The basic structure of pulp and paper sheets is a felted mat of cellulose fibres held together by hydrogen bonds. Cellulose is a polysaccharide with 600 to 1,500 repeated sugar units. The fibres have high tensile strength, will absorb the additives used to modify pulp into paper and board products, and are supple, chemically stable and white. The purpose of pulping is to separate cellulose fibres from the other components of the fibre source. In the case of wood, these include hemicelluloses (with 15 to 90 repeated sugar units), lignins (highly polymerized and complex, mainly phenyl propane units; they act as the “glue” that cements the fibres together), extractives (fats, waxes, alcohols, phenols, aromatic acids, essential oils, oleoresins, stearols, alkaloids and pigments), and minerals and other inorganics. As shown in table 1, the relative proportions of these components vary according to the fibre source.
Table 1. Chemical constituents of pulp and paper fibre sources (%)
|
Softwoods |
Hardwoods |
Straw |
Bamboo |
Cotton |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
|||||
|
a-cellulose |
38–46 |
38–49 |
28–42 |
26–43 |
80–85 |
|
Hemicellulose |
23–31 |
20–40 |
23–38 |
15–26 |
nd |
|
Lignin |
22–34 |
16–30 |
12–21 |
20–32 |
nd |
|
Extractives |
1–5 |
2–8 |
1–2 |
0.2–5 |
nd |
|
Minerals and other |
|
|
|
|
|
nd = no data available.
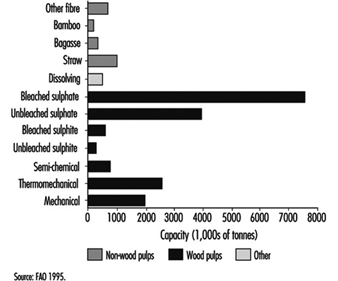
Coniferous and deciduous trees are the major fibre sources for pulp and paper. Secondary sources include straws from wheat, rye and rice; canes, such as bagasse; woody stalks from bamboo, flax and hemp; and seed, leaf or bast fibres, such as cotton, abaca and sisal. The majority of pulp is made from virgin fibre, but recycled paper accounts for an increasing proportion of production, up from 20% in 1970 to 33% in 1991. Wood-based production accounted for 88% of worldwide pulp capacity in 1994 (176 million tonnes, figure 1); therefore, the description of pulp and paper processes in the following article focuses on wood-based production. The basic principles apply to other fibres as well.
Figure 1. Worldwide pulp capacities, by pulp type