilities at the worksite has been found to be an effective strategy for enhancing employees’ health practices and stress management (O’Donnell and Harris 1994). Finally, the presence of legible signs and wayfinding aids, attractive lounge and dining areas, and child-care facilities at the worksite have been identified as design strategies that enhance employees’ job satisfaction and stress management (Becker 1990; Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Danko, Eshelman and Hedge 1990; Steele 1986; Stellman and Henifin 1983; Vischer 1989).
Exterior amenities and site planning
Exterior environmental conditions adjacent to the worksite may also carry health consequences. One study reported an association between employees’ access to landscaped, outdoor recreational areas and reduced levels of job stress (Kaplan and Kaplan 1989). Other researchers have suggested that the geographic location and site planning of the worksite can influence the mental and physical well-being of workers to the extent that they afford greater access to parking and public transit, restaurants and retail services, good regional air quality and the avoidance of violent or otherwise unsafe areas in the surrounding neighbourhood (Danko, Eshelman and Hedge 1990; Michelson 1985; Vischer and Mees 1991). However, the health benefits of these design strategies have not yet been evaluated in empirical studies.
Directions for Future Research
Prior studies of environmental design and occupational health reflect certain limitations and suggest several issues for future investigation. First, earlier research has emphasized the health effects of specific design features (e.g., workstation enclosure, furnishings, lighting systems), while neglecting the joint influence of physical, interpersonal and organizational factors on well-being. Yet the health benefits of improved environmental design may be moderated by the social climate and organizational qualities (as moderated, for example, by a participative versus non-participative structure) of the workplace (Becker 1990; Parkes 1989; Klitzman and Stellman 1989; Sommer 1983; Steele 1986). The interactive links between physical design features, employee characteristics, social conditions at work and occupational health, therefore, warrant greater attention in subsequent studies (Levi 1992; Moos 1986; Stokols 1992). At the same time, an important challenge for future research is to clarify the operational definitions of particular design features (e.g., the “open plan” office), which have varied widely in earlier studies (Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Marans and Yan 1989; Wineman 1986).
Secondly, employee characteristics such as job status, gender and dispositional styles have been found to mediate the health consequences of worksite design (Burge et al. 1987; Oldham 1988; Hedge 1986; Sundstrom 1986). Yet, it is often difficult to disentangle the separate effects of environmental features and individual differences (these differences may have to do with, for example, workstation enclosures, comfortable furnishings, and job status) because of ecological correlations among these variables (Klitzman and Stellman 1989). Future studies should incorporate experimental techniques and sampling strategies that permit an assessment of the main and interactive effects of personal and environmental factors on occupational health. Moreover, specialized design and ergonomic criteria to enhance the health of diverse and vulnerable employee groups (e.g., disabled, elderly and single-parent female workers) remain to be developed in future research (Michelson 1985; Ornstein 1990; Steinfeld 1986).
Thirdly, prior research on the health outcomes of worksite design has relied heavily on survey methods to assess employees’ perceptions of both their work environments and health status, placing certain constraints (for example, “common method variance”) on the interpretation of data (Klitzman and Stellman 1989; Oldham and Rotchford 1983). Furthermore, the majority of these studies have used cross-sectional rather than longitudinal research designs, the latter incorporating comparative assessments of intervention and control groups. Future studies should emphasize both field-experimental research designs and multi-method strategies that combine survey techniques with more objective observations and recordings of environmental conditions, medical exams and physiological measures.
Finally, the health consequences of building organization, exterior amenities and site-planning decisions have received considerably less attention in prior studies than those associated with the more immediate, ambient qualities of employees’ work areas. The health relevance of both proximal and remote aspects of workplace design should be examined more closely in future research.
Role of Workplace Design in Illness Prevention and Health Promotion
Several environmental design resources and their potential health benefits are summarized in table 1, based on the preceding review of research findings. These resources are grouped according to the four levels of design noted above and emphasize physical features of work settings that have been empirically linked to improved mental, physical and social health outcomes (especially those found at levels 1 and 2), or have been identified as theoretically plausible leverage points for enhancing employee well-being (e.g., several of the features subsumed under levels 3 and 4).
Table 1. Workplace design resources and potential health benefits
| Levels of environmental design | Environmental design features of the workplace | Emotional, social and physical health outcomes |
| Immediate work area | Physical enclosure of the work area Adjustable furniture and equipment Localized controls of acoustics, lighting and ventilation Natural elements and personalized decor Presence of windows in work area |
Enhanced privacy and job satisfaction Reduced eyestrain and repetitive-strain and lower-back injuries Enhanced comfort and stress reduction Enhanced sense of identity and involvement at the workplace Job satisfaction and stress reduction |
| Ambient qualities of the work area |
Speech privacy and noise control Comfortable levels of social density Good mix of private and team spaces Symbols of corporate and team identity Natural, task, and lensed indirect lighting Natural ventilation vs. chilled-air systems |
Lower physiological, emotional stress Lower physiological, emotional stress Improved social climate, cohesion Improved social climate, cohesion Reduced eyestrain, enhanced satisfaction Lower rates of respiratory problems |
| Building organization | Adjacencies among interacting units Legible signage and wayfinding aids Injury-resistant architecture Attractive lounge and food areas onsite Availability of worksite child care Physical fitness facilities onsite |
Enhanced coordination and cohesion Reduced confusion and distress Lower rates of unintentional injuries Enhanced satisfaction with job, worksite Employee convenience, stress reduction Improved health practices, lower stress |
| Exterior amenities and site planning |
Availability of outside recreation areas Access to parking and public transit Proximity to restaurants and stores Good air quality in surrounding area Low levels of neighbourhood violence |
Enhanced cohesion, stress reduction Employee convenience, stress reduction Employee convenience, stress reduction Improved respiratory health Reduced rates of intentional injuries |
The incorporation of these resources into the design of work environments should, ideally, be combined with organizational and facilities management policies that maximize the health- promoting qualities of the workplace. These corporate policies include:
- the designation of worksites as “smoke-free” (Fielding and Phenow 1988)
- the specification and use of non-toxic, ergonomically sound furnishings and equipment (Danko, Eshelman and Hedge 1990)
- managerial support for employees’ personalization of their workspace (Becker 1990; Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Sommer 1983; Steele 1986)
- job designs that prevent health problems linked with computer-based work and repetitive tasks (Hackman and Oldham 1980; Sauter, Hurrell and Cooper 1989; Smith and Sainfort 1989)
- the provision of employee training programmes in the areas of ergonomics and occupational safety and health (Levy and Wegman 1988)
- incentive programmes to encourage employees’ use of physical fitness facilities and compliance with injury prevention protocols (O’Donnell and Harris 1994)
- flexitime, telecommuting, job-sharing and ride-sharing programmes to enhance workers’ effectiveness in residential and corporate settings (Michelson 1985; Ornstein 1990; Parkes 1989; Stokols and Novaco 1981)
- the involvement of employees in the planning of worksite relocations, renovations and related organizational developments (Becker 1990; Brill, Margulis and Konar 1984; Danko, Eshelman and Hedge 1990; Miller and Monge 1986; Sommer 1983; Steele 1986; Stokols et al. 1990).
Organizational efforts to enhance employee well-being are likely to be more effective to the extent that they combine complementary strategies of environmental design and facilities management, rather than relying exclusively on either one of these approaches.
Ergonomic Factors
The purpose of this article is to afford the reader an understanding of how ergonomic conditions can affect the psychosocial aspects of working, employee satisfaction with the work environment, and employee health and well-being. The major thesis is that, with respect to physical surroundings, job demands and technological factors, improper design of the work environment and job activities can cause adverse employee perceptions, psychological stress and health problems (Smith and Sainfort 1989; Cooper and Marshall 1976).
Industrial ergonomics is the science of fitting the work environment and job activities to the capabilities, dimensions and needs of people. Ergonomics deals with the physical work environment, tools and technology design, workstation design, job demands and physiological and biomechanical loading on the body. Its goal is to increase the degree of fit among the employees, the environments in which they work, their tools and their job demands. When the fit is poor, stress and health problems can occur. The many relationships between the demands of the job and psychological distress are discussed elsewhere in this chapter as well as in Smith and Sainfort (1989), in which a definition is given of the balance theory of job stress and job design. Balance is the use of different aspects of job design to counteract job stressors. The concept of job balance is important in the examination of ergonomic considerations and health. For instance, the discomforts and disorders produced by poor ergonomic conditions can make an individual more susceptible to job stress and psychological disorders, or can intensify the somatic effects of job stress.
As spelled out by Smith and Sainfort (1989), there are various sources of job stress, including
- job demands such as high workload and work pace
- poor job content factors that produce boredom and lack of meaningfulness
- limited job control or decision latitude
- organizational policies and procedures that alienate the workforce
- supervisory style affecting participation and socialization
- environmental contamination
- technology factors
- ergonomic conditions.
Smith (1987) and Cooper and Marshall (1976) discuss the characteristics of the workplace that can cause psychological stress. These include improper workload, heavy work pressure, hostile environment, role ambiguity, lack of challenging tasks, cognitive overload, poor supervisory relations, lack of task control or decision-making authority, poor relationship with other employees and lack of social support from supervisors, fellow employees and family.
Adverse ergonomic characteristics of work can cause visual, muscular and psychological disturbances such as visual fatigue, eye strain, sore eyes, headaches, fatigue, muscle soreness, cumulative trauma disorders, back disorders, psychological tension, anxiety and depression. Sometimes these effects are temporary and may disappear when the individual is removed from work or given an opportunity to rest at work, or when the design of the work environment is improved. When exposure to poor ergonomic conditions is chronic, then the effects can become permanent. Visual and muscular disturbances, and aches and pains can induce anxiety in employees. The result may be psychological stress or an exacerbation of the stress effects of other adverse working conditions that cause stress. Visual and musculoskeletal disorders that lead to a loss of function and disability can lead to anxiety, depression, anger and melancholy. There is a synergistic relationship among the disorders caused by ergonomic misfit, so that a circular effect is created in which visual or muscular discomfort generates more psychological stress, which then leads to a greater sensitivity in pain perception in the eyes and muscles, which leads to more stress and so on.
Smith and Sainfort (1989) have defined five elements of the work system that are significant in the design of work that relate to the causes and control of stress. These are: (1) the person; (2) the physical work environment; (3) tasks; (4) technology; and (5) work organization. All but the person are discussed.
Physical Work Environment
The physical work environment produces sensory demands which affect an employee’s ability to see, hear and touch properly, and includes such features as air quality, temperature and humidity. In addition, noise is one of the most prominent of the ergonomic conditions that produce stress (Cohen and Spacapan 1983). When physical working conditions produce a “poor fit” with employees’ needs and capabilities, generalized fatigue, sensory fatigue and performance frustration are the result. Such conditions can lead to psychological stress (Grandjean 1968).
Technology and Workstation Factors
Various aspects of technology have proved troublesome for employees, including incompatible controls and displays, poor response characteristics of controls, displays with poor sensory sensitivity, difficulty in operating characteristics of the technology, equipment that impairs employee performance and equipment breakdowns (Sanders and McCormick 1993; Smith et al. 1992a). Research has shown that employees with such problems report more physical and psychological stress (Smith and Sainfort 1989; Sauter, Dainoff and Smith 1990).
Tasks
Two very critical ergonomic task factors that have been tied to job stress are heavy workloads and work pressure (Cooper and Smith 1985). Too much or too little work produces stress, as does unwanted overtime work. When employees must work under time pressure, for example, to meet deadlines or when the workload is unrelentingly high, then stress is also high. Other critical task factors that have been tied to stress are machine pacing of the work process, a lack of cognitive content of the job tasks and low task control. From an ergonomic perspective, workloads should be established using scientific methods of time and motion evaluation (ILO 1986), and not be set by other criteria such as economic need to recover capital investment or by the capacity of the technology.
Organizational Factors
Three ergonomic aspects of the management of the work process have been identified as conditions that can lead to employee psychological stress. These are shift work, machine-paced work or assembly-line work, and unwanted overtime (Smith 1987). Shift work has been shown to disrupt biological rhythms and basic physiological functioning (Tepas and Monk 1987; Monk and Tepas 1985). Machine-paced work or assembly-line work that produces short-cycle tasks with little cognitive content and low employee control over the process leads to stress (Sauter, Hurrell and Cooper 1989). Unwanted overtime can lead to employee fatigue and to adverse psychological reactions such as anger and mood disturbances (Smith 1987). Machine-paced work, unwanted overtime and perceived lack of control over work activities have also been linked to mass psychogenic illness (Colligan 1985).
Autonomy and Control
Autonomy and job control are concepts with a long history in the study of work and health. Autonomy—the extent to which workers can exercise discretion in how they perform their work—is most closely associated with theories that are concerned with the challenge of designing work so that it is intrinsically motivating, satisfying and conducive to physical and mental well-being. In virtually all such theories, the concept of autonomy plays a central role. The term control (defined below) is generally understood to have a broader meaning than autonomy. In fact, one could consider autonomy to be a specialized form of the more general concept of control. Because control is the more inclusive term, it will be used throughout the remainder of this article.
Throughout the 1980s, the concept of control formed the core of perhaps the most influential theory of occupational stress (see, for example, the review of the work stress literature by Ganster and Schaubroeck 1991b). This theory, usually known as the Job Decision Latitude Model (Karasek 1979) stimulated many large-scale epidemiological studies that investigated the joint effects of control in conjunction with a variety of demanding work conditions on worker health. Though there has been some controversy regarding the exact way that control might help determine health outcomes, epidemiologists and organizational psychologists have come to regard control as a critical variable that should be given serious consideration in any investigation of psychosocial work stress conditions. Concern for the possible detrimental effects of low worker control was so high, for example, that in 1987 the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) of the United States organized a special workshop of authorities from epidemiology, psychophysiology, and industrial and organizational psychology to critically review the evidence concerning the impact of control on worker health and well-being. This workshop eventually culminated in the comprehensive volume Job Control and Worker Health (Sauter, Hurrell and Cooper 1989) that provides a discussion of the global research efforts on control. Such widespread acknowledgement of the role of control in worker well-being also had an impact on governmental policy, with the Swedish Work Environment Act (Ministry of Labour 1987) stating that “the aim must be for work to be arranged in such a way so that the employee himself can influence his work situation”. In the remainder of this article I summarize the research evidence on work control with the goal of providing the occupational health and safety specialist with the following:
- a discussion of aspects of worker control that might be important
- guidelines about how to assess job control in the worksite
- ideas on how to intervene so as to reduce the deleterious effects of low worker control.
First, what exactly is meant by the term control? In its broadest sense it refers to workers’ ability to actually influence what happens in their work environment. Moreover, this ability to influence the work setting should be considered in light of the worker’s goals. The term refers to the ability to influence matters that are relevant to one’s personal goals. This emphasis on being able to influence the work environment distinguishes control from the related concept of predictability. The latter refers to one’s being able to anticipate what demands will be made on oneself, for example, but does not imply any ability to alter those demands. Lack of predictability constitutes a source of stress in its own right, particularly when it produces a high level of ambiguity about what performance strategies one ought to adopt to perform effectively or if one even has a secure future with the employer. Another distinction that should be made is that between control and the more inclusive concept of job complexity. Early conceptualizations of control considered it together with such aspects of work as skill level and availability of social interaction. Our discussion here discriminates control from these other domains of job complexity.
One can consider mechanisms by which workers can exercise control and the domains over which that control can apply. One way that workers can exercise control is by making decisions as individuals. These decisions can be about what tasks to complete, the order of those tasks, and the standards and processes to follow in completing those tasks, to name but a few. The worker might also have some collective control either through representation or by social action with co-workers. In terms of domains, control might apply to such matters as the work pace, the amount and timing of interaction with others, the physical work environment (lighting, noise and privacy), scheduling of vacations or even matters of policy at the worksite. Finally, one can distinguish between objective and subjective control. One might, for example, have the ability to choose one’s work pace but not be aware of it. Similarly, one might believe that one can influence policies in the workplace even though this influence is essentially nil.
How can the occupational health and safety specialist assess the level of control in a work situation? As recorded in the literature, basically two approaches have been taken. One approach has been to make an occupational-level determination of control. In this case every worker in a given occupation would be considered to have the same level of control, as it is assumed to be determined by the nature of the occupation itself. The disadvantage to this approach, of course, is that one cannot obtain much insight as to how workers are faring in a particular worksite, where their control might have been determined as much by their employer’s policies and practices as by their occupational status. The more common approach is to survey workers about their subjective perceptions of control. A number of psychometrically sound measures have been developed for this purpose and are readily available. The NIOSH control scale (McLaney and Hurrell 1988), for example, consists of sixteen questions and provides assessments of control in the domains of task, decision, resources and physical environment. Such scales can easily be incorporated into an assessment of worker safety and health concerns.
Is control a significant determinant of worker safety and health? This question has driven many large-scale research efforts since at least 1985. Since most of these studies have consisted of non- experimental field surveys in which control was not purposely manipulated, the evidence can only show a systematic correlation between control and health and safety outcome variables. The lack of experimental evidence prevents us from making direct causal assertions, but the correlational evidence is quite consistent in showing that workers with lower levels of control suffer more from mental and physical health complaints. The evidence is strongly suggestive, then, that increasing worker control constitutes a viable strategy for improving the health and welfare of workers. A more controversial question is whether control interacts with other sources of psychosocial stress to determine health outcomes. That is, will high control levels counteract the deleterious effects of other job demands? This is an intriguing question, for, if true, it suggests that the ill effects of high workloads, for example, can be negated by increasing worker control with no corresponding need to lower workload demands. The evidence is clearly mixed on this question, however. About as many investigators have reported such interaction effects as have not. Thus, control should not be considered a panacea that will cure the problems brought on by other psychosocial stressors.
Work by organizational researchers suggests that increasing worker control can significantly improve health and well-being. Moreover, it is relatively easy to make a diagnosis of low worker control through the use of brief survey measures. How can the health and safety specialist intervene, then, to increase worker control levels? As there are many domains of control, there are many ways to increase workplace control. These range from providing opportunities for workers to participate in decisions that affect them to the fundamental redesign of jobs. What is clearly important is that control domains be targeted that are relevant to the primary goals of the workers and that fit the situational demands. These domains can probably best be determined by involving workers in joint diagnosis and problem-solving sessions. It should be noted, however, that the kinds of changes in the workplace that in many cases are necessary to achieve real gains in control involve fundamental changes in management systems and policies. Increasing control might be as simple as providing a switch that allows machine-paced workers to control their pace, but it is just as likely to involve important changes in the decision-making authority of workers. Thus, organizational decision makers must usually be full and active supporters of control enhancing interventions.
More...
Work Pacing
In this article, the reasons machine-pacing is utilized in the workplace are reviewed. Furthermore, a classification of machine-paced work, information on the impact of machine-paced work on well-being and methodologies by which the effects can be alleviated or reduced, are set forth.
Benefits of Machine-Paced Work
The effective utilization of machine-paced work has the following benefits for an organization:
- It increases customer satisfaction: for example, it provides speedier service in drive-in restaurants when a number of stations are assigned to serve the customers sequentially.
- It reduces overhead cost through economic use of high technology, reduction of stock set aside for processing, reduction in factory floor space and reduction in supervisory costs.
- It reduces direct costs through reduced training time, lower hourly wages and high production return per unit of wages.
- It contributes to national productivity through provision of employment for unskilled workers and reduction in the production costs of goods and services.
Classification of Machine-Paced Work
A classification of paced work is provided in figure 1.
Figure 1. The Job Stress Model of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
Effect of Machine-Paced Work on Well-Being
Machine-paced research has been carried out in laboratory settings, in industry (by case studies and controlled experiments) and by epidemiological studies (Salvendy 1981).
An analysis was performed of 85 studies dealing with machine-paced and self-paced work, of which 48% were laboratory studies, 30% industrial, 14% review studies, 4% combined laboratory and industrial, and 4% conceptual studies (Burke and Salvendy 1981). Of the 103 variables used in these studies, 41% were physiological, 32% were performance variables and 27% psychological. From this analysis, the following practical implications were derived for the use of machine-paced versus self-paced work arrangements :
- Tasks with high cognitive or perceptual load should be administered under self-paced as opposed to machine-paced conditions.
- To reduce error and low productivity, jobs should be allocated according to the worker’s personality and capacities.
- Intelligent, shrewd, creative and self-sufficient operators prefer to work on self-paced rather than machine-paced tasks. (See table 1 for more complete psychological profiles.)
- Workers should be encouraged to select a workload capacity which is optimum for them in any given situation.
- To maintain a high activation level (or the required level for performing the task), the work sessions should be interrupted by rest periods or by other types of work. This type of break should be implemented before the onset of deactivation.
- Maximal work speeds are not economical and can result in workers’ becoming overstrained when they continue to work excessively fast for a long time. On the other hand, too low a speed may also be detrimental to workers’ performance.
In studying industrial workers for an entire year in our experimentally controlled situation, in which over 50 million data points were collected, it was shown that 45% of the labour force prefers self-paced work, 45% prefers machine-paced work, and 10% does not like work of any type (Salvendy1976).
Table 1. Psychological profiles of operators who prefer self-paced and machine-paced work
|
Machine-paced work |
Self-paced work |
|
Less intelligent |
More intelligent |
|
Humble |
Assertive |
|
Practical |
Imaginative |
|
Forthright |
Shrewd |
|
Group-dependent |
Self-sufficient |
Uncertainty is the most significant contributor to stress and can be effectively managed by performance feedback (see figure 2) (Salvendy and Knight 1983).
Figure 2. Effects of performance feedback on reduction of stress
Electronic Work Monitoring
The computerization of work has made possible the development of a new approach to work monitoring called electronic performance monitoring (EPM). EPM has been defined as the “computerized collection, storage, analysis, and reporting of information about employees’ activities on a continuous basis” (USOTA 1987). Although banned in many European countries, electronic performance monitoring is increasing throughout the world on account of intense competitive pressures to improve productivity in a global economy.
EPM has changed the psychosocial work environment. This application of computer technology has significant implications for work supervision, workload demands, performance appraisal, performance feedback, rewards, fairness and privacy. As a result, occupational health researchers, worker representatives, government agencies and the public news media have expressed concern about the stress-health effects of electronic performance monitoring (USOTA 1987).
Traditional approaches to work monitoring include direct observation of work behaviours, examination of work samples, review of progress reports and analysis of performance measures (Larson and Callahan 1990). Historically, employers have always attempted to improve on these methods of monitoring worker performance. Considered as part of a continuing monitoring effort across the years, then, EPM is not a new development. What is new, however, is the use of EPM, particularly in office and service work, to capture employee performance on a second-by-second, keystroke-by-keystroke basis so that work management in the form of corrective action, performance feedback, delivery of incentive pay, or disciplinary measures can be taken at any time (Smith 1988). In effect, the human supervisor is being replaced by an electronic supervisor.
EPM is used in office work such as word processing and data entry to monitor keystroke production and error rates. Airline reservation clerks and directory assistance operators are monitored by computers to determine how long it takes to service customers and to measure the time interval between calls. EPM also is used in more traditional economic sectors. Freight haulers, for example, are using computers to monitor driver speed and fuel consumption, and tire manufacturers are electronically monitoring the productivity of rubber workers. In sum, EPM is used to establish performance standards, track employee performance, compare actual performance with predetermined standards and administer incentive pay programmes based on these standards (USOTA 1987).
Advocates of EPM assert that continuous electronic work monitoring is essential to high performance and productivity in the contemporary workplace. It is argued that EPM enables managers and supervisors to organize and control human, material and financial resources. Specifically, EPM provides for:
- increased control over performance variability
- increased objectivity and timeliness of performance evaluation and feedback
- efficient management of large office and customer service operations through the electronic supervision of work, and
- establishment and enforcement of performance standards (for example, number of forms processed per hour).
Supporters of electronic monitoring also claim that, from the worker’s perspective, there are several benefits. Electronic monitoring, for example, can provide regular feedback of work performance, which enables workers to take corrective action when necessary. It also satisfies the worker’s need for self-evaluation and reduces performance uncertainty.
Despite the possible benefits of EPM, there is concern that certain monitoring practices are abusive and constitute an invasion of employee privacy (USOTA 1987). Privacy has become an issue particularly when workers do not know when or how often they are being monitored. Since work organizations often do not share performance data with workers, a related privacy issue is whether workers should have access to their own performance records or the right to question possible wrong information.
Workers also have raised objections to the manner in which monitoring systems have been implemented (Smith, Carayon and Miezio 1986; Westin 1986). In some workplaces, monitoring is perceived as an unfair labour practice when it is used to measure individual, as opposed to group, performance. In particular, workers have taken exception to the use of monitoring to enforce compliance with performance standards that impose excessive workload demands. Electronic monitoring also can make the work process more impersonal by replacing a human supervisor with an electronic supervisor. In addition, the overemphasis on increased production may encourage workers to compete instead of cooperate with one another.
Various theoretical paradigms have been postulated to account for the possible stress-health effects of EPM (Amick and Smith 1992; Schleifer and Shell 1992; Smith et al. 1992b). A fundamental assumption made by many of these models is that EPM indirectly influences stress-health outcomes by intensifying workload demands, diminishing job control and reducing social support. In effect, EPM mediates changes in the psychosocial work environment that result in an imbalance between the demands of the job and the worker’s resources to adapt.
The impact of EPM on the psychosocial work environment is felt at three levels of the work system: the organization-technology interface, the job-technology interface and the human-technology interface (Amick and Smith 1992). The extent of work system transformation and the subsequent implications for stress outcomes are contingent upon the inherent characteristics of the EPM process; that is, the type of information gathered, the method of gathering the information and the use of the information (Carayon 1993). These EPM characteristics can interact with various job design factors and increase stress-health risks.
An alternative theoretical perspective views EPM as a stressor that directly results in strain independent of other job-design stress factors (Smith et al. 1992b; Carayon 1994). EPM, for example, can generate fear and tension as a result of workers being constantly watched by “Big Brother”. EPM also may be perceived by workers as an invasion of privacy that is highly threatening.
With respect to the stress effects of EPM, empirical evidence obtained from controlled laboratory experiments indicates that EPM can produce mood disturbances (Aiello and Shao 1993; Schleifer, Galinsky and Pan 1995) and hyperventilatory stress reactions (Schleifer and Ley 1994). Field studies have also reported that EPM alters job-design stress factors (for example, workload), which, in turn, generate tension or anxiety together with depression (Smith, Carayon and Miezio 1986; Ditecco et al. 1992; Smith et al. 1992b; Carayon 1994). In addition, EPM is associated with symptoms of musculoskeletal discomfort among telecommunication workers and data-entry office workers (Smith et al. 1992b; Sauter et al. 1993; Schleifer, Galinsky and Pan 1995).
The use of EPM to enforce compliance with performance standards is perhaps one of the most stressful aspects of this approach to work monitoring (Schleifer and Shell 1992). Under these conditions, it may be useful to adjust performance standards with a stress allowance (Schleifer and Shell 1992): a stress allowance would be applied to the normal cycle time, as is the case with other more conventional work allowances such as rest breaks and machine delays. Particularly among workers who have difficulty meeting EPM performance standards, a stress allowance would optimize workload demands and promote well-being by balancing the productivity benefits of electronic performance monitoring against the stress effects of this approach to work monitoring.
Beyond the question of how to minimize or prevent the possible stress-health effects of EPM, a more fundamental issue is whether this “Tayloristic” approach to work monitoring has any utility in the modern workplace. Work organizations are increasingly utilizing sociotechnical work-design methods, “total quality management” practices, participative work groups, and organizational, as opposed to individual, measures of performance. As a result, electronic work monitoring of individual workers on a continuous basis may have no place in high-performance work systems. In this regard, it is interesting to note that those countries (for example, Sweden and Germany) that have banned EPM are the same countries which have most readily embraced the principles and practices associated with high-performance work systems.
Role Clarity and Role Overload
Roles represent sets of behaviours that are expected of employees. To understand how organizational roles develop, it is particularly informative to see the process through the eyes of a new employee. Starting with the first day on the job, a new employee is presented with considerable information designed to communicate the organization’s role expectations. Some of this information is presented formally through a written job description and regular communications with one’s supervisor. Hackman (1992), however, states that workers also receive a variety of informal communications (termed discretionary stimuli) designed to shape their organizational roles. For example, a junior school faculty member who is too vocal during a departmental meeting may receive looks of disapproval from more senior colleagues. Such looks are subtle, but communicate much about what is expected of a junior colleague.
Ideally, the process of defining each employee’s role should proceed such that each employee is clear about his or her role. Unfortunately, this is often not the case and employees experience a lack of role clarity or, as it is commonly called, role ambiguity. According to Breaugh and Colihan (1994), employees are often unclear about how to do their jobs, when certain tasks should be performed and the criteria by which their performance will be judged. In some cases, it is simply difficult to provide an employee with a crystal-clear picture of his or her role. For example, when a job is relatively new, it is still “evolving” within the organization. Furthermore, in many jobs the individual employee has tremendous flexibility regarding how to get the job done. This is particularly true of highly complex jobs. In many other cases, however, role ambiguity is simply due to poor communication between either supervisors and subordinates or among members of work groups.
Another problem that can arise when role-related information is communicated to employees is role overload. That is, the role consists of too many responsibilities for an employee to handle in a reasonable amount of time. Role overload can occur for a number of reasons. In some occupations, role overload is the norm. For example, physicians in training experience tremendous role overload, largely as preparation for the demands of medical practice. In other cases, it is due to temporary circumstances. For example, if someone leaves an organization, the roles of other employees may need to be temporarily expanded to make up for the missing worker’s absence. In other instances, organizations may not anticipate the demands of the roles they create, or the nature of an employee’s role may change over time. Finally, it is also possible that an employee may voluntarily take on too many role responsibilities.
What are the consequences to workers in circumstances characterized by either role ambiguity, role overload or role clarity? Years of research on role ambiguity has shown that it is a noxious state which is associated with negative psychological, physical and behavioural outcomes (Jackson and Schuler 1985). That is, workers who perceive role ambiguity in their jobs tend to be dissatisfied with their work, anxious, tense, report high numbers of somatic complaints, tend to be absent from work and may leave their jobs. The most common correlates of role overload tend to be physical and emotional exhaustion. In addition, epidemiological research has shown that overloaded individuals (as measured by work hours) may be at greater risk for coronary heart disease. In considering the effects of both role ambiguity and role overload, it must be kept in mind that most studies are cross-sectional (measuring role stressors and outcomes at one point in time) and have examined self-reported outcomes. Thus, inferences about causality must be somewhat tentative.
Given the negative effects of role ambiguity and role overload, it is important for organizations to minimize, if not eliminate, these stressors. Since role ambiguity, in many cases, is due to poor communication, it is necessary to take steps to communicate role requirements more effectively. French and Bell (1990), in a book entitled Organization Development, describe interventions such as responsibility charting, role analysis and role negotiation. (For a recent example of the application of responsibility charting, see Schaubroeck et al. 1993). Each of these is designed to make employees’ role requirements explicit and well defined. In addition, these interventions allow employees input into the process of defining their roles.
When role requirements are made explicit, it may also be revealed that role responsibilities are not equitably distributed among employees. Thus, the previously mentioned interventions may also prevent role overload. In addition, organizations should keep up to date regarding individuals’ role responsibilities by reviewing job descriptions and carrying out job analyses (Levine 1983). It may also help to encourage employees to be realistic about the number of role responsibilities they can handle. In some cases, employees who are under pressure to take on too much may need to be more assertive when negotiating role responsibilities.
As a final comment, it must be remembered that role ambiguity and role overload are subjective states. Thus, efforts to reduce these stressors must consider individual differences. Some workers may in fact enjoy the challenge of these stressors. Others, however, may find them aversive. If this is the case, organizations have a moral, legal and financial interest in keeping these stressors at manageable levels.
Sexual Harassment
Historically, the sexual harassment of female workers has been ignored, denied, made to seem trivial, condoned and even implicitly supported, with women themselves being blamed for it (MacKinnon 1978). Its victims are almost entirely women, and it has been a problem since females first sold their labour outside the home.
Although sexual harassment also exists outside the workplace, here it will be taken to denote harassment in the workplace.
Sexual harassment is not an innocent flirtation nor the mutual expression of attraction between men and women. Rather, sexual harassment is a workplace stressor that poses a threat to a woman’s psychological and physical integrity and security, in a context in which she has little control because of the risk of retaliation and the fear of losing her livelihood. Like other workplace stressors, sexual harassment may have adverse health consequences for women that can be serious and, as such, qualifies as a workplace health and safety issue (Bernstein 1994).
In the United States, sexual harassment is viewed primarily as a discrete case of wrongful conduct to which one may appropriately respond with blame and recourse to legal measures for the individual. In the European Community it tends to be viewed rather as a collective health and safety issue (Bernstein 1994).
Because the manifestations of sexual harassment vary, people may not agree on its defining qualities, even where it has been set forth in law. Still, there are some common features of harassment that are generally accepted by those doing work in this area:
- Sexual harassment may involve verbal or physical sexual behaviours directed at a specific woman (quid pro quo), or it may involve more general behaviours that create a “hostile environment” that is degrading, humiliating and intimidating towards women (MacKinnon 1978).
- It is unwelcome and unwanted.
- It can vary in severity.
When directed towards a specific woman it can involve sexual comments and seductive behaviours, “propositions” and pressure for dates, touching, sexual coercion through the use of threats or bribery and even physical assault and rape. In the case of a “hostile environment”, which is probably the more common state of affairs, it can involve jokes, taunts and other sexually charged comments that are threatening and demeaning to women; pornographic or sexually explicit posters; and crude sexual gestures, and so forth. One can add to these characteristics what is sometimes called “gender harassment”, which more involves sexist remarks that demean the dignity of women.
Women themselves may not label unwanted sexual attention or sexual remarks as harassing because they accept it as “normal” on the part of males (Gutek 1985). In general, women (especially if they have been harassed) are more likely to identify a situation as sexual harassment than men, who tend rather to make light of the situation, to disbelieve the woman in question or to blame her for “causing” the harassment (Fitzgerald and Ormerod 1993). People also are more likely to label incidents involving supervisors as sexually harassing than similar behaviour by peers (Fitzgerald and Ormerod 1993). This tendency reveals the significance of the differential power relationship between the harasser and the female employee (MacKinnon 1978.) As an example, a comment that a male supervisor may believe is complimentary may still be threatening to his female employee, who may fear that it will lead to pressure for sexual favours and that there will be retaliation for a negative response, including the potential loss of her job or negative evaluations.
Even when co-workers are involved, sexual harassment can be difficult for women to control and can be very stressful for them. This situation can occur where there are many more men than women in a work group, a hostile work environment is created and the supervisor is male (Gutek 1985; Fitzgerald and Ormerod 1993).
National data on sexual harassment are not collected, and it is difficult to obtain accurate numbers on its prevalence. In the United States, it has been estimated that 50% of all women will experience some form of sexual harassment during their working lives (Fitzgerald and Ormerod 1993). These numbers are consistent with surveys conducted in Europe (Bustelo 1992), although there is variation from country to country (Kauppinen-Toropainen and Gruber 1993). The extent of sexual harassment is also difficult to determine because women may not label it accurately and because of underreporting. Women may fear that they will be blamed, humiliated and not believed, that nothing will be done and that reporting problems will result in retaliation (Fitzgerald and Ormerod 1993). Instead, they may try to live with the situation or leave their jobs and risk serious financial hardship, a disruption of their work histories and problems with references (Koss et al. 1994).
Sexual harassment reduces job satisfaction and increases turnover, so that it has costs for the employer (Gutek 1985; Fitzgerald and Ormerod 1993; Kauppinen-Toropainen and Gruber 1993). Like other workplace stressors, it also can have negative effects on health that are sometimes quite serious. When the harassment is severe, as with rape or attempted rape, women are seriously traumatized. Even where sexual harassment is less severe, women can have psychological problems: they may become fearful, guilty and ashamed, depressed, nervous and less self-confident. They may have physical symptoms such as stomach-aches, headaches or nausea. They may have behavioural problems such as sleeplessness, over- or undereating, sexual problems and difficulties in their relations with others (Swanson et al. 1997).
Both the formal American and informal European approaches to combating harassment provide illustrative lessons (Bernstein 1994). In Europe, sexual harassment is sometimes dealt with by conflict resolution approaches that bring in third parties to help eliminate the harassment (e.g., England’s “challenge technique”). In the United States, sexual harassment is a legal wrong that provides victims with redress through the courts, although success is difficult to achieve. Victims of harassment also need to be supported through counselling, where needed, and helped to understand that they are not to blame for the harassment.
Prevention is the key to combating sexual harassment. Guidelines encouraging prevention have been promulgated through the European Commission Code of Practice (Rubenstein and DeVries 1993). They include the following: clear anti-harassment policies that are effectively communicated; special training and education for managers and supervisors; a designated ombudsperson to deal with complaints; formal grievance procedures and alternatives to them; and disciplinary treatment of those who violate the policies. Bernstein (1994) has suggested that mandated self-regulation may be a viable approach.
Finally, sexual harassment needs to be openly discussed as a workplace issue of legitimate concern to women and men. Trade unions have a critical role to play in helping place this issue on the public agenda. Ultimately, an end to sexual harassment requires that men and women reach social and economic equality and full integration in all occupations and workplaces.
" DISCLAIMER: The ILO does not take responsibility for content presented on this web portal that is presented in any language other than English, which is the language used for the initial production and peer-review of original content. Certain statistics have not been updated since the production of the 4th edition of the Encyclopaedia (1998)."