The essential mission of occupational health and safety is to protect and enhance the health, well-being and productivity of workers, individually and collectively. That mission cannot be accomplished without an understanding of stress and the mechanisms through which it affects individuals and organizations, and without a well-planned programme that will both alleviate its deleterious effects and, more important, prevent them.
Stress is an inescapable ingredient of the lives of all people everywhere. It stems from—and simultaneously affects—individuals’ inner sense of well-being; their relationships with family, friends, co-workers and strangers; and their capacity to function in the home, the workplace and the community. When excessive, it leads to physical or psychological symptoms and, when prolonged, it may lead to disability and disease. It modifies individuals’ perceptions, feelings, attitudes and behaviour and affects the organizations whose activities they direct or carry out. The subject of stress is covered extensively elsewhere in this Encyclopaedia.
Designing a Stress Management Programme
The effective workplace stress management programme will contain a number of overlapping elements operating concurrently. Some are formalized under the designation of a stress management programme while others are simply part of general organizational management even when they are explicitly aimed at controlling stress. Some of these are aimed at employees individually and in groups; others are aimed at stressors arising in the workplace; and still others address the stressors impinging on the organization as an entity in itself which inevitably filter down to affect some or all of the employees. The elements of a workplace stress management programme will be examined under the following headings.
1. Managing stress-related symptoms. This element deals with individuals already suffering from the effects of stress. Labelled the “medical model,” it attempts to identify individuals with signs and symptoms and to persuade them to come forward voluntarily or accept referral to professionals able to evaluate their problems, diagnose the causes and offer appropriate treatment. It may be based in the employee health service or in the employee assistance programme, or it may be associated with any other counselling services provided by the organization. The services may cover a broad range extending from one-on-one interviews and examinations to telephone “hot-lines” for emergency situations to comprehensive centres with multidisciplinary staffs of qualified professionals. It may be served by full- or part-time professionals or by contractual or casual referral arrangements with professionals who come to the worksite or are based in nearby facilities in the community. Some units deal with any and all problems, while others may more or less focus on such specific stress-related syndromes as hypertension, backache, alcoholism, drug abuse or family problems. The contributions of these service elements to the stress management programme are based on the following capabilities:
- An awareness that many recurrent or persistent somatic complaints such as muscular aches and pains, backache, headache, gastrointestinal upsets, and so on, are attributable to stress. Instead of simply providing palliative medications and advice, the alert health professional or counsellor will recognize the pattern and direct attention to the stressors that are actually responsible.
- Recognition that when a number of employees in a particular unit or area of the workplace present such functional complaints, a search should be initiated for a causative factor in the work environment which may prove to be a controllable stressor.
- Reaching out to individuals involved in or witnessing a cataclysmic occurrence such as a fatal accident, or an episode of violence.
- Seizing the opportunity to stay a disciplinary action faced by an employee because of inadequate performance or aberrant behaviour pending an opportunity to lower the stress level and restore his or her normal equanimity and work capacity.
2. Reducing individual vulnerability. The most common elements in stress management programmes are those that help individuals to cope with stress by reducing their vulnerability. These include series of seminars and workshops, supplemented by audiotapes or videotapes and pamphlets or other publications that educate employees to cope with stress more effectively. Their common denominators are these:
- Training in self-awareness and problem analysis to detect signs of increasing stress and identify the stressors that are responsible
- Assertiveness training enabling workers to become more dynamic in dealing with them
- Techniques that will reduce stress to more tolerable levels
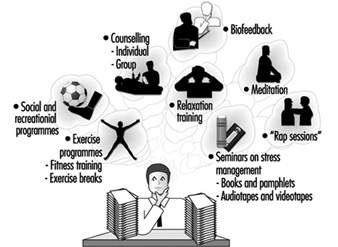
Some of the tools they employ are listed in figure 1. For those not familiar with the term, “rap sessions” are meetings of groups of employees, with or without supervisors being present, in which experiences and problems are discussed and complaints freely ventilated. They are analogous to the shop meetings held under union auspices.
Figure 1. Some approaches to reducing vulnerability.
3. Interpersonal relations in the workplace. Organizations are being increasingly made aware of stressors emanating from the diversity of the workforce and the interpersonal problems they often present. Prejudice and bigotry do not stop at the gates of the worksite and are often compounded by insensitive or discriminatory behaviour on the part of managers and supervisors. Sexual and racial bias may take the form of harassment and may even be expressed in or evoke acts of violence. When rampant, such attitudes demand prompt correction through enunciation of an explicit policy that includes disciplinary actions against those who are guilty, coupled with protecting victims emboldened to complain against reprisals.
4. Managing job-related stressors. It is the organization’s responsibility to minimize job-related stressors that may have an adverse effect on employees’ capacity to function effectively. It is most important to ensure that supervisors and managers on all levels receive appropriate training to recognize and to deal promptly and effectively with the “people problems” that will inevitably arise in the workplace.
5. Managing the organization’s stress. The organization as an entity is exposed to stressors which, if not properly managed, filter down through the workforce, inevitably impinging on employees on all levels. This state of affairs requires the establishment of challenging but attainable goals and objectives, early identification and assessment of potential stressors that may thwart those plans, coordination of the organization’s capacities to deal with them and the communication of the results of those efforts to the workforce. The last-mentioned need is particularly critical at times of economic stringency, when employee collaboration and optimal productivity are especially important in dealing with such crises as changes in top management, threatened mergers and takeovers, plant closings or relocations. and downsizing.
6. Helping to manage personal stressors. While the management of stressors arising in the home and in the community is fundamentally a problem for the individual, employers are discovering that the stress they generate is inevitably brought into the workplace where, either on their own or in conjunction with job-related stressors, they often affect employees’ well-being and compromise their work performance. Accordingly, employers are finding it expedient (and in some instances, necessary) to establish programmes designed to assist employees to cope with stressors of this sort. A list of the most common personal stressors and workplace programmes aimed at them is presented in figure 2.
Figure 2. Stressors in the workplace and workplace programmes to help with them.
Basic Principles of the Programme
In establishing a worksite stress management programme, some basis principles must be emphasized.
First, it must be remembered that there are no boundaries between stress arising in the workplace, in the home and in the community. Each individual presents a unique composite of all of the factors which are carried wherever he or she may go. This means that while the programme must focus on those problems arising in the workplace, it must recognize that these continue to affect the worker’s outside life, nor can it ignore those originating off the job. Indeed, it has been shown that work itself and the support derived from co-workers and the organization may have a therapeutic value in dealing with personal and family problems. In fact, the loss of this support probably accounts for much of the disability associated with retirement, even when it is voluntary.
Second, stress is highly “contagious”. It not only affects particular individuals but also those about them with whom they must relate and collaborate. Thus, dealing with stress is simultaneously therapeutic and preventive.
Third, coping with stress is inherently an individual responsibility. Troubled employees can be identified and offered counselling and guidance. They can be given support and encouragement and taught to improve their coping skills. When necessary, they can be referred to qualified health professionals in the community for more intensive or prolonged therapy. But, in the last analysis, all this requires the consent and participation of the individual which, in turn, depends on the structure of the programme, its status in the organization, the competence of its staff and the reputations they earn, and its accessibility. Perhaps the most important determinant of programme success is the establishment of and strict adherence to a policy of observing the confidentiality of personal information.
Fourth, control of workplace stress is fundamentally a managerial responsibility. The programme must be based on an explicit organizational policy that places high value on employee’s health and well-being. And that policy must be reflected in the day-to-day operations by the attitudes and behaviour of managers on all levels,
Fifth, employee involvement in the programme’s design and operation and, particularly, in identifying stressors and devising ways to control them is an important ingredient of programme success. This is facilitated in many workplaces where safety and health joint labour-management committees function or where worker participation in managerial decision-making is encouraged.
Finally, a successful stress management programme requires an intimate understanding of the employees and the environment in which they work. It is most successful when stress-related problems are identified and resolved before any damage is done.
Conclusion
The essential mission of occupational health and safety is to protect and enhance the health, well-being and productivity of workers, individually and collectively. That mission cannot be accomplished without an understanding of stress and the mechanisms through which it affects individuals and organizations, and a well-planned programme that will both alleviate its deleterious effects and, more important, prevent them.